Abstract
Background
The tobacco thrips (Frankliniella fusca Hinds; family Thripidae; order Thysanoptera) is an important pest that can transmit viruses such as the tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus to numerous economically important agricultural row crops and vegetables. The structural and functional genomics within the order Thysanoptera has only begun to be explored. Within the > 7000 known thysanopteran species, the melon thrips (Thrips palmi Karny) and the western flower thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis Pergrande) are the only two thysanopteran species with assembled genomes.
Results
A genome of F. fusca was assembled by long-read sequencing of DNA from an inbred line. The final assembly size was 370 Mb with a single copy ortholog completeness of ~ 99% with respect to Insecta. The annotated genome of F. fusca was compared with the genome of its congener, F. occidentalis. Results revealed many instances of lineage-specific differences in gene content. Analyses of sequence divergence between the two Frankliniella species’ genomes revealed substitution patterns consistent with positive selection in ~ 5% of the protein-coding genes with 1:1 orthologs. Further, gene content related to its pest status, such as xenobiotic detoxification and response to an ambisense-tripartite RNA virus (orthotospovirus) infection was compared with F. occidentalis. Several F. fusca genes related to virus infection possessed signatures of positive selection. Estimation of CpG depletion, a mutational consequence of DNA methylation, revealed that F. fusca genes that were downregulated and alternatively spliced in response to virus infection were preferentially targeted by DNA methylation. As in many other insects, DNA methylation was enriched in exons in Frankliniella, but gene copies with homology to DNA methyltransferase 3 were numerous and fragmented. This phenomenon seems to be relatively unique to thrips among other insect groups.
Conclusions
The F. fusca genome assembly provides an important resource for comparative genomic analyses of thysanopterans. This genomic foundation allows for insights into molecular evolution, gene regulation, and loci important to agricultural pest status.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
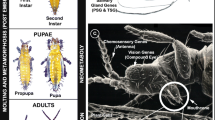
The family Thripidae, which includes the genus Frankliniella, contains > 7,000 thrips species [1]. However, the tobacco thrips (Frankliniella fusca Hinds) (Fig. 1) genome presented in this paper represents only the third thysanopteran genome assembly published to date, after the melon thrips (Thrips palmi Karny) [2] and the western flower thrips (Frankliniella occidentalis Pergrande) [3].
Ecologically, F. fusca is native to North America and is a major agricultural pest [4]. However, it can also be found inhabiting three other continents [5,6,7], and its dispersal tends to vary by season [8, 9]. F. fusca is highly polyphagous and has been, for example, observed to feed on economically important plants in at least fifteen plant families including Amaryllidaceae, Fabaceae, Malvaceae, and Solanaceae [7]. The primary damage from the thrips feeding is limited to the plant epidermal cells, causing dark brown spots on the leaves, and inhibiting plant growth [5, 10]. F. fusca management on various crops has been a growing concern, as their populations have been developing resistance to insecticides [11].
While feeding damage can itself be detrimental to plants, the transmission of debilitating viruses to susceptible crops is of much greater concern [12,13,14]. Thrips, such as F. fusca, can transmit viruses belonging to the genus Orthotospovirus and family Tospoviridae. Approximately twenty species of orthotospoviruses are known and are exclusively transmitted by about a dozen thrips species in a persistent and propagative manner (the virus persists for life after acquisition in thrips and replicates within their tissues) [14]. Upon acquisition, the orthotospovirus traverses the midgut membrane barrier via receptor-mediated endocytosis and further translocates to other tissues including the salivary glands, where it replicates [15]. From the salivary glands, the virus is typically inoculated to plant hosts in the saliva during feeding [16,17,18,19,20,21]. The virus is also transmitted in a stage-dependent manner: for adult thrips to inoculate the virus successfully, they must acquire the virus as first or second instar larvae [20, 22]. This phenomenon is attributed to anatomical differences in tissue types between the stages [23,24,25]. Interestingly, tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus (TSWV) acquisition by F. fusca has been shown to exhibit context-specific effects on fitness [14, 26,27,28]. The interactions between thrips and orthotospoviruses are intricate and indicate co-evolution [19, 29].
F. fusca along with F. occidentalis are the two most important orthotospovirus vector species in temperate and sub-tropical regions worldwide, whereas T. palmi is generally regarded as a tropical pest [7, 30, 31]. F. fusca and F. occidentalis, despite their congeneric status, exhibit ecological differences reflected by different abundances among host plant taxa [12]. In this study, the F. fusca genome was assembled and compared with the existing F. occidentalis genome to gain insights into the molecular evolution, expression [32], and epigenetics of factors associated with thrips-plant-virus trophic interactions.
Results
Genome assembly and annotations
The F. fusca genome assembly contained 46 ungapped scaffolds measuring ~ 370 Mb (Table 1). The assembly length and N50 of the long-read based F. fusca genome indicated a more complete (1.4x) assembly compared with the earlier short-read based assembly of its congener F. occidentalis [3, 33] (Table 1; Fig. 2). Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs (BUSCO) analysis was conducted to assess assembly completeness relating to inclusion of core Insecta genes [34]. The F. fusca genome assembly showed 99.0% completeness with 1,325 universal single copy and 29 duplicated orthologs. Universal single copy orthologs are defined as those genes present in over 90% of species within the class Insecta [34]. The F. fusca assembly was annotated with gene models using the MAKER pipeline (Additional file 1: Fig. S1 and Table S1) [35]. F. fusca gene annotations included 96.6% of the complete BUSCO Insecta sequences (Additional file 1: Fig. S2).
Visual comparison of two Frankliniella genomes. The F. fusca genome assembly (numeric only accessions) in comparison with the F. occidentalis genome assembly (NW accessions) [3]. Contigs of the F. fusca genome assembly ≥ 2.5 Mb in length were selected for visualization. Gene locations are shown below the respective assembly fragment. Regions that were ≥ 1 kb in length and ≥ 90 percent identity were linked
Phylogenetic context
Functional annotation of F. fusca gene models based on sequence homology was performed with the eggNOG database, which is comprised of the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways, Pfam domains, and gene ontology (GO) [36,37,38,39,40,41]. A total of 17,389 F. fusca proteins were assigned functional information (Additional file 2: Table S2). To infer F. fusca species relatedness, a consensus tree was generated from twenty arthropod species with high-quality genome assemblies including the congener F. occidentalis, three additional thysanopteran species (two based on de novo transcriptome assemblies), six non-thysanopterans in class Insecta, and two non-insect arthropods (Fig. 3A). An ortholog comparison between the F. fusca and F. occidentalis species assigned 87.3% of 26,761 F. fusca MAKER genes and 85% of 23,356 F. occidentalis RefSeq genes to 12,596 and 12,197 orthogroups respectively (Additional file 1: Table S3). There were 7,912 (1:1) orthologs identified between the two Frankliniella species using Orthofinder (Additional file 3: Tables S4 & S5).
F. fusca phylogenetic relationships and orthology. A Species tree produced from ortholog comparisons across six insect orders and two additional non-insect arthropod orders (orders denoted at right; *de novo transcriptome data used for F. tritici and T. tabaci; scale bar denotes amino acid substitutions per site) [2, 3, 33, 42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59]. Clade bootstrap support values are labelled on the respective node. B Gene family orthologous clusters shared between four insect species. Venn diagram constructed from F. fusca, F. occidentalis [3], T. palmi [2], and A. pisum [42]
Gene family membership was assigned to a set of four species (three thrips and the pea aphid) using OrthoVenn2 [60], which runs OrthoMCL [61]. A total of 6,255 gene families (orthologous clusters) were found to be shared between F. fusca, F. occidentalis [3], T. palmi [2], and the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum Harris) [42] (Fig. 3B). Another 887 gene families were shared between the two Frankliniella species, of which 1,297 gene families were specific to F. fusca (Fig. 3B).
Gene content relevant to pest status
The feeding behavior of thrips exposes them to a variety of xenobiotics including plant defensive chemicals (secondary metabolites) and insecticides [62, 63]. Thrips have developed mechanisms to efficiently metabolize xenobiotics [64]. Some of the relevant detoxification molecules include: Acyl-CoA desaturases [65], ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters [66], cathepsins [67], carboxylesterases (CE) [68], cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (CYP) [69], Dicer dimerization domains [70], glutathione S-transferases (GST) [71], heat shock proteins 70 & 90 (Hsp70 & Hsp90) [72], the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases, and Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) [73] (Additional file 4: Tables S6 & S7).
CYPs, CEs, and GSTs are known to detoxify plant xenobiotics such as phytochemicals and insecticides [69, 74, 75]. Forty-seven 1:1 orthologs of CYPs (IPR001128) were found between F. fusca and F. occidentalis. Fewer were detected among more distantly related species; 15, 15, and nine 1:1 orthologs of CYPs (IPR001128) were found between F. fusca and A. pisum, F. fusca and Z. termopsis, and F. fusca and D. melanogaster, respectively. CYPs can be taxonomically broken down into two classes (B-class and E-class), with E-class being found primarily within eukaryotes and itself subdivided into five groups [76]. Cytochrome P450, E-class, group I (IPR002401), is the largest of the five and contains CYPs specialized in the metabolism of exogenous substrates and physiologically active compounds. There were seventy-eight and ninety-one genes containing CYP E-class group I families in F. fusca and F. occidentalis assemblies, respectively. Out of the detoxification molecules, both thrips species were found to contain two CE (IPR003140) containing genes, which also were 1:1 orthologs. Additionally, eleven GST (IPR004045) 1:1 orthologs were identified.
Previously reported genes involved with thrips-plant-virus interactions include those involved with cell surface reception, virus replication, and innate immunity. Such genes include aminopeptidase N, endopeptidases, peroxiredoxins, peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRPs), lysozymes, trypsin, 40S ribosomal protein, and serine proteases [21, 32]. Notably, PGRPs detect and fight infection and initiate a humoral response of the Toll or Imd pathways [77]. Importin (IPR002652), a nuclear transport complex, may be involved in the binding of the virus to the cell membrane and control entry of the virus into the vector’s salivary glands [78], whereas cathepsins and peptidases may play a role in uptake of the virus into the vector [67, 79]. Glucose metabolism associated genes such as alpha glucosidase may inhibit binding and reduce replication of the virus within the vector [80]. Additionally, Hsp70 and Hsp90 were involved in inhibiting virus infection in vectors [72]. Heparan sulfate (IPR037359) genes are known to facilitate binding of the virus to the salivary cells in vectors [78].
The copy numbers of genes with evidence for molecular interaction between the two thrips vectors (F. fusca and F. occidentalis) and the virus revealed widespread variation between species (Fig. 4). On an average, higher copy number variation (CNV) of genes in relation to the pest status were documented in F. occidentalis (x̄ ≈ 40) than in F. fusca (x̄ ≈ 28); however, the mean counts were not statistically different (t-test, p = 0.2452).
Detoxification and virus interaction related gene counts. Unique genes and non-1:1 orthologs are combined from F. fusca and F. occidentalis and compared with the 1:1 orthologs (F. fusca + F. occidentalis). Gene counts refers to the number of genes which contain a given protein domain identity. Genes may contain more than one of the given protein domains
Molecular evolution of pest status genes
The availability of genome assemblies from F. occidentalis and F. fusca made it possible to assess rates of protein evolution following their divergence from a common ancestor and the ratio between the rate of non-synonymous to synonymous substitutions (dN/dS; Additional file 3: Tables S4 & S5). Variation in dN/dS can reflect differences in the strengths of positive selection or purifying selection. Genes with dN/dS > 1 when averaged across all codons were identified. A dN/dS > 1 ratio is generally considered a signal of positive selection operating on a locus [81]. Of the 7,817 assessed ortholog pairs detected from F. occidentalis and F. fusca, 388 (4.96%) exhibited values of dN/dS greater than one (Additional file 5: Tables S8-S11).
Assessment of molecular evolution in thrips further helped to address whether the selective constraints experienced by genes that respond to virus infection and detoxification differ from those that do not. Of the 223 genes with 1:1 orthologs belonging to fifteen InterProScan categories relating to pest status, five were found to have a dN/dS > 1: atrial natriuretic peptide-converting enzyme isoform X1 (FUS_00002678-RA), hypothetical predicted protein (FUS_00019172-RA), trypsin 3A1-like isoform X2 (FUS_00004482-RA), cytochrome P450 4d2-like (FUS_00010490-RA), and probable cytochrome P450 12a5, mitochondrial (FUS_00026641-RA).
Previously generated RNA-seq gene expression data from three life stages of F. fusca, with and without orthospovirus-infection [32], were mapped to the F. fusca reference assembly. As previously reported [32], most of the differential gene expression between orthotospovirus-viruliferous and non-viruliferous individuals occurred in larval and adult stages, with fewer differentially expressed genes (DEGs) detected at the pupal stage (Additional file 6: Tables S12-S14). Upon assessing the distributions of dN/dS values for DEGs and non-DEGs across the three developmental stages, it was found that there were significant differences in dN/dS for DEGs and non-DEGs as classified from the larval and adult stages, but there was not a consistent directional signal of elevated or reduced rates of protein evolution for those DEGs (Additional file 1: Fig. S4A & S4B). The proportion of genes with dN/dS > 1 among DEGs (based on differential expression in any stage) was 4.6% and among non-DEGs was 5.3%, which did not represent a significant difference (Fisher’s Exact Test, p = 0.1882).
The presence of the F. fusca reference genome facilitated the analysis of alternative splicing of transcripts for the first time between orthotospovirus-viruliferous and non-viruliferous individuals from the previously generated RNA-seq data [32] using a metric of differential exon usage normalized by sequencing depth (Additional file 7: Tables S15-S17). Significant alternative splicing in response to orthotospovirus-infection, plant feeding, and detoxification was most prevalent in adults, and, as in the case of differential expression, alternative splicing was sparse in the pupal stage (Fig. 5). Upon assessing the distribution of dN/dS values for alternatively spliced (AS) and non-AS genes across the three developmental stages, it was found that there were significant differences in dN/dS for AS and non-AS genes as classified from the pupal and adult stages, but there was not a consistent directional signal of elevated or reduced rates of protein evolution for these comparisons (Additional file 1: Fig. S5A & S5B). The proportion of genes with dN/dS > 1 among AS genes (based on alternative splicing events in any stage) was 3.2% and among non-AS genes was 6.9%, indicating a significant depletion of genes with dN/dS > 1 among AS genes (Fisher’s Exact Test, p < 0.00001).
Within the virus responsive genes, 170 DEGs and 134 AS genes within at least one developmental stage had dN/dS > 1, consistent with positive selection operating on these loci in the Frankliniella genus (Additional file 1: Fig. S3, Additional file 5: Tables S8 & S9). One of these genes was differentially expressed in all three developmental stages –putative metal responsive transcript (FUS_00001516-RA) and one was alternatively spliced in all three stages –cytochrome c oxidase subunit III (FUS_00005990-RA). The intersection between DEGs and AS genes revealed that 2,233 genes exhibited changes to both their expression levels and splicing patterns in response to orthotospovirus-infection in F. fusca when considering significant differences in any of the three developmental stages. Eighty-two genes with a dN/dS > 1 were both differentially expressed and alternatively spliced in response to orthotospovirus-infection (Additional file 5: Table S10). DEGs (Fig. 6A, Additional File 1: Fig. S6A), AS genes (Fig. 6B, Additional File 1: Fig. S6B), and the intersection between DEGs and AS genes (Additional File 1: Fig. S7 & Fig. S8) with dN/dS > 1 were checked for GO term enrichment within the biological process (BP) category of GO terms. This revealed enrichment of various metabolism related GO terms (Fig. 6).
Tree map GO term enrichment for virus-responsive genes with dN/dS > 1. Biological processes category GO term distribution is shown for A differentially expressed genes and B alternatively spliced genes. Each individual box represents an enriched (p < 0.05) GO term, with one representative term per supercluster. The size of each box relates to the relative frequency of the respective GO term
Genome wide DNA methylation
Gene regulatory responses to orthotospovirus-infection may be influenced by epigenetic modifications leading to changes in accessibility for transcription factors. In insects, the levels of DNA methylation are generally low and concentrated within gene bodies [82, 83], where intragenic DNA methylation is hypothesized to influence alternative splicing and perhaps gene expression levels [84]. The mutational signatures of DNA methylation profiles from F. fusca and F. occidentalis were assessed by calculating normalized CpG content (CpGo/e), which can serve as a proxy measure for DNA methylation because CpG dinucleotides are the primary targets of DNA methylation in animals and methylated cytosines undergo deamination to thymine with high frequency [85,86,87]. The CpGo/e of the 26,416 and 23,148 coding sequences (CDS) in F. fusca and F. occidentalis, respectively, were found to have bimodal distributions with a mean CpGo/e of 0.68 for both (Additional file 1: Fig. S9A & S9B; Additional file 8: Table S18). The presence of many CpG-depleted coding sequences suggested that DNA methylation is targeted to those regions. Further investigation into the DNA methylation patterns of the genome was performed by examining CpGo/e distributions for various genomic features including exons, introns, promoter regions 1.5 kb upstream of the transcription start site (TSS), and transposable elements (TEs; Fig. 7A, Additional file 1: Fig. S10).
DNA methylation targets and molecular mediators. A CpGo/e of the F. fusca genomic features: exons, introns, and promoters and transposable elements (TEs) compared with the distribution of coding sequences (CDS). B DNA methyltransferase and DNMT-like gene expression level (gene count) in non-viruliferous individuals compared with the average expression level of all genes for each developmental stage. Individual points correspond to gene expression levels, whereas the boxplots are representative of the expression level distribution of the whole transcriptome per each developmental stage. The C5 methyltransferase domain presence or absence was classified by the InterPro Scan domain search (n = 52). C DNMT phylogenetic tree from F. fusca, F. occidentalis, A. mellifera, N. vitripennis, A. pisum, and H. sapiens. Numbers at branch nodes are confidence values based on 1000 bootstrap replications
DNA methylation is controlled by the addition of a methyl group to cytosine by the maintenance DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) and the de novo DNA methyltransferase 3 (DNMT3) in insects and other eukaryotes [88]. The DNMT3s found in the F. fusca assembly were numerous but incomplete. The F. fusca DNMT3-like sequences collectively contained the expected domains, such as C5 methyltransferase (IPR001525) [89]. However, among the 50 DNMT3-like sequences identified, no single sequence contained all expected DNMT3 domains. The incomplete DNMT3s were mostly scattered across the genome assembly, with 27 having been found on separate contigs. Additionally, ten contigs were found to contain two DNMT3s and one contig contained three DNMT3s, which may represent tandem duplication. The expression levels of the F. fusca DNMT1 and DNMT3-like genes were compared against global gene expression levels for each F. fusca developmental stage (Fig. 7B) [90]. There was notable transcriptional activity of DNMT1 and many of the DNMT3-like sequences within F. fusca (Fig. 7B).
A phylogenetic tree of Blast-derived DNMTs was generated to investigate the relationship of a few confidently annotated F. fusca DNMT1 and DNMT3s to those from other insects and a vertebrate outgroup (Fig. 7C). DNMT1 hits were present in F. fusca, T. palmi, pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum Harris), western honeybee (Apis mellifera Linnaeus), parasitoid wasp (Nasonia vitripennis Walker), and human (Homo sapiens Linnaeus), forming a clade in the phylogenetic tree consistent with expectations. However, the DNMT3 sequences did not resolve into a monophyletic group and were instead paraphyletic with respect to DNMT1 (Fig. 7C).
Investigating the CpGo/e patterns for DEGs and AS genes in response to orthotospovirus-infection revealed that some classes of genes, as grouped according to their transcriptional attributes, were more likely to be targeted by DNA methylation than others (Fig. 8). Genes downregulated in response to orthotospovirus-infection exhibited significantly lower CpGo/e values than non-DEGs, suggesting these downregulated genes are preferentially targets of DNA methylation (Fig. 8A). In contrast, genes that were upregulated in response to orthotospovirus-infection exhibited significantly higher CpGo/e values than non-DEGs, suggesting these upregulated genes are less likely to be targets of DNA methylation than non-DEGs (Fig. 8A). Genes that were alternatively spliced in orthotospovirus-viruliferous versus non-viruliferous adults also were more likely to be targets of DNA methylation than genes that were not alternatively spliced (Fig. 8B).
CpGo/e distributions of virus-responsive genes in F. fusca. A Differentially expressed genes and B alternatively spliced genes with differential exon usage across F. fusca developmental life stages. Lower CpGo/e reflects higher DNA methylation levels. Boxplot outliers not shown. Corresponding p-values: *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001
Discussion
This high-quality genome for the tobacco thrips is the third genome assembled in the order Thysanoptera after F. occidentalis [3] and T. palmi [2]. The quality of this genome can be attributed to PacBio sequencing, which reduced the total number of gaps relative to an assembly based on short-read sequences [3, 91, 92]. Despite the taxonomic closeness between the two Frankliniella species, their ecological interactions between hosts and viruses vary [12]. This study aimed at understanding those variations from physiological, evolutionary, and epigenetic perspectives.
Determination of dN/dS [93] was conducted for orthologous gene pairs between F. fusca and F. occidentalis to assess variation in selective pressures among genes. Genes with dN/dS > 1, consistent with positive selection, were identified among differentially regulated and alternative spliced genes following virus infection. ~ 97% of these genes were differentially regulated in F. fusca larvae and adults, but not in the least metabolically active pupal stage. Of the forty-seven 1:1 orthologous xenobiotic-metabolizing CYP enzymes [69, 94] identified, two exhibited dN/dS values consistent with positive selection. Acyl-CoA, which is also involved detoxification of xenobiotics in insects [65, 95, 96], also exhibited a signature of positive selection and was differentially expressed in larvae. Additional genes putatively subject to positive selection that were differentially regulated and/or alternatively spliced included heat shock proteins, which are known to inhibit virus infection in insects [72, 97]. Similarly, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) dehydrogenase exhibited a signature of positive selection and was differentially expressed in larvae and adults [98, 99]. The expression of these immunity-related genes may be influenced by epigenetic mechanisms that alter transcriptional activity in response to infection [100].
The CpGo/e of the F. fusca genome serves as a proxy to determine where DNA methylation has been present in the genome during recent evolutionary history [86, 101]. F. fusca exhibited a bimodal distribution of CpGo/e for exons, whereas other genomic features such as promoters and introns were found to have skewed/higher CpGo/e values, indicating less DNA methylation than exons, as is typical in insects [102]. A bimodal distribution showing high and low CpGo/e has been documented in the coding sequences of many insect species [88], including F. occidentalis [88], A. mellifera [86], two cricket species [59, 103], A. pisum [104], and two termite species [105].
When we assessed the signature of DNA methylation patterns for differentially expressed and alternatively spliced genes following virus infection, methylation was revealed to be preferentially targeted to genes alternatively spliced in adults and downregulated in adults and larvae following virus infection. Virus infection-induced changes in DNA methylation have been observed to occur among insects in the silkworm (Bombyx mori Linnaeus) following infection by B. mori cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus (BmCPV) [106]. Methylation patterns in eukaryotes are established and maintained by DNA methyltransferases DNMT3 and DNMT1 respectively [107, 108]. While the function of the multiple DNMT3s we observed in F. fusca has yet to be resolved, one possible explanation for the high copy number is that some of these DNMT3s have undergone subfunctionalization, in which two or more copies of a duplicated genes divide the function of the ancestral gene [109, 110]. Another possibility is neofunctionalization of DNMT3 alleles [111]. It has been suggested that some DNMTs in other arthropod species may have varying biological processes [108, 112, 113]. Further exploration into the DNMTs in F. fusca may resolve functionality of these genes.
Conclusions
This study generated a genomic resource for F. fusca using long-read sequence data. The genome assembly allowed for investigation into the evolutionary history of F. fusca in more depth than was possible with a transcriptome. The assembly allowed for the reanalyzing of previously published RNA-seq data [32] for differential expression and novel analysis of alternative splicing events following orthotospovirus-infection. By comparing the sequence divergence of protein-coding genes in F. fusca with orthologs in F. occidentalis, we revealed many genes that may be evolving under positive selective pressure relating to orthotospovirus-infection. Within the genus Orthotospovirus, TSWV is one of the most studied thrips-transmitted viruses, which has contributed broadly to our understanding of virus-insect interactions [114].
The CpGo/e patterns of differentially expressed and alternatively spliced genes indicated different patterns of potential methylation events in relation to orthotospovirus-infection. Additionally, high counts of incomplete DNA methyltransferases were found within the genome, consistent with sub- or neo-functionalization. This genomic resource should facilitate further investigation into the potential roles of DNA methylation in thrips gene regulation and virus transmission. The addition of more high-quality thrips genomes will broaden these inferences.
Materials and methods
Sampling, extraction, and sequencing
One thousand male F. fusca heads from an 11th generation inbred line were used for DNA extraction. Samples were pooled to obtain enough material for high quality library construction. Heads were chosen to reduce potential sources of contamination. The Qiagen DNeasy Blood & Tissue kit was used for extraction with half the recommended volumes for each reagent and 50 μL elution. An Illumina sequencing library was constructed, and samples were sequenced on a HiSeq 2000 used with 150PE reads at the University of Maryland Genomic Facility. PacBio library preparation was performed with the Sequel-2 chemistry kit and sequenced on two single-molecule real-time (SMRT) cells, also at the University of Maryland Genomic Facility. Voucher specimens were retained and stored in 95% alcohol at -20C at North Carolina State University.
Genome assembly and quality control
The assembly was performed with the use of the program Flye v2.6 [115, 116], which ran for two iterations with the expected haploid genome size being 400 Mb [117]. This unphased assembly had Illumina sequence data mapped to it using Minimap2 v2.17 [118] and Samtools v1.10 [119, 120]. Error correction was performed with Pilon v1.10 [121] using the mapped Illumina reads. Assembly quality was checked with Quality Assessment Tool for Genome Assemblies (QUAST) v5.0.2 [122] and BUSCO v4.0.5 [34]. Assembly fragments larger than 2.5 Mb were extracted with Seqtk (https://github.com/lh3/seqtk). The genome assembly was visualized using Bandage v0.8.1 [123] and Circos v0.69 [124]. The BUSCO scores were searched against the Insecta odb10 with the species set to the default of “Fly”. The BUSCO scores were checked against the 1,367 core genes that exist in the Insecta odb10. The BUSCO Insecta odb10 is comprised of core genes from 75 insect species across 14 orders, which includes Thysanoptera as represented by F. occidentalis. Screening was performed with recommended VecScreen [125] parameters being “-task blastn -reward 1 -penalty -5 -gapopen 3 -gapextend 3 -dust yes -soft_masking true -evalue 700 -searchsp 1,750,000,000,000” to remove any potential contamination. The quality of the gene models were assessed using BUSCO v4 and the lineage Insecta odb10 ortholog set with 1,367 core genes [34]. Counting of k-mers was conducted using the tool JELLYFISH for k-mers of length 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 31, and 100 (Additional file 1: Fig. S11A) [126].
Genome annotation
To run the annotation steps efficiently, the main assembly file was split up into smaller subfiles using BBMap v38.73 parition.sh [127]. Each subfile contained about 5% (or 72) of the contigs from the main file. The tool MAKER v3.01.02-beta [35] was used and run through four rounds to refine the annotation quality. The first round of MAKER included external evidence from a F. fusca and F. tritici transcriptome, F. occidentalis transcriptome and proteome, and additional proteomes from UniProt: fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster Meigen) (UP000000803), A. pisum (UP000007819), red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum Herbst) (UP000007266), body louse (Pediculus humanus subsp. Corporis Linneaus) (UP000009046), and the Nevada termite (Zootermopsis nevadensis Hagen) (UP000027135). Subsequent rounds of MAKER required training with SNAP-Zoe v2006-07–28 (http://www.hiv.lanl.gov) [128] and AUGUSTUS v3.2.3 [129] with the output from the previous MAKER run (AUGUSTUS also requires BEDTools v2.29.2 for proper formatting). The total quality of each round of MAKER was assessed using annotation edit distance (AED) scores, which is a metric describing how well genome annotations are supported by evidence such as the sequence homology and expressed sequence tags (ESTs) [130]. Repeat masking was handled internally within MAKER using RepeatMasker v4.0.7 (A.F.A. Smit, R. Hubley & P. Green RepeatMasker at http://repeatmasker.org). All rounds of MAKER were set to generate a single annotation for each gene using the default parameter (alt_splice = 0). The functional annotations were performed using the OmicsBox v1.4.11 toolkit [131]. Web Gene Ontology Annotation Plot (WEGO) v2 was used to visualize and determine significant enrichment of GO terms [132, 133].
Orthologous gene detection
OrthoFinder v2.3.7 [134, 135] was used to construct a species tree based on several insect proteomes, using the following parameters: gene tree inference (-M) msa, multiple sequence alignment (-A) mafft [136], and tree inference program (-T) raxml [137]. This tree was generated from OrthoFinder2, which internally uses the programs STRIDE and STAG for comparing proteins and generating orthogroups [138]. The tree was viewed using the tool FigTree v1.4.4 (https://github.com/rambaut/figtree/) from the output from IQ-TREE v1.6.12 after 1000 iterations to calculate bootstrap values [139,140,141]. Additional gene family comparisons were made with OrthoVenn2 using a cutoff of e−10 [60]. Eggnog-mapper v1.0.3 was used to assign GO terms using the eggNOG database [36, 142]. This was accomplished using default parameters and checking across all available species and genes in the database.
Gene counts for detoxification and virus responsive genes were determined by searching the InterPro database [143]. Genes containing the following domains were considered: heat shock protein 70 family (IPR013126), heat shock protein Hsp90, N-terminal (IPR020575), acyl-CoA desaturase (IPR015876), mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, JNK (IPR008351), dicer dimerisation domain (IPR005034), chytochrome P450 (IPR001128), ABC transporter-like, ATP-binding domain (IPR003439), glutathione S-transferase, N-terminal (IPR004045), phospholipase/ carboxylesterase/ thioesterase (IPR003140), aminopeptidase N-like (IPR033581), peroxiredoxin, C-terminal (IPR019479), peptidoglycan recognition protein (IPR015510), amino acid transporter, transmembrane domain (IPR013057), serine proteases, trypsin domain (IPR001254), and 40S ribosomal protein (IPR032277).
Differentially expressed and alternatively spliced genes
The RNA-Seq data comes from the NCBI sequence read archives (SRA): SRX2788009, SRX2788011, SRX2788013, SRX2788010, SRX2788012, and SRX2788014 [57]. RNA-Seq by Expectation–Maximization (RSEM) v1.3.3 and Bowtie2 v2.4.1 were used for mapping to the reference gene models and determination of gene counts with default parameters (~ 42–65% alignment; Additional file 1: Table S19) [144, 145]. DESeq2 v3.13 was used for differential expression analysis [146]. STAR aligner v2.7.9 was used with default parameters to map reads to the genome (~ 87–94% alignment; Additional file 1: Table S20) [147]. SAMtools v1.10 was used to sort the alignments [119]. DEXSeq was used with default parameters to calculate the amount of alternative splicing of exons [148].
Protein evolution rate
The 1:1 orthologs detected from Orthofinder2 were used for dN/dS calculations. Pal2Nal v14 [149] and PAML v4.9 [150] were used to calculate the respective dN/dS values. Using custom R script, genes were partitioned into significantly and non-significantly expressed genes for each stage.
GO term enrichment
The Bioconductor package topGO (https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/topGO.html) was used to determine the significantly enriched GO terms from genes of interest under the DEG, AS genes, and the intersection between DEGs and AS genes. Revigo and rrvgo (https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/rrvgo.html), with respect to the D. melanogaster ortholog database, were used downstream to visualize the GO term enrichment [151].
DNA methylation targeting of genomic elements
Determination of the observed to expected CpG content in the coding regions of the genome was performed using CpG.pl (https://github.com/swebb1/cpg_tools) using the default parameters. GffRead v0.9.12 was used to extract the CDS [152]. BEDTools v2.26.0 was used to extract the exons, introns, and promoter regions [153]. EDTA v1.9.9 was used to annotate the TEs using default parameters (Additional file 1: Fig. S11B) [154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161]. Promoter regions were parsed out using (https://github.com/milesroberts-123/extract-promoter-sequences), with the parameters upstream (-u) 1500 and downstream (-d) 0 from the transcription start site. Characterization of the DNMTs in F. fusca was performed using the OmicsBox v1.4.11 toolkit [131], which includes Blast2GO [162] and Pfam database search [41]. The resulting OmicsBox annotations were compared with MAKER v3.01.02-beta [35] annotations, which were assigned by InterProScan [163]. The DNMT tree was built from an InterProScan of A. mellifera DNMT domain BlastP [164] with default parameters against the following species: F. fusca, F. occidentalis, A. mellifera, N. vitripennis, A. pisum, and H. sapiens. The tree was viewed using the tool FigTree v1.4.4 (https://github.com/rambaut/figtree/) from the output from IQ-TREE v1.6.12 after 1000 iterations over the mafft multiple alignments [136] to calculate bootstrap values [139,140,141].
Availability of data and materials
The data for this article can be found in the NCBI GenBank repository at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ under the BioProject PRJNA742006. Raw sequence data for the BioSample SAMN19606609 are deposited in the SRA accessions: SRR15147323-SRR15147327. The genome and transcriptome shotgun assembly (TSA) submission accessions are JAHWGI000000000 and GJHY00000000, respectively. Supplementary information and captions can be found in Additional file 1: Figures S1-S11 and Tables S1-S20. Respective supplementary tables can be found in Additional file 2: Table S2, Additional file 3: Tables S4 & S5, Additional file 4: Tables S6 & S7, Additional file 5: Tables S8-S11, Additional file 6: Tables S12-S14, Additional file 7: Tables S15-S17, and Additional file 8: Table S18.
Abbreviations
- TSWV:
-
Tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus
- CNV:
-
Copy number variation
- ABC:
-
ATP-binding cassette
- CE:
-
Carboxylesterase
- CYP:
-
Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase
- HSP:
-
Heat shock protein
- MAP:
-
Mitogen-activated protein
- JNK:
-
Jun N-terminal kinase
- PGRP:
-
Peptidoglycan recognition protein
- dN/dS:
-
Non-synonymous substitutions and synonymous substitutions ratio
- CpGo/e:
-
CpG observed/expected
- TE:
-
Transposable element
- DNMT:
-
DNA methyltransferase
- BUSCO:
-
Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- DEG:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- AS:
-
Alternatively spliced
- CDS:
-
Coding sequence
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- TSS:
-
Transcription start site
- NADH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- SMRT:
-
Single-molecule real-time
- QUAST:
-
Quality Assessment Tool for Genome Assemblies
- WEGO:
-
Web Gene Ontology Annotation Plot
- RBH:
-
Reciprocal best hits
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- SRA:
-
Sequence read archives
- RSEM:
-
RNA-Seq by Expectation–Maximization
- TSA:
-
Transcriptome shotgun assembly
References
Reitz SR. Biology and ecology of the Western flower thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae): the making of a pest. Florida Entomologist. 2009;92(1):7–13.
Guo SK, Cao LJ, Song W, Shi P, Gao YF, Gong YJ, Chen JC, Hoffmann AA, Wei SJ. Chromosome-level assembly of the melon thrips genome yields insights into evolution of a sap-sucking lifestyle and pesticide resistance. Mol Ecol Resour. 2020;20(4):1110–25.
Rotenberg D, Baumann AA, Ben-Mahmoud S, Christiaens O, Dermauw W, Ioannidis P, Jacobs CGC, Vargas Jentzsch IM, Oliver JE, Poelchau MF, et al. Genome-enabled insights into the biology of thrips as crop pests. BMC Biol. 2020;18(1):142.
Diffie S, Edwards GB, Mound LA: Thysanoptera of Southeastern U.S.A.: a checklist for Florida and Georgia. Zootaxa 2008, 1787(1).
Cook D, Herbert A, Akin DS, Reed J. Biology, crop injury, and management of thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) infesting cotton seedlings in the United States. Journal of Integrated Pest Management. 2011;2(2):1–9.
Morsello SC, Groves RL, Nault BA, Kennedy GG. Temperature and precipitation affect seasonal patterns of dispersing tobacco thrips, <I>Frankliniella fusca</I>, and Onion Thrips, <I>Thrips tabaci</I> (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) caught on sticky traps. Environ Entomol. 2008;37(1):79–86.
LaTora AG, Lai P-C, Chen Y-J, Gautam S, Abney MR, Srinivasan R, Kesheimer K: Frankliniella fusca (Thysanoptera: Thripidae), the vector of tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus infecting peanut in the Southeastern United States. J Integr Pest Manag. 2022, 13(1).
Nault BA, Speese Iii J, Jolly D, Groves RL. Seasonal patterns of adult thrips dispersal and implications for management in eastern Virginia tomato fields. Crop Prot. 2003;22(3):505–12.
Goethe J, Dorman S, Wang H, Kennedy G, Huseth A. Spatial and temporal patterns of Frankliniella fusca (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in wheat agroecosystems. J Appl Entomol. 2022;146(5):570–8.
Riley DG, Joseph SV, Srinivasan R, Diffie S. Thrips vectors of tospoviruses. J Integr Pest Manag. 2011;2(1):I1–10.
Huseth AS, Chappell TM, Langdon K, Morsello SC, Martin S, Greene JK, Herbert A, Jacobson AL, Reay-Jones FP, Reed T, et al. Frankliniella fusca resistance to neonicotinoid insecticides: an emerging challenge for cotton pest management in the eastern United States. Pest Manag Sci. 2016;72(10):1934–45.
Kahn ND, Walgenbach JF, Kennedy GG. Summer weeds as hosts for Frankliniella occidentalis and Frankliniella fusca (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) and as reservoirs for tomato spotted wilt Tospovirus in North Carolina. J Econ Entomol. 2005;98(6):1810–5.
Arthurs SP, Heinz KM, Mitchell FL. Comparison of frankliniella fusca and frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) as vectors for a peanut strain of tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus. Environ Entomol. 2018;47(3):623–8.
Shrestha A, Srinivasan R, Riley DG, Culbreath AK. Direct and indirect effects of a thrips-transmittedTospoviruson the preference and fitness of its vector. Frankliniella fusca Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata. 2012;145(3):260–71.
de Assis Filho FM, Naidu RA, Deom CM, Sherwood JL. Dynamics of tomato spotted wilt virus replication in the alimentary canal of two thrips species. Phytopathology. 2002;92(7):729–33.
Bandla MD, Campbell LR, Ullman DE, Sherwood JL. Interaction of Tomato Spotted Wilt Tospovirus (TSWV) glycoproteins with a thrips midgut protein, a potential cellular receptor for TSWV. Phytopathology. 1998;88(2):98–104.
Badillo-Vargas IE, Chen Y, Martin KM, Rotenberg D, Whitfield AE. Discovery of novel thrips vector proteins that bind to the viral attachment protein of the plant bunyavirus tomato spotted wilt virus. J Virol. 2019;93(21):e00699-19.
Ohnishi J, Knight LM, Hosokawa D, Fujisawa I, Tsuda S. Replication of tomato spotted wilt virus after ingestion by adult thrips setosus is restricted to midgut epithelial cells. Phytopathology. 2001;91(12):1149–55.
Zhao K, Rosa C. Thrips as the transmission bottleneck for mixed infection of two orthotospoviruses. Plants (Basel). 2020;9(4):509.
Rotenberg D, Jacobson AL, Schneweis DJ, Whitfield AE. Thrips transmission of tospoviruses. Curr Opin Virol. 2015;15:80–9.
Han J, Rotenberg D. Integration of transcriptomics and network analysis reveals co-expressed genes in Frankliniella occidentalis larval guts that respond to tomato spotted wilt virus infection. BMC Genomics. 2021;22(1):810.
Hogenhout SA, el Ammar D, Whitfield AE, Redinbaugh MG. Insect vector interactions with persistently transmitted viruses. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2008;46:327–59.
Moritz G, Kumm S, Mound L. Tospovirus transmission depends on thrips ontogeny. Virus Res. 2004;100(1):143–9.
Nagata T, Inoue-Nagata AK, van Lent J, Goldbach R, Peters D. Factors determining vector competence and specificity for transmission of Tomato spotted wilt virus. J Gen Virol. 2002;83(Pt 3):663–71.
Han J, Nalam VJ, Yu IC, Nachappa P. Vector competence of thrips species to transmit soybean vein necrosis virus. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:431.
Stumpf CF, Kennedy GG. Effects of tomato spotted wilt virus isolates, host plants, and temperature on survival, size, and development time of Frankliniella occidentalis. Entomol Exp Appl. 2007;123(2):139–47.
Stumpf CF, Kennedy GG. Effects of tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) isolates, host plants, and temperature on survival, size, and development time of Frankliniella fusca. Entomol Exp Appl. 2005;114(3):215–25.
Belliure B, Janssen A, Maris PC, Peters D, Sabelis MW. Herbivore arthropods benefit from vectoring plant viruses. Ecol Lett. 2004;8(1):70–9.
Jacobson AL, Kennedy GG. Specific insect-virus interactions are responsible for variation in competency of different Thrips tabaci isolines to transmit different Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus isolates. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(1): e54567.
Cannon RJC, Matthews L, Collins DW. A review of the pest status and control options for thrips palmi. Crop Prot. 2007;26(8):1089–98.
He Z, Guo JF, Reitz SR, Lei ZR, Wu SY. A global invasion by the thrip, frankliniella occidentalis: current virus vector status and its management. Insect Sci. 2020;27(4):626–45.
Shrestha A, Champagne DE, Culbreath AK, Rotenberg D, Whitfield AE, Srinivasan R. Transcriptome changes associated with tomato spotted wilt virus infection in various life stages of its thrips vector, frankliniella fusca (Hinds). J Gen Virol. 2017;98(8):2156–70.
Thomas GWC, Dohmen E, Hughes DST, Murali SC, Poelchau M, Glastad K, Anstead CA, Ayoub NA, Batterham P, Bellair M, et al. Gene content evolution in the arthropods. Genome Biol. 2020;21(1):15.
Simao FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM. BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(19):3210–2.
Holt C, Yandell M. MAKER2: an annotation pipeline and genome-database management tool for second-generation genome projects. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:491.
Huerta-Cepas J, Szklarczyk D, Heller D, Hernandez-Plaza A, Forslund SK, Cook H, Mende DR, Letunic I, Rattei T, Jensen LJ, et al. eggNOG 5.0: a hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D309–14.
Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(1):27–30.
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Morishima K, Tanabe M. New approach for understanding genome variations in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D590–5.
The Gene Ontology C: The Gene Ontology Resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47(D1):D330-D338.
El-Gebali S, Mistry J, Bateman A, Eddy SR, Luciani A, Potter SC, Qureshi M, Richardson LJ, Salazar GA, Smart A, et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D427–32.
Mistry J, Chuguransky S, Williams L, Qureshi M, Salazar GA, Sonnhammer ELL, Tosatto SCE, Paladin L, Raj S, Richardson LJ, et al. Pfam: the protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D412–9.
International Aphid Genomics C: Genome sequence of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. PLoS Biol 2010, 8(2):e1000313.
Harrison MC, Jongepier E, Robertson HM, Arning N, Bitard-Feildel T, Chao H, Childers CP, Dinh H, Doddapaneni H, Dugan S, et al. Hemimetabolous genomes reveal molecular basis of termite eusociality. Nat Ecol Evol. 2018;2(3):557–66.
Terrapon N, Li C, Robertson HM, Ji L, Meng X, Booth W, Chen Z, Childers CP, Glastad KM, Gokhale K, et al. Molecular traces of alternative social organization in a termite genome. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3636.
Xue J, Zhou X, Zhang CX, Yu LL, Fan HW, Wang Z, Xu HJ, Xi Y, Zhu ZR, Zhou WW, et al. Genomes of the rice pest brown planthopper and its endosymbionts reveal complex complementary contributions for host adaptation. Genome Biol. 2014;15(12):521.
Zhu J, Jiang F, Wang X, Yang P, Bao Y, Zhao W, Wang W, Lu H, Wang Q, Cui N, et al. Genome sequence of the small brown planthopper. Laodelphax striatellus Gigascience. 2017;6(12):1–12.
Wang L, Tang N, Gao X, Chang Z, Zhang L, Zhou G, Guo D, Zeng Z, Li W, Akinyemi IA, et al. Genome sequence of a rice pest, the white-backed planthopper (Sogatella furcifera). Gigascience. 2017;6(1):1–9.
Kirkness EF, Haas BJ, Sun W, Braig HR, Perotti MA, Clark JM, Lee SH, Robertson HM, Kennedy RC, Elhaik E, et al. Genome sequences of the human body louse and its primary endosymbiont provide insights into the permanent parasitic lifestyle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(27):12168–73.
Chen W, Hasegawa DK, Kaur N, Kliot A, Pinheiro PV, Luan J, Stensmyr MC, Zheng Y, Liu W, Sun H, et al. The draft genome of whitefly Bemisia tabaci MEAM1, a global crop pest, provides novel insights into virus transmission, host adaptation, and insecticide resistance. BMC Biol. 2016;14(1):110.
Panfilio KA, Vargas Jentzsch IM, Benoit JB, Erezyilmaz D, Suzuki Y, Colella S, Robertson HM, Poelchau MF, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, et al. Molecular evolutionary trends and feeding ecology diversification in the Hemiptera, anchored by the milkweed bug genome. Genome Biol. 2019;20(1):64.
Sparks ME, Bansal R, Benoit JB, Blackburn MB, Chao H, Chen M, Cheng S, Childers C, Dinh H, Doddapaneni HV, et al. Brown marmorated stink bug, Halyomorpha halys (Stal), genome: putative underpinnings of polyphagy, insecticide resistance potential and biology of a top worldwide pest. BMC Genomics. 2020;21(1):227.
Hoskins RA, Carlson JW, Wan KH, Park S, Mendez I, Galle SE, Booth BW, Pfeiffer BD, George RA, Svirskas R, et al. The Release 6 reference sequence of the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Genome Res. 2015;25(3):445–58.
Herndon N, Shelton J, Gerischer L, Ioannidis P, Ninova M, Donitz J, Waterhouse RM, Liang C, Damm C, Siemanowski J, et al. Enhanced genome assembly and a new official gene set for Tribolium castaneum. BMC Genomics. 2020;21(1):47.
Tribolium Genome Sequencing C, Richards S, Gibbs RA, Weinstock GM, Brown SJ, Denell R, Beeman RW, Gibbs R, Beeman RW, Brown SJ et al: the genome of the model beetle and pest Tribolium castaneum. Nature 2008, 452(7190):949–955.
Lee BY, Choi BS, Kim MS, Park JC, Jeong CB, Han J, Lee JS. The genome of the freshwater water flea Daphnia magna: a potential use for freshwater molecular ecotoxicology. Aquat Toxicol. 2019;210:69–84.
Grbic M, Van Leeuwen T, Clark RM, Rombauts S, Rouze P, Grbic V, Osborne EJ, Dermauw W, Ngoc PC, Ortego F, et al. The genome of Tetranychus urticae reveals herbivorous pest adaptations. Nature. 2011;479(7374):487–92.
Shrestha A, Champagne DE, Culbreath AK, Abney MR, Srinivasan R. Comparison of transcriptomes of an orthotospovirus vector and non-vector thrips species. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(10): e0223438.
Rosen R, Lebedev G, Kontsedalov S, Ben-Yakir D, Ghanim M. A de novo transcriptomics approach reveals genes involved in thrips tabaci resistance to spinosad. Insects. 2021;12(1):67.
Ylla G, Nakamura T, Itoh T, Kajitani R, Toyoda A, Tomonari S, Bando T, Ishimaru Y, Watanabe T, Fuketa M, et al. Insights into the genomic evolution of insects from cricket genomes. Commun Biol. 2021;4(1):733.
Xu L, Dong Z, Fang L, Luo Y, Wei Z, Guo H, Zhang G, Gu YQ, Coleman-Derr D, Xia Q, et al. OrthoVenn2: a web server for whole-genome comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W52–8.
Enright AJ, Van Dongen S, Ouzounis CA. An efficient algorithm for large-scale detection of protein families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(7):1575–84.
Srinivasan R, Abney MR, Lai PC, Culbreath AK, Tallury S, Leal-Bertioli SCM. Resistance to thrips in peanut and implications for management of thrips and thrips-transmitted orthotospoviruses in peanut. Front Plant Sci. 2018;9:1604.
Stafford CA, Walker GP, Ullman DE. Infection with a plant virus modifies vector feeding behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(23):9350–5.
Darnell-Crumpton C, Catchot AL, Cook DR, Gore J, Dodds DM, Morsello SC, Musser FR. Neonicotinoid Insecticide resistance in tobacco thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) of mississippi. J Econ Entomol. 2018;111(6):2824–30.
Breitenbach JE, Shelby KS, Popham HJ. Baculovirus induced transcripts in hemocytes from the larvae of Heliothis virescens. Viruses. 2011;3(11):2047–64.
Wu C, Chakrabarty S, Jin M, Liu K, Xiao Y. Insect ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) transporters: roles in xenobiotic detoxification and Bt insecticidal activity. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11):2829.
Guo H, Zhang Y, Tong J, Ge P, Wang Q, Zhao Z, Zhu-Salzman K, Hogenhout SA, Ge F, Sun Y. An aphid-secreted salivary protease activates plant defense in phloem. Curr Biol. 2020;30(24):4826-4836 e4827.
Jackson CJ, Liu JW, Carr PD, Younus F, Coppin C, Meirelles T, Lethier M, Pandey G, Ollis DL, Russell RJ, et al. Structure and function of an insect alpha-carboxylesterase (alphaEsterase7) associated with insecticide resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(25):10177–82.
Lu K, Song Y, Zeng R. The role of cytochrome P450-mediated detoxification in insect adaptation to xenobiotics. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2021;43:103–7.
Galiana-Arnoux D, Dostert C, Schneemann A, Hoffmann JA, Imler JL. Essential function in vivo for Dicer-2 in host defense against RNA viruses in drosophila. Nat Immunol. 2006;7(6):590–7.
Durand N, Pottier MA, Siaussat D, Bozzolan F, Maibeche M, Chertemps T. Glutathione-S-transferases in the olfactory organ of the noctuid moth spodoptera littoralis, diversity and conservation of chemosensory clades. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1283.
Gorovits R, Czosnek H. The involvement of heat shock proteins in the establishment of tomato yellow leaf curl virus infection. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:355.
Wang W, Zhao W, Li J, Luo L, Kang L, Cui F. The c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway of a vector insect is activated by virus capsid protein and promotes viral replication. Elife. 2017;6:e26591.
Chen C, Liu Y, Shi X, Desneux N, Han P, Gao X. Elevated carboxylesterase activity contributes to the lambda-cyhalothrin insensitivity in quercetin fed Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner). PLoS ONE. 2017;12(8): e0183111.
Pavlidi N, Vontas J, Van Leeuwen T. The role of glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) in insecticide resistance in crop pests and disease vectors. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2018;27:97–102.
Degtyarenko KN. Structural domains of P450-containing monooxygenase systems. Protein Eng. 1995;8(8):737–47.
Jiang L, Liu W, Guo H, Dang Y, Cheng T, Yang W, Sun Q, Wang B, Wang Y, Xie E, et al. Distinct functions of bombyx mori peptidoglycan recognition protein 2 in immune responses to bacteria and viruses. Front Immunol. 2019;10:776.
Ma Y, Lu H, Wang W, Zhu J, Zhao W, Cui F. Membrane association of importin alpha facilitates viral entry into salivary gland cells of vector insects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(30):e2103393118.
Oliveira FAA, Buri MV, Rodriguez BL, Costa-da-Silva AL, Araujo HRC, Capurro ML, Lu S, Tanaka AS. The first characterization of a cystatin and a cathepsin L-like peptidase from Aedes aegypti and their possible role in DENV infection by the modulation of apoptosis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;146(1879–0003 (Electronic)):141–9.
Tchankouo-Nguetcheu S, Khun H, Pincet L, Roux P, Bahut M, Huerre M, Guette C, Choumet V. Differential protein modulation in midguts of Aedes aegypti infected with chikungunya and dengue 2 viruses. PLoS One. 2010;5(10):e13149.
Yang Z, Bielawski JP. Statistical methods for detecting molecular adaptation. Trends Ecol Evol. 2000;15(12):496–503.
Lewis SH, Ross L, Bain SA, Pahita E, Smith SA, Cordaux R, Miska EA, Lenhard B, Jiggins FM, Sarkies P. Widespread conservation and lineage-specific diversification of genome-wide DNA methylation patterns across arthropods. PLoS Genet. 2020;16(6): e1008864.
Glastad KM, Hunt BG, Goodisman MAD. Epigenetics in insects: genome regulation and the generation of phenotypic diversity. Annu Rev Entomol. 2019;64:185–203.
Lev Maor G, Yearim A, Ast G. The alternative role of DNA methylation in splicing regulation. Trends Genet. 2015;31(5):274–80.
Shen JC, Rideout WM 3rd, Jones PA. The rate of hydrolytic deamination of 5-methylcytosine in double-stranded DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22(6):972–6.
Elango N, Hunt BG, Goodisman MA, Yi SV. DNA methylation is widespread and associated with differential gene expression in castes of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(27):11206–11.
Moore LD, Le T, Fan G. DNA methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;38(1):23–38.
Bewick AJ, Vogel KJ, Moore AJ, Schmitz RJ. Evolution of DNA Methylation across Insects. Mol Biol Evol. 2017;34(3):654–65.
Posfai J, Bhagwat AS, Roberts RJ. Sequence motifs specific for cytosine methyltransferases. Gene. 1988;74(1):261–5.
OmicsBox – Bioinformatics Made Easy [https://www.biobam.com/omicsbox]
Rhoads A, Au KF. PacBio sequencing and its applications. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015;13(5):278–89.
Hotaling S, Sproul JS, Heckenhauer J, Powell A, Larracuente AM, Pauls SU, Kelley JL, Frandsen PB. Long reads are revolutionizing 20 years of insect genome sequencing. Genome Biol Evol. 2021;13(8):evab138.
Kryazhimskiy S, Plotkin JB. The population genetics of dN/dS. PLoS Genet. 2008;4(12): e1000304.
Calla B. Signatures of selection and evolutionary relevance of cytochrome P450s in plant-insect interactions. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2021;43:92–6.
Li X, Zheng T, Zheng X, Han N, Chen X, Zhang D: Molecular Characterization of Two Fatty Acyl-CoA Reductase Genes From Phenacoccus solenopsis (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae). J Insect Sci 2016, 16(1).
Wang DL, Dillwith JW, Ryan RO, Blomquist GJ, Reitz RC. Characterization of the acyl-CoA desaturase in the housefly. Musca domestica L Insect Biochemistry. 1982;12(5):545–51.
Gotz M, Popovski S, Kollenberg M, Gorovits R, Brown JK, Cicero JM, Czosnek H, Winter S, Ghanim M. Implication of Bemisia tabaci heat shock protein 70 in Begomovirus-whitefly interactions. J Virol. 2012;86(24):13241–52.
Selot R, Kumar V, Shukla S, Chandrakuntal K, Brahmaraju M, Dandin SB, Laloraya M, Kumar PG. Identification of a soluble NADPH oxidoreductase (BmNOX) with antiviral activities in the gut juice of Bombyx mori. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2007;71(1):200–5.
Ge J, Wei Z, Huang Y, Yin J, Zhou Z, Zhong J. AcMNPV ORF38 protein has the activity of ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase and is important for virus replication. Virology. 2007;361(1):204–11.
Mukherjee K, Dubovskiy I, Grizanova E, Lehmann R, Vilcinskas A. Epigenetic mechanisms mediate the experimental evolution of resistance against parasitic fungi in the greater wax moth Galleria mellonella. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1626.
Yi SV, Goodisman MAD. The impact of epigenetic information on genome evolution. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1826;2021(376):20200114.
Hunt BG, Glastad KM, Yi SV, Goodisman MA. Patterning and regulatory associations of DNA methylation are mirrored by histone modifications in insects. Genome Biol Evol. 2013;5(3):591–8.
Lyko F, Foret S, Kucharski R, Wolf S, Falckenhayn C, Maleszka R. The honey bee epigenomes: differential methylation of brain DNA in queens and workers. PLoS Biol. 2010;8(11): e1000506.
Hunt BG, Brisson JA, Yi SV, Goodisman MA. Functional conservation of DNA methylation in the pea aphid and the honeybee. Genome Biol Evol. 2010;2:719–28.
Glastad KM, Hunt BG, Goodisman MA. Evidence of a conserved functional role for DNA methylation in termites. Insect Mol Biol. 2013;22(2):143–54.
Wu P, Jie W, Shang Q, Annan E, Jiang X, Hou C, Chen T, Guo X. DNA methylation in silkworm genome may provide insights into epigenetic regulation of response to Bombyx mori cypovirus infection. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16013.
Schmitz RJ, Lewis ZA, Goll MG. DNA Methylation: shared and divergent features across eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 2019;35(11):818–27.
Kausar S, Abbas MN, Cui H. A review on the DNA methyltransferase family of insects: aspect and prospects. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;186:289–302.
Rastogi S, Liberles DA. Subfunctionalization of duplicated genes as a transition state to neofunctionalization. BMC Evol Biol. 2005;5:28.
Cusack BP, Wolfe KH. When gene marriages don’t work out: divorce by subfunctionalization. Trends Genet. 2007;23(6):270–2.
Assis R, Bachtrog D. Neofunctionalization of young duplicate genes in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(43):17409–14.
Fallon TR, Lower SE, Chang CH, Bessho-Uehara M, Martin GJ, Bewick AJ, Behringer M, Debat HJ, Wong I, Day JC, et al. Firefly genomes illuminate parallel origins of bioluminescence in beetles. Elife. 2018;7:e36495.
Kim B-M, Mirbahai L, Mally A, Kevin Chipman J, Rhee J-S, Lee J-S. Correlation between the DNA methyltransferase (Dnmt) gene family and genome-wide 5-methylcytosine (5mC) in rotifer, copepod, and fish. Genes & Genomics. 2015;38(1):13–23.
Ullman DE, Whitfield AE, German TL. Thrips and tospoviruses come of age: mapping determinants of insect transmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(14):4931–2.
Kolmogorov M, Yuan J, Lin Y, Pevzner PA. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37(5):540–6.
Lin Y, Yuan J, Kolmogorov M, Shen MW, Chaisson M, Pevzner PA. Assembly of long error-prone reads using de Bruijn graphs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(52):E8396–405.
Jacobson AL, Johnston JS, Rotenberg D, Whitfield AE, Booth W, Vargo EL, Kennedy GG. Genome size and ploidy of Thysanoptera. Insect Mol Biol. 2013;22(1):12–7.
Li H. Minimap2: pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics. 2018;34(18):3094–100.
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R. Genome project data processing s: the sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(16):2078–9.
Li H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2011;27(21):2987–93.
Walker BJ, Abeel T, Shea T, Priest M, Abouelliel A, Sakthikumar S, Cuomo CA, Zeng Q, Wortman J, Young SK, et al. Pilon: an integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(11): e112963.
Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G. QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(8):1072–5.
Wick RR, Schultz MB, Zobel J, Holt KE. Bandage: interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(20):3350–2.
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ, Marra MA. Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009;19(9):1639–45.
Schaffer AA, Nawrocki EP, Choi Y, Kitts PA, Karsch-Mizrachi I, McVeigh R. VecScreen_plus_taxonomy: imposing a tax(onomy) increase on vector contamination screening. Bioinformatics. 2018;34(5):755–9.
Marcais G, Kingsford C. A fast, lock-free approach for efficient parallel counting of occurrences of k-mers. Bioinformatics. 2011;27(6):764–70.
Bushnell B, Rood J, Singer E. BBMerge - accurate paired shotgun read merging via overlap. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(10): e0185056.
Korf I. Gene finding in novel genomes. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004;5:59.
Stanke M, Morgenstern B. AUGUSTUS: a web server for gene prediction in eukaryotes that allows user-defined constraints. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(Web Server issue):W465-467.
Yandell M, Ence D. A beginner’s guide to eukaryotic genome annotation. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13(5):329–42.
Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Williams TD, Nagaraj SH, Nueda MJ, Robles M, Talon M, Dopazo J, Conesa A. High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(10):3420–35.
Ye J, Fang L, Zheng H, Zhang Y, Chen J, Zhang Z, Wang J, Li S, Li R, Bolund L, et al. WEGO: a web tool for plotting GO annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(Web Server issue):W293-297.
Ye J, Zhang Y, Cui H, Liu J, Wu Y, Cheng Y, Xu H, Huang X, Li S, Zhou A, et al. WEGO 2.0: a web tool for analyzing and plotting GO annotations, 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(1):W71–5.
Emms DM, Kelly S. OrthoFinder: phylogenetic orthology inference for comparative genomics. Genome Biol. 2019;20(1):238.
Emms DM, Kelly S. OrthoFinder: solving fundamental biases in whole genome comparisons dramatically improves orthogroup inference accuracy. Genome Biol. 2015;16:157.
Katoh K, Standley DM. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30(4):772–80.
Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(9):1312–3.
Emms DM, Kelly S. STRIDE: Species Tree Root Inference from Gene Duplication Events. Mol Biol Evol. 2017;34(12):3267–78.
Minh BQ, Schmidt HA, Chernomor O, Schrempf D, Woodhams MD, von Haeseler A, Lanfear R. IQ-TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol Biol Evol. 2020;37(5):1530–4.
Hoang DT, Chernomor O, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ, Vinh LS. UFBoot2: improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol Biol Evol. 2018;35(2):518–22.
Nguyen LT, Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ. IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol. 2015;32(1):268–74.
Huerta-Cepas J, Forslund K, Coelho LP, Szklarczyk D, Jensen LJ, von Mering C, Bork P. Fast genome-wide functional annotation through orthology assignment by eggNOG-mapper. Mol Biol Evol. 2017;34(8):2115–22.
Blum M, Chang HY, Chuguransky S, Grego T, Kandasaamy S, Mitchell A, Nuka G, Paysan-Lafosse T, Qureshi M, Raj S, et al. The InterPro protein families and domains database: 20 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D344–54.
Li B, Dewey CN. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:323.
Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 2012;9(4):357–9.
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15(12):550.
Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M, Gingeras TR. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(1):15–21.
Anders S, Reyes A, Huber W. Detecting differential usage of exons from RNA-seq data. Genome Res. 2012;22(10):2008–17.
Suyama M, Torrents D, Bork P. PAL2NAL: robust conversion of protein sequence alignments into the corresponding codon alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(Web Server issue):W609-612.
Yang Z. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24(8):1586–91.
Supek F, Bosnjak M, Skunca N, Smuc T. REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of gene ontology terms. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(7): e21800.
Pertea G, Pertea M: GFF Utilities: GffRead and GffCompare. F1000Res 2020, 9.
Quinlan AR, Hall IM. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(6):841–2.
Xu Z, Wang H. LTR_FINDER: an efficient tool for the prediction of full-length LTR retrotransposons. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(Web Server issue):W265-268.
Ou S, Jiang N. LTR_FINDER_parallel: parallelization of LTR_FINDER enabling rapid identification of long terminal repeat retrotransposons. Mob DNA. 2019;10:48.
Shi J, Liang C. Generic repeat finder: a high-sensitivity tool for genome-wide de novo repeat detection. Plant Physiol. 2019;180(4):1803–15.
Su W, Gu X, Peterson T. TIR-Learner, a new ensemble method for TIR transposable element annotation, provides evidence for abundant new transposable elements in the maize genome. Mol Plant. 2019;12(3):447–60.
Xiong W, He L, Lai J, Dooner HK, Du C. HelitronScanner uncovers a large overlooked cache of Helitron transposons in many plant genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(28):10263–8.
Ou S, Jiang N. LTR_retriever: a highly accurate and sensitive program for identification of long terminal repeat retrotransposons. Plant Physiol. 2018;176(2):1410–22.
Ou S, Su W, Liao Y, Chougule K, Agda JRA, Hellinga AJ, Lugo CSB, Elliott TA, Ware D, Peterson T, et al. Benchmarking transposable element annotation methods for creation of a streamlined, comprehensive pipeline. Genome Biol. 2019;20(1):275.
Ellinghaus D, Kurtz S, Willhoeft U. LTRharvest, an efficient and flexible software for de novo detection of LTR retrotransposons. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:18.
Conesa A, Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Talon M, Robles M. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics. 2005;21(18):3674–6.
Jones P, Binns D, Chang HY, Fraser M, Li W, McAnulla C, McWilliam H, Maslen J, Mitchell A, Nuka G, et al. InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(9):1236–40.
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden TL. BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009;10:421.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the University of Maryland Brain & Behavior Institute – Advanced Genomic Technologies Core for conducting the sequencing of our samples.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Hatch Project ALA015-4–19062 (A.L.J.), Hatch Project GEO00671 (R.S.), Hatch Project GEO00863 (B.G.H.), the National Peanut Research Initiative, and the Georgia Peanut Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.A.C., A.L.J., B.G.H., and R.S. conceived the project. A.L.J., G.G.K., and P.E.L. reared insect colonies for this study. A.L.J., G.G.K., and P.E.L. provided resources for sequencing. P.E.L. performed the extractions and library prep for sequencing. M.A.C. performed the computational analysis. M.A.C., B.G.H., and R.S. designed the analysis and wrote the manuscript. All authors have read, edited, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Catto, M.A., Labadie, P.E., Jacobson, A.L. et al. Pest status, molecular evolution, and epigenetic factors derived from the genome assembly of Frankliniella fusca, a thysanopteran phytovirus vector. BMC Genomics 24, 343 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-023-09375-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-023-09375-5