Abstract
Background
As one of the largest transcription factor families in plants, AP2/ERF gene superfamily plays important roles in plant growth, development, fruit ripening and biotic and abiotic stress responses. Despite the great progress has been made in kiwifruit genomic studies, little research has been conducted on the AP2/ERF genes of kiwifruit. The increasing kiwifruit genome resources allowed us to reveal the tissue expression profiles of AP2/ERF genes in kiwifruit on a genome-wide basis.
Results
In present study, a total of 158 AP2/ERF genes in A. eriantha were identified. All genes can be mapped on the 29 chromosomes. Phylogenetic analysis divided them into four main subfamilies based on the complete protein sequences. Additionally, our results revealed that the same subfamilies contained similar gene structures and conserved motifs. Ka/Ks calculation indicated that AP2/ERF gene family was undergoing a strong purifying selection and the evolutionary rates were slow. RNA-seq showed that the AP2/ERF genes were expressed differently in different flower development stages and 56 genes were considered as DEGs among three contrasts. Moreover, qRT-PCR suggested partial genes showed significant expressions as well, suggesting they could be key regulators in flower development in A. eriantha. In addition, two genes (AeAP2/ERF061, AeAP2/ERF067) had abundant transcription level based on transcriptomes, implying that they may play a crucial role in plant flower development regulation and flower tissue forming.
Conclusions
We identified AP2/ERF genes and demonstrated their gene structures, conserved motifs, and phylogeny relationships of AP2/ERF genes in two related species of kiwifruit, A. eriantha and A. chinensis, and their potential roles in flower development in A. eriantha. Such information would lay the foundation for further functional identification of AP2/ERF genes involved in kiwifruit flower development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Transcription factors (TFs) are a class of proteins that take part in various biological processes including fruit ripening, plant growth and development, as well as biotic and abiotic stress responses such as drought, low temperature, pathogen infecting [1]. With the increasing reports of the plant genomes, numerous transcription factor families including MYB [2], bHLH [3], WRKY [1] and AP2/ERF in different species were clearly detected. Among them, AP2/ERF (APETALA 2/Ethylene Responsive Element Binding Factor) superfamily was early confirmed in Arabidopsis thaliana, and involved in flower and seed development [4,5,6]. Subsequently, all 147 genes were finally identified in A. thaliana [7,8,9]. Then, AP2/ERF family was gradually confirmed in diverse species and showed various numbers with different genome sizes. For example, 114 AP2/ERF genes were found in Ricinus communis (~ 336 Mb) [10] and 131 AP2/ERF genes were identified in peach (Prunus persica) (~ 228 Mb) [11].
According to the previous studies, a striking feature of all members from AP2/ERF gene family is containing at least one AP2 domain consists of about 60–70 amino acids [6]. Based on the number of AP2 domain, they are mainly regarded as AP2 genes with variable amount of AP2 domains and ERF genes with only single AP2 domain [12]. AP2/ERF gene family can be divided into five subfamilies, APETELA2 (AP2), ABI3/VP1 (RAV) containing both of AP2 and B3 domain, DREB (dehydration-responsive element-binding protein), ERF (ethylene-responsive factor) subfamily and other proteins (Soloist). Additionally, DREB subfamily can be grouped into A1 to A6, and ERF subfamily can be grouped into B1- B6 as well [8]. AP2/ERF genes were closely related to flowering in previous studies, especially genes in the AP2 family [13, 14]. Flowering was widely recognized as a key symbol in transition from vegetative growth to reproductive growth in plants [15]. Illustrating the mechanisms of flower development and flower transition has great significance for plant adaptation to poor environment and plant breeding [16]. There is plenty of evidence of implication of AP2/ERF genes in flower development processes. For instance, in ‘ABC’ model of flower development, APETALA2 (AP2) as an A-class gene took part in flower formation [17]. Recently, researchers have found that the expressions of two DoAP2 genes (DoAP2–8 and DoAP2–10) were down-regulated and another two AP2 genes (DoAP2–2 and DoAP2–3) were up-related during flower development, which suggested that DoAP2 genes contribute to plant regeneration and flower development in Dendrobium officinale [18]. Overexpression of miR172, whose target is AP2-like gene, resulted in the double flower phenotype in roses [19]. Additionally, the AP2-like transcriptional factor TOE1 could also regulate FT expression to control flowering [20]. In flowering plants, SOC1 might combine with the promoter of CBFs to influence flowering in cold environment [21].
Kiwifruit is a dicotyledonous, perennial, deciduous plant belonging to the genus Actinidia (Actinidiaceae) [22]. It has great morphological variations for stems, leaves, flowers and fruits. As a vital fruit contains huge commercial value and considerable nutritive value, it is called “the King of fruits” [23]. Kiwifruit originated from China and gradually spread to other countries [24]. In the early twentieth century, kiwifruit was beginning to be domesticated and cultivated, and some excellent cultivars were selected such as ‘Hayward’, ‘Bruno’ for Actinidia chinensis Planch. var. deliciosa, ‘Hongyang’ for Actinidia chinensis Planch. and ‘White’ for Actinidia eriantha Benth. Recently, kiwifruit breeding and genetic studies have been carried out for different purposes all over the world [25], however, there are few studies on the flower development and timing of kiwifruit. As we know, breeding early flowering cultivars to decrease the risk of frost damage is an important breeding goal. Therefore, it is very necessary to reveal the genes involved in flower development and timing. AP2/ERFs play a vital role in plant flower development. However, little is known about the importance of AP2/ERF genes in kiwifruit flowering.
Recently, high-quality genomes for A. eriantha and A. chinensis were available, which provides an opportunity to reveal the tissues specificity and expression profiles of AP2/ERF genes in kiwifruit on a genome-wide basis [26, 27]. In this study, we systematically conducted genome-wide analysis of AP2/ERF gene superfamily in A. eriantha through investigating the sequence conservation, gene locations, gene structures and evolutionary relationships. In addition, we investigated the expression profiles of AP2/ERF genes in three flower development stages (flower buds, unopened flowers and full-opening stage) of A. eriantha (Fig. 1). Our study provided a unique and fundamental insight in the molecular evolution of AP2/ERF genes in kiwifruit and added valuable information for screening important AP2/ERF genes in regulating floral development and blooming in woody perennials.
Results
Identifications and characterizations of AP2/ERF family members in kiwifruit
We obtained 175 candidate genes in A. eriantha through the HMMER software [28]. Similarly, 191 unique protein sequences were selected in kiwifruit by BLASTP [29] program. Then, the common genes confirmed by above two methods were filtered via three common databases. Finally, 158 genes in A. eriantha were retained. According to their orders on the chromosomes, we renamed all the genes AeAP2/ERF001 to AeAP2/ERF158. The whole proteins and coding sequences were listed in Additional file 1 Table S1.
Among them, 141 genes had one complete AP2 domain in A. eriantha while 17 genes had two or more domains such as AeAP2/ERF039 which contained three domains (Additional file 2 Table S2). The length of protein in A. eriantha ranged from 95 aa (AeAP2/ERF040) to 783 aa (AeAP2/ERF026) with an average of 297 amino acids. Consistent with the number of amino acids, the longest coding sequence contained 2,349 bp (AeAP2/ERF026) and the shortest was only 288 bp (AeAP2/ERF040). The molecular weight (MW) ranged from 10.57 (AeAP2/ERF040) to 89.36 kDa (AeAP2/ERF026) and the isoelectric point (PI) ranged from 4.5 (AeAP2/ERF152) to 11.97 (AeAP2/ERF060).
In order to explore the evolution of AP2/ERF gene family in Actinidia, 189 AP2/ERF genes in A. chinensis renamed AcAP2/ERF001 to AcAP2/ERF189 were also identified and analyzed (Additional file 1 Table S1). The protein length varied from 81 (AcAP2/ERF129) to 922 aa (AcAP2/ERF052). The coding sequence length ranged from 246 (AcAP2/ERF129) to 2,769 bp (AcAP2/ERF052). MW ranged from 9.24 to 102 kDa. PI ranged from 4.51 (AcAP2/ERF080) to 10.71 (AcAP2/ERF066). The detailed information about AP2/ERF gene family in both A. eriantha and A. chinensis were presented in Additional file 3 Table S3.
Classification and phylogenetic analysis of AP2/ERF gene family
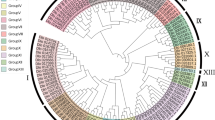
To evaluate the evolutionary relationships of AP2/ERF superfamily among A. eriantha, A. chinensis and A. thaliana, the full-length protein sequences were first aligned. Then, 494 protein sequences were used to conduct a phylogenetic tree using Neighbor-joining (NJ) method with 1,000 bootstrap replications, poisson model and pairwise deletion. Referred to classification of AP2/ERF genes in A. thaliana [9], all genes from kiwifruit were divided into four primary subfamilies referring to RAV, AP2, ERF and DREB subfamily (Fig. 2). In A. eriantha, 72 genes belonged to ERF subfamily and 47 genes were clustered to DREB subfamily. About 22% (34 genes) of genes were assigned to AP2 subfamily. Three genes contained one AP2 domain and a B3 domain were divided into RAV family. ERF subfamily contained most genes, followed by DREB and AP2 subfamily, and RAV subfamily was made up of the fewest genes. ERF subfamily genes accounted for 51% (96 genes) in A. chinensis and the rate of DREB subfamily genes was only 28% (53 genes). Then 35 genes were segmented into AP2 subfamily (Additional file 3 Table S3). In addition, four genes (AeAP2/ERF089, AeAP2/ERF154, AcAP2/ERF133, AcAP2/ERF166) were identified as Soloist in A. eriantha and A. chinensis as they had high homology with AT4G13040.1 in A. thaliana. Interestingly, there were several genes belonging to the AP2 family clustered in the ERF subgroup in both species (Fig. 2).
Structural and conserved motif analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily
To better understand the evolutionary relationships and structural components of AP2/ERF superfamily in kiwifruit, the exon–intron gene structures based on genome sequences and conserved motifs based on protein sequences were analyzed. Structural analysis suggested that not all AP2/ERF genes in A. eriantha had at least one intron, in contrast, 65 genes (41.1%) had no intron. Most genes existed one or two exons, comprised 58.8% of the total. But there are still a small subset of genes contained 9, 10 or 22 exons (Fig. 3A; Additional file 4 Table S4). Overall, the number of exons in A. eriantha varied from 1 to 22, while from 1 to 17 in A. chinensis. The genes containing the maximum number of exons were AeAP2/ERF026 and AcAP2/ERF056 in A. eriantha and A. chinensis, respectively.
Gene structures and distributions of conserve motifs of AP2/ERF genes in different subfamilies in A. eriantha. A The phylogenetic tree of AP2/ERF genes in A. eriantha (left); Motifs contained in AP2/ERF proteins (middle) and the exon-intron structures of kiwifruit AP2/ERF genes (right). B Protein sequences of conserved motifs identified in A. eriantha. Red pentacle means the bootstrap value (20–100%)
Meanwhile, ten motifs were searched in 158 AP2/ERF proteins sequences in A. erianth (Fig. 3B), and only three motifs (motif 1, motif 2 and motif 4) were identified as locating in the AP2 domain (Additional file 5 Table S5). All AP2/ERF proteins contained motif 2 or motif 1 (except AeAP2/ERF032). However, only 22 proteins contained motif 4, and 21 out of which belonged to AP2 family (Fig. 3). The frequency of motif 3 was higher than that of motif 5, although both of them were common in 158 protein sequences. In the gene family, some motifs were only found in a subfamily. For example, motif 9 just existed in several ERF-B6 subfamily genes and motif 10 was only identified in part of AP2 subfamily (Fig. 3A).
Cis-acting regulatory elements analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily
A total of 3,992 cis-elements including 21 primary types were identified and divided into following three main parts, plant development, abiotic and biotic stress responses contained drought-inducibility, light-responsiveness, low-temperature responsiveness, defense and stress responsiveness such as wounds and salts, and plant hormone responses including SA-responsiveness, ABA-responsiveness, MeJA-responsiveness, GA-responsiveness and Auxin-responsiveness (Additional file 6 Fig. S1). Among these, the light-responsiveness was detected in all genes. Additionally, ABA-responsiveness, MeJA-responsiveness also appeared in most genes. As the important components, biotic and abiotic stresses occurred in all families. The more detailed information was listed in Additional file 7 Table S6.
Gene distribution and gene duplication events in A. eriantha
To obtain the intuitionistic distributions of AP2/ERF gene family on the chromosomes, a draft was painted. All AP2/ERF genes in A. eriantha could be detected on the chromosomes and each chromosome had at least one gene (Fig. 4). Most genes were located on chromosomes 14 (twelve genes, 7.5%), followed by chromosomes 24, 13 and 3, consisting of nine, eight and eight genes, respectively. Notably, only one gene (AeAP2/ERF152) was found on Chr27. A large number of genes were located on the bottom of chromosome, such as Chr04, Chr08, Chr12, Chr13 and Chr14. However, less genes were near the centromere.
The expansions or contractions of gene family were concerned with gene duplications such as WGD/segmental, tandem, and others including proximal, dispersed and lost. We analyzed the types of duplications in kiwifruit by MCScanX [30]. All types of duplications were found and WGD/segmental account for the largest proportion (76.8%), followed by the type of dispersed (20.6%). Three genes (AeAP2/ERF073, AeAP2/ERF126, AeAP2/ERF135) were tandem duplications. Only one gene (AeAP2/ERF082) was proximal. While in A. chinensis, more than 90% of the genes were WGD/segmental, only three genes were identified as tandem genes. In addition, nine genes were sought to be singleton (Additional file 3 Table S3). Consequently, WGD/segmental was the crucial factor in the expansion of AP2/ERF gene family.
Collinearity analysis of three putative species and Ka/Ks calculation
Intra- and intergenomic relationships demonstrated a favorable collinearity (Fig. 5). A quite number of AP2/ERF genes in A. eriantha showed a great syntenic relationship with genes from different species. Similarly, compared with analysis in A. eriantha, more collinear blocks were clarified and existed between A. eriantha and A. chinensis, which suggested their kinship was close (Fig. 5B). Specifically, 97 pairs of paralogous genes in A. eriantha and 142 pairs in A. chinensis were obtained and some genes were involved two or more processes of collinearity evolution. Meantime, 237 gene pairs were confirmed between A. eriantha and A. chinensis as we expected (Additional file 8 Table S7). Besides, we also detected 75 duplicated gene pairs whose similarities were high than 85%. Among these, about half of gene pairs were collinear (Additional file 9 Fig. S2).
Synteny analysis of AP2/ERF gene family in three species. Red line represented the collinear gene pairs in AP2/ERF gene family. Chr represents the different chromosome in A. eriantha. LG represents the different chromosome in A. chinensis. At represents the different chromosome in A. thaliana. Synteny analysis of AP2/ERF gene family within A. eriantha (A), between A. eriantha and A. chinensis (B), between A. eriantha and A. thaliana (C)
Most Ka/Ks values were less than 1 for A. eriantha and A. chinensis. However, the ratios of Ka/Ks for three orthologous gene pairs (AeAP2/ERF029 - AcAP2/ERF075, AeAP2/ERF041 - AcAP2/ERF106, AeAP2/ERF059 - AcAP2/ERF181) between A. eriantha and A. chinensis were more than 1, which suggested that several AP2/ERF genes involved in adaptive evolution. Based on homologous gene pairs, we calculated the Ks values and obtained the ranges of peaks of 0.23–0.28 in A. eriantha, 0.25–0.30 in A. chinensis and 0.01–0.07 between A. eriantha and A. chinensis corresponding to three divergence time (33–41 MYA, 36–44 MYA and 1.4–10.3 MYA), respectively. Besides, the divergence time of each pair were approximately 4.49–198 MYA, 3.48–134 MYA and 0.26–70 MYA in A. eriantha, A. chinensis and combination of A. eriantha and A. chinensis, respectively (Fig. 6; Additional file 8 Table S7).
The biological functions of AP2/ERF genes in kiwifruit flower development
To investigate the potential biological functions of AeAP2/ERF genes in kiwifruit flower development, flowers in different development stages were prepared for RNA-seq. A total of 232,160,000 clean reads (54 Gb) were obtained with 6 Gb per sample. The mapping rates varied from 84.49 to 85.46% with an average of 84.91% (Additional file 10 Table S8). In addition, we estimated the expression bias of AeAP2/ERFs in different flowering periods of A. eriantha, and results showed that ten genes (TPM = 0) were not expressed in any stages and three genes (AeAP2/ERF025, AeAP2/ERF061 and AeAP2/ERF067) were always abundantly expressed (TPM > 150) (Fig. 7A, B; Additional file 11 Table S9). Interestingly, many of duplicated gene pairs kept the similar expression trends, although their expression levels were not consistent (Additional file 9 Fig. S2). For example, the expression abundances of AeAP2/ERF023 and AeAP2/ERF118 gradually increased in the process of flower development. However, there were still a small number of duplicated gene pairs showed the opposite trends as well. For instance, AeAP2/ERF006 was downregulated, but AeAP2/ERF033 was upregulated. Besides, 56 DEGs (different expression genes) in AP2/ERF family were detected among three combinations (stage1 versus stage 2, stage2 versus stage 3 and stage1 versus stage 3) to explore the primary functions of AeAP2/ERFs, and false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 and abs (log-fold-change) > 1 served as the standard (Fig. 7C).
Expression profiles of AeAP2/ERFs. A The expression profile of AeAP2/ERF genes in the kiwifruit at different flower developmental stages. B The expression profiles of different expression genes in the three contrasts. C Venn diagram of DEGs in three combinations. D The relative expressions of several AeAP2/ERF genes analyzed by qRT-PCR. *: P < 0.05; **: P < 0.01; ***: P < 0.001. The colors blue and red correspond to low and high values of gene expression
To further examine the expression patterns and check the reliability of expression of AeAP2/ERFs by RNA-seq, qRT-PCR was performed. Nineteen genes in DEGs with high expressions were randomly selected for validating the accuracy of RNA-seq and primarily confirmed their influence on flower development as well (Fig. 7D). The main expression trends were similar in qRT-PCR and RNA-seq as a whole. These DEGs were expressed significantly in three stages especially between stage 1 and stage 2. Among these DEGs, eleven genes were up-regulate expressed trends as the flowers opening especially from stage 1 to stage 2. On the contrary, expressions of eight genes decreased during the whole process of flower transitions. Thereinto, corresponding with transcriptome data, AeAP2/ERF061 and AeAP2/ERF094 showed high expressions in three stage flowers as well. Additionally, in the process of flower development, most of genes exhibited continuous trends (e.g. AeAP2/ERF042, AeAP2/ERF096), while some genes reached a highest expression level at the stage 2 including AeAP2/ERF078 and AeAP2/ERF118.
Discussion
AP2/ERF transcription factor family as the essential regulator in many biological processes plays vital roles in the diverse processes including plant growth, fruit ripening and softening, flower development and biotic and abiotic stress responses. Recently, many AP2/ERF genes have been confirmed in different species, but the number of AP2/ERF genes varies greatly. For instance, 193 AP2/ERF genes in Dactylis glomerata (~ 1.84 Gb) [31], 134 in tartary buckwheat (Fagopyum Tataricum) (~ 489 Mb) [32], 125 in longan (Dimocarpus longan) (~ 471 Mb) [33], 200 in Populus trichocarpa (~ 394 Mb) [34], and 132 in the grapevine (Vitis vinifera) (~ 475 Mb) genome were identified [35]. In this study, we identified 158 AP2/ERF genes in A. eriantha and 189 in A. chinensis. However, 270 AP2/ERF genes were identified in A. chinensis in the previous study, which might be resulted from different methods, criteria or reference genomes [36]. Although both A. eriantha and A. chinensis had a similar-sized genome, there is a large difference in gene numbers of AP2/ERF family. Compared with A. eriantha, more AP2/ERF genes were identified in A. chinensis (Additional file 3 Tables S3). Thus, the numbers of transcription factors were not tightly associated with the genome sizes, which was mainly caused by the creation of new genes or gene losses in speciation [37]. Plant genome had experienced duplication, polyploidization and transposon insertion in their long evolutionary process. Different evolutionary patterns were likely to produce new genes or new functions [38]. The different number of AP2/ERF genes in related species indicates that they probably have extensively expanded in their evolutionary processes. For example, two likely auto-tetraploidization events occurred during the speciation of kiwifruit compared with grape, which might explain why more AP2/ERF genes exited in kiwifruit [39]. Collinearity analysis showed that AP2/ERF gene family has experienced more duplication events in kiwifruit as well (Fig. 5). Therefore, kiwifruit could be also regarded as a good model to expound the relationship between gene number and genome size in the same genus owing to its complex evolutionary history [40].
Various numbers of introns would result in splice variants and it allowed genes to perform various functions. Besides, it also represents different selective pressures [41]. In the present study, the number of exons in kiwifruit varied greatly and the average number of exons for A. eriantha (2.98) was lower than that of A. chinensis (3.58) (Additional file 4 Table S4). In other words, our results revealed that there was great difference in the number of introns in whole AP2/ERF family in kiwifruit. However, the number of introns within each subfamily varied slightly, and more introns were identified in AP2 subfamily. Compared with AP2 subfamily, genes from ERF and DREB subfamilies had fewer introns, which has been confirmed in A. thaliana and Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba) [8, 42]. Previous studies revealed that intron was lost slowly during evolution in rice (Oryza sativa) and A. thaliana [43]. The low rate of intron loss might gradually increase the complexity of evolution patterns, gene functions or the number of genes in gene family in the process of constant change. Consequently, it could be a good explanation for why there are more genes in the ERF and DREB subfamilies where both are less conservative than AP2 subfamily [44].
It has been made clear that some evolutionary events have been increased the members of gene family. While point mutations in exon regions and upstream site of new members could also affect the functions and expression patterns of gene family members [45, 46]. Besides, multifarious motifs and cis-elements appeared in different subfamilies, which also caused differences in functions for various stress responses. For example, in A. thaliana, overexpression of TINY, one member of AP2/ERF family, increased the survival under the drought stress [47]. However, another gene AtERF111 was not sensitive to drought but influenced strongly by wounding stress [48]. Even so, as was expected, most closely related family members had similar sections, which indicated they were quite conservative and functional similarity between the AP2/ERF proteins in the same subgroup or in homologous gene pairs. It still needs to be emphasized that even though there were differences, they share some common aspects. For example, they might be sensitive to light signal and likely participated in phytohormone responses induced by abscisic acid (ABA) and jasmonic acid (JA) owing that cis-elements of ABA-responsiveness, MeJA-responsiveness and light-responsiveness.
Notably, the values of Ka/Ks for all gene pairs in A. eriantha suggested that they were under the strong negative selection pressures [49]. Additionally, most Ka/Ks values of intron-poor subfamily (ERF and DREB subfamilies) were further away from 1 and lower than the values of AP2 subfamily, suggesting that they experienced stronger selective pressures and needed shorter genes to duplicate easily that took less time [50]. Interestingly, divergence time of AP2/ERF genes within A. eriantha and between A. eriantha and A. chinensis were closer to the time of WGD event (Ad-α, 17.7–26.5 MYA) and divergence between A. eriantha and A. chinensis (~ 11 MYA), suggested that either WGD or species differentiation would have a great influence on the generation, loss and differentiation of genes [26, 27, 39].
Gene functions were deeply associated with their expression patterns [32]. RNA-seq analysis of different stage tissues showed that most genes (104 genes, 65%) were expressed in at least one samples, and one third of genes almost never expressed (Fig. 7A). They might work in a putative condition or have a strong tissue-specific expression. It was also possible that they were pseudogenes. For example, AeAP2/ERF018 as a representative gene from DREB subfamily was not detected in the present study. Based on the phylogenetic tree, we consider that they had a more recent evolutionary relationship with AT2G40220.1 (AtABI4) in Arabidopsis. AtABI4, as an important gene related to seed dormancy, was primarily expressed in seeds and rarely detected in other vegetative organs [51]. Our results would provide us a good reference for determining gene functions in kiwifruit. Another homologous gene AeAP2/ERF011 also followed this rule. Besides, AtWRI1 were revealed to be involved in seedling development in A. thaliana and had a high abundance in seeds [52]. The expression pattern might shed light on the tissue-specific expression of AeAP2/ERF049 as its homologous gene was also confirmed in tartary buckwheat [32]. AeAP2/ERF081 was identified as a relative gene with AT1G63030.1 (AtDDF2), but it was distinct in expression profiles. AtDDF2 most abundantly expressed in rosette leaves and stems, conversely, AeAP2/ERF081 did not express, which suggested that the functions gradually appeared divergence during evolution. The similar pattern was found in ginger (Zingiber officinale) [53]. Additionally, partial genes have high transcription abundance. For instance, the high expression of gene AeAP2/ERF096 is founded in flowers. According to the previous reports [54], the orthologous gene AT1G15360.1 (AtSHIN1) in A. thaliana was just expressed in the flowers and involved in wax biosynthesis. It can be supposed that AeAP2/ERF096 may perform the same function. Over-expression of the gene might result in glossy leaf phenotype and increase drought tolerance. Interestingly, although both AeAP2/ERF060 and AeAP2/ERF096 can be regarded as homologous genes of AT1G15360.1, AeAP2/ERF060 was not detected, suggesting function lose in the evolution process of kiwifruit.
As an important part of plant life history, flowering plays a great role in plant reproduction and survival [55]. Besides, kiwifruit is a perennial vine and breeding early flowering cultivars is an important direction in future breeding. However, few studies were carried out on the molecular mechanism of flowering biology in kiwifruit especially for AP2/ERF genes. To intuitively interpret the potential biological functions of AP2/ERF gene in flowering, we rechecked several genes identified in RNA-seq using qRT-PCR in A. eriantha. About 50% of genes had a positive relation with flowering and mainly reached the peak at stage 2 and seven genes (38%) were negatively correlated. In this study, two genes (AeAP2/ERF061, AeAP2/ERF094) still showed high expression levels (Fig. 7). Both AeAP2/ERF061 and AeAP2/ERF111 were classified into ERF subfamily according to the phylogenetic relationship, their functions were a little different owing that AeAP2/ERF061 were positive correlated with floral development and AeAP2/ERF111 negatively controlled flowering although their expressions increased at stage 2. However, their homologue genes AT1G53910.1 (AtERF74) and AT3G14230.1 played a major role in controlling an RbohD-dependent mechanism or response to various stresses, respectively [56, 57]. Therefore, it is a vital aspect for us to investigate more features of both genes in kiwifruit. Both in Chrysanthemum morifolium and A. thaliana, ERF110 was identified to have an influence on flowering [58]. Likewise, the orthologous gene AeAP2/ERF058 showed increased expression on flowering process. DDF1 (dwarf and delayed-flowering 1) encoding a member of AP2/ERF family was considered to be related to floral development in rice [59]. Its homologues were referred to as AtDDF1 and AtDDF2 in A. thaliana while they displayed different functions due to duplications [60]. AeAP2/ERF081 and AeAP2/ERF102 were found to be closely related to AtDDF2 and seemed to be not involved in flowering. (Fig. 7B; Additional file 11 Table S9).
Interestingly, AeAP2/ERF006, AeAP2/ERF033 and AeAP2/ERF051 had a high similarity with AT5G67180.1 (AtTOE3) in A. thaliana. AtTOE3 was associated with floral patterning via interacting with miR172 [61]. However, according to the results of RNA-seq, opposite expressions may indicate various functions in A. eriantha owing to function differentiation in their evolution process (decreased expressions of AeAP2/ERF006 and AeAP2/ERF051, and increased expression of AeAP2/ERF033 in the kiwifruit flower development processes) (Additional file 11 Table S9). Thus, more detailed studies are needed to explore their biological functions in kiwifruit flowering.
Conclusion
In the present study, we totally identified 158 AP2/ERF genes which were divided into four major subfamilies in A. eriantha. Synteny analysis showed that these genes demonstrated a favorable collinearity within A. eriantha, and many of AP2/ERF genes experienced duplication events and were undergoing a purifying selection. Gene structure and protein motif analysis suggested that AP2/ERFs in different families were more conservative. Furthermore, our results also showed that one third of AeAP2/ERFs were strongly associated with flower transition. Particularly, two genes (AeAP2/ERF061, AeAP2/ERF067) were expressed abundantly, which indicated that they may act a vital role in plant flower development regulation and flower tissue forming. In summary, the results of this study displayed the first comprehensive analysis of AP2/ERF genes in kiwifruit, and it would provide help for screening genes for further functional identification and for genetic improvement of agronomic traits of kiwifruit.
Methods
Plant materials
To validate the functions of partial AP2/ERF genes in kiwifruit, the flowers in three states (Flower buds, unopened flowers and full-opened flowers) of A. eriantha were collected in National Actinidia Germplasm Repository (NAGR) in Wuhan Botanical Garden, the Chinese Academic Science in Hubei province (Fig. 1). To reduce the environmental influences, we collected all samples in 7th May of 2022. One sample was mixed from six individuals of same stage and three repeats were prepared. Then all fresh materials were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at − 80 °C for RNA extraction.
Transcriptome analysis
The flower tissues were sent to BGI company (Wuhan) for transcriptome sequencing. The clean RNA-seq data was mapping onto the reference genome using Hisat2 [62] and generated SAM files were converted to BAM files with SAMtools [63]. Transcriptional abundance and gene expression counts matrix were calculated by featureCounts [64]. The TPM (transcripts per million) value was considered as the expression level and standardized by log10 (TPM + 1). Furthermore, analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) with FDR < 0.05 and absolute log-fold-change > 1 was performed by edgeR software [65]. The Venn diagram was drawn using jvenn (http://jvenn.toulouse.inra.fr/app/example.html) and the heatmaps were visualized in TBtools [66].
RNA extraction, and real-time quantitative PCR
All total RNA of samples was exacted by kits (Magen, Hubei, China) according to the manuals. The cDNA was synthesizing using Hifair®II1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Super Mix with the instructions. The cDNA was amplified and quantified by qRT-PCR with 7500FAST (Applied Biosystems) following the manufacturing instructions. The two steps of qRT-PCR were listed as follows: 94 °C for 30s, followed by 45 cycles at 94 °C for 5 s and 60 °C for 30 s. AeACTIN were used as internal reference for qRT-PCR analyses based on low variability of expression and stability index values. Expression abundance was calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt method and one-way analysis of variance was used to compare the gene expressions in different periods. The primers sequences were listed in the Additional file 12 Table S10.
Identification of AP2/ERF genes in kiwifruit
We downloaded the genomes of A. eriantha and A. chinensis in the kiwifruit database (http://kiwifruitgenome.org/) [67]. Subsequently, the update data including 147 AP2/ERF amino acid sequences in A. thaliana were retrieved on the Plant Transcription Factor Database (PlantTFDB, http://plntfdb.bio.uni-potsdam.de/v3.0/) [68], and they were used as query sequences to carry out BLASTP program [29] against the whole protein sequences of A. eriantha (E-value <1e-10 and identity > = 40). Besides, the Hidden Markov Model profile (PF00847) of AP2/ERF domain in Pfam database (http://pfam.xfam.org/) was obtained for searching the potential genes in kiwifruit by HMMER 3.0 software [28] with default parameters. All sequences confirmed by above two methods were sought to feasible genes. Then, three databases including Pfam (https://pfam.xfam.org/), SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/) and NCBI Conserved Domains Database (CDD, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) were used to checking whether these candidate genes comprised of AP2 domain. Sequences contained at least one complete AP2 domain were retained for next analysis. The molecular weight (MW) and isoelectric point (PI) were calculated with the online tool ExPASy (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/). The AP2/ERF genes were identified in A. chinensis with the same procedures.
Chromosomal locations and structure analysis of AP2/ERF genes
The positions of all genes were extracted from the kiwifruit GFF3 profile, and displayed on the 29 chromosomes via TBtools software [66]. Each exon-intron structure of full coding sequence was presented by iTOL (https://itol.embl.de/).
Multiple sequence alignments and phylogenetic analysis
Alignments of 497 AP2/ERF protein sequences from A. thaliana, A. eriantha and A. chinensis were conducted by Clustal W [69]. Neighbor-joining (NJ) tree was established using MEGA-X [70] with 1000 replicates of bootstrap. The genes were divided into different clades on the basis of studies on A. thaliana [71].
Conserved motifs and cis-acting regulatory elements analysis
Conserved motifs were identified via Motif-based sequence analysis tools (MEME, http://meme-suite.org/) [72] with the width of motifs changed from 6 to 200. Simultaneously, the selected number of motifs was set to 10.
Cis-acting elements were referred to the motifs used to be testified to deeply influence gene expressions or functions including regulation of plant development, defense of pathogen and adaptation to various environments in the upstream or downstream of the sequences. To preliminarily investigate how to regulate the functions of AP2/ERF genes, different types and numbers of cis-elements in A. eriantha were predicted via submitting 2,000 bp sequences upstream of the start codon (ATG) in genomic DNA sequences to Plant CARE database (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) [73]. All consequences were visualized with TBtools [66].
Analysis of gene duplication events and Ka/Ks calculation
MCScanx software [30] was used to detect the collinearity and duplication events among the genomes of A. thaliana and two related species of Actinidia. Likewise, synteny between A. eriantha and A. chinensis genomes was analyzed.
Ks (synonymous substitution rate), Ka (nonsynonymous substitution rate) and Ka/Ks were calculated to understand whether the AP2/ERF family was undergoing the selections during the evolution process. Briefly, 1 stands for neutral selection; less than 1 represents for negative selection and more than 1 means positive selection [49]. The ratios of synonymous (Ks) and non-synonymous (Ka) nucleotide substitutions (Ka/Ks) between homologous gene pairs were also calculated via Simple Ka/Ks Calculator module in TBtools [66]. Additionally, the divergence time was calculated using the formula T = Ks/2r. Thereinto, Ks referred to the ratio of synonymous and r was equal to 3.39 × 10− 9 synonymous substitutions per site per year [26]. The syntenic analysis maps were also drawn using the Dual Systeny Plotter software in TBtools [66]. Distribution of the synonymous substitution rate (Ks) was shown by ggplot2 packages [74].
Availability of data and materials
The clean RNA-seq reads were deposited at NCBI SRA database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra) under the Bioproject accession number PRJNA855574.
Abbreviations
- AP2/ERF:
-
APETALA 2/Ethylene Responsive Element Binding Factor
- DREB:
-
Dehydration-responsive element-binding protein
- HMM:
-
Hidden Markov Model
- DEGs:
-
Different expression genes
- qRT-PCR:
-
Real-time quantitative PCR
- MCScanx:
-
Multiple Collinearity Scan toolkit X
References
Chi YJ, Yang Y, Zhou Y, Zhou J, Fan BF, Yu JQ, et al. Protein-protein interactions in the regulation of WRKY transcription factors. Mol Plant. 2013;6(2):287–300.
Chen YH, Yang XY, He K, Liu MH, Li JG, Gao ZF, et al. The MYB transcription factor superfamily of Arabidopsis: expression analysis and phylogenetic comparison with the rice MYB family. Plant Mol Biol. 2006;60(1):107–24.
Guo XJ, Wang JR. Global identification, structural analysis and expression characterization of bHLH transcription factors in wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2017;17:12.
Elliott RC, Betzner AS, Huttner E, Oakes MP, Tucker WQ, Gerentes D, et al. AINTEGUMENTA, an APETALA2-like gene of Arabidopsis with pleiotropic roles in ovule development and floral organ growth. Plant Cell. 1996;8(2):155–68.
Irish VF, Sussex IM. Function of the apetala-1 gene during Arabidopsis floral development. Plant Cell. 1990;2(8):741–53.
Jofuku KD, den Boer BG, Van Montagu M, Okamuro JK. Control of Arabidopsis flower and seed development by the homeotic gene APETALA2. Plant Cell. 1994;6(9):1211–25.
Feng JX, Liu D, Pan Y, Gong W, Ma LG, Luo JC, et al. An annotation update via cDNA sequence analysis and comprehensive profiling of developmental, hormonal or environmental responsiveness of the Arabidopsis AP2/EREBP transcription factor gene family. Plant Mol Biol. 2005;59(6):853–68.
Sakuma Y, Liu Q, Dubouzet JG, Abe H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;290(3):998–1009.
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006;140(2):411–32.
Xu W, Li F, Ling LZ, Liu AZ. Genome-wide survey and expression profiles of the AP2/ERF family in castor bean (Ricinus communis L.). BMC Genomics. 2013;14(1):785.
Zhang CH, Shangguan LF, Ma RJ, Sun X, Tao R, Guo L, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily in peach (Prunus persica). Genet Mol Res. 2012;11(4):4789–809.
Shigyo M, Hasebe M, Ito M. Molecular evolution of the AP2 subfamily. Gene. 2006;366(2):256–65.
Okamuro JK, Caster B, Villarroel R, Van Montagu M, Jofuku KD. The AP2 domain of APETALA2 defines a large new family of DNA binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(13):7076–81.
Riechmann JL, Ratcliffe OJ. A genomic perspective on plant transcription factors. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2000;3(5):423–34.
Vijayraghavan U. Genetic regulation of flower development. J Biosci. 1996;21(3):379–95.
Hassankhah A, Rahemi M, Ramshini H, Sarikhani S, Vahdati K. Flowering in Persian walnut: patterns of gene expression during flower development. BMC Plant Biol. 2020;20(1):10.
Yoshida H, Nagato Y. Flower development in rice. J Exp Bot. 2011;62(14):4719–30.
Zeng DQ, da Silva JAT, Zhang MZ, Yu ZM, Si C, Zhao CH, et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the APETALA2 (AP2) transcription factor in Dendrobium officinale. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):21.
François L, Verdenaud M, Fu X, Ruleman D, Dubois A, Vandenbussche M, et al. A miR172 target-deficient AP2-like gene correlates with the double flower phenotype in roses. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):12912.
Du S-S, Li L, Li L, Wei X, Xu F, Xu P, et al. Photoexcited Cryptochrome2 interacts directly with TOE1 and TOE2 in flowering regulation. Plant Physiol. 2020;184(1):487–505.
Seo E, Lee H, Jeon J, Park H, Kim J, Noh YS, et al. Crosstalk between cold response and flowering in Arabidopsis is mediated through the flowering-time gene SOC1 and its upstream negative regulator FLC. Plant Cell. 2009;21(10):3185–97.
Maghdouri M, Ghasemnezhad M, Rabiei B, Golmohammadi M, Atak A. Optimizing seed germination and seedling growth in different kiwifruit genotypes. Horticulturae. 2021;7(9):314.
Wang SN, Qiu Y, Zhu F. Kiwifruit ( Actinidia spp.): a review of chemical diversity and biological activities. Food Chem. 2021;350:30.
Richardson DP, Ansell J, Drummond LN. The nutritional and health attributes of kiwifruit: a review. Eur J Nutr. 2018;57(8):2659–76.
Mitalo OW, Tokiwa S, Kasahara Y, Tosa Y, Kondo Y, Asiche WO, et al. Determination of optimum temperature for long-term storage and analysis of ripening-related genes in 'Rainbow Red' kiwifruit. Acta Hortic. 2018;1218: 517–23.
Wu H, Ma T, Kang M, Ai F, Zhang J, Dong G, et al. A high-quality Actinidia chinensis (kiwifruit) genome. Hortic Res. 2019;6(1):117.
Yao X, Wang S, Wang Z, Li D, Jiang Q, Zhang Q, et al. The genome sequencing and comparative analysis of a wild kiwifruit Actinidia eriantha. Mol Hortic. 2022;2(1):13.
Wheeler TJ, Eddy SR. Nhmmer: DNA homology search with profile HMMs. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(19):2487–9.
Boratyn GM, Camacho C, Cooper PS, Coulouris G, Fong A, Ma N, et al. BLAST: a more efficient report with usability improvements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:W29–33.
Wang YP, Tang HB, DeBarry JD, Tan X, Li JP, Wang XY, et al. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(7):14.
Xu L, Feng G, Yang Z, Xu X, Huang L, Yang Q, et al. Genome-wide AP2/ERF gene family analysis reveals the classification, structure, expression profiles and potential function in orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata). Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(7):5225–41.
Liu M, Sun W, Ma Z, Zheng T, Huang L, Wu Q, et al. Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in tartary buckwheat (Fagopyum Tataricum). BMC Plant Biol. 2019;19(1):84.
Zhang S, Zhu C, Lyu Y, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Lai Z, et al. Genome-wide identification, molecular evolution, and expression analysis provide new insights into the APETALA2/ethylene responsive factor (AP2/ERF) superfamily in Dimocarpus longan Lour. BMC Genomics. 2020;21(1):62.
Zhuang J, Cai B, Peng RH, Zhu B, Jin XF, Xue Y, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Populus trichocarpa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;371(3):468–74.
Zhuang J, Peng R-H, Cheng Z-M, Zhang J, Cai B, Zhang Z, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the putative AP2/ERF family genes in Vitis vinifera. Sci Hortic. 2009;123(1):73–81.
Brian L, Warren B, McAtee P, Rodrigues J, Nieuwenhuizen N, Pasha A, et al. A gene expression atlas for kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis) and network analysis of transcription factors. BMC Plant Biol. 2021;21(1):121.
Scannell DR, Byrne KP, Gordon JL, Wong S, Wolfe KH. Multiple rounds of speciation associated with reciprocal gene loss in polyploid yeasts. Nature. 2006;440(7082):341–5.
Panchy N, Lehti-Shiu M, Shiu SH. Evolution of gene duplication in plants. Plant Physiol. 2016;171(4):2294–316.
Wang JP, Yu JG, Li J, Sun PC, Wang L, Yuan JQ, et al. Two likely auto-tetraploidization events shaped kiwifruit genome and contributed to establishment of the Actinidiaceae family. iScience. 2018;7:230–40.
Pushker R, Mira A, Rodríguez-Valera F. Comparative genomics of gene-family size in closely related bacteria. Genome Biol. 2004;5(4):R27.
Rosloski SM, Singh A, Jali SS, Balasubramanian S, Weigel D, Grbic V. Functional analysis of splice variant expression of MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 2 of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol. 2013;81(1–2):57–69.
Zhang Z, Li X. Genome-wide identification of AP2/ERF superfamily genes and their expression during fruit ripening of Chinese jujube. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):15612.
Roy SW, Penny D. Patterns of intron loss and gain in plants: intron loss–dominated evolution and genome-wide comparison of O. sativa and A. thaliana. Mol Biol Evol. 2006;24(1):171–81.
Carmel L, Wolf YI, Rogozin IB, Koonin EV. Three distinct modes of intron dynamics in the evolution of eukaryotes. Genome Res. 2007;17(7):1034–44.
Faraji S, Filiz E, Kazemitabar SK, Vannozzi A, Palumbo F, Barcaccia G, et al. The AP2/ERF gene family in Triticum durum: genome-wide identification and expression analysis under drought and salinity stresses. Genes (Basel). 2020;11(12):1464.
Heidari P, Abdullah FS, Poczai P. Magnesium transporter gene family: genome-wide identification and characterization in Theobroma cacao, Corchorus capsularis, and Gossypium hirsutum of family Malvaceae. Agronomy. 2021;11(8):1651.
Xie Z, Nolan T, Jiang H, Tang B, Zhang M, Li Z, et al. The AP2/ERF transcription factor TINY modulates Brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and grought responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2019;31(8):1788–806.
Baumler J, Riber W, Klecker M, Muller L, Dissmeyer N, Weig AR, et al. AtERF#111/ABR1 is a transcriptional activator involved in the wounding response. Plant J. 2019;100(5):969–90.
Huang ZN, Duan WK, Song XM, Tang J, Wu P, Zhang B, et al. Retention, molecular evolution, and expression divergence of the auxin/indole acetic acid and auxin response factor gene families in brassica Rapa shed light on their evolution patterns in plants. Genome Biol Evol. 2016;8(2):302–16.
Liu H, Lyu HM, Zhu K, Van de Peer Y, Max Cheng ZM. The emergence and evolution of intron-poor and intronless genes in intron-rich plant gene families. Plant J. 2021;105(4):1072–82.
Shu K, Zhang H, Wang S, Chen M, Wu Y, Tang S, et al. ABI4 regulates primary seed dormancy by regulating the biogenesis of abscisic acid and gibberellins in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(6):e1003577.
Kong Q, Yang Y, Guo L, Yuan L, Ma W. Molecular basis of plant oil biosynthesis: insights gained from studying the WRINKLED1 transcription factor. Front Plant Sci. 2020;11:24.
Xing H, Jiang Y, Zou Y, Long X, Wu X, Ren Y, et al. Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in ginger: evolution and expression profiling during development and abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol. 2021;21(1):561.
Oshima Y, Shikata M, Koyama T, Ohtsubo N, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M. MIXTA-like transcription factors and WAX INDUCER1/SHINE1 coordinately regulate cuticle development in Arabidopsis and Torenia fournieri. Plant Cell. 2013;25(5):1609–24.
Salome PA, Bomblies K, Laitinen RA, Yant L, Mott R, Weigel D. Genetic architecture of flowering-time variation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics. 2011;188(2):421–33.
Yao Y, He RJ, Xie QL, Zhao XH, Deng XM, He JB, et al. ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 74 (ERF74) plays an essential role in controlling a respiratory burst oxidase homolog D (RbohD)-dependent mechanism in response to different stresses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2017;213(4):1667–81.
Zhao Y, Wei T, Yin KQ, Chen Z, Gu H, Qu LJ, et al. Arabidopsis RAP2.2 plays an important role in plant resistance to Botrytis cinerea and ethylene responses. New Phytol. 2012;195(2):450–60.
Xing X, Jiang J, Huang Y, Zhang Z, Song A, Ding L, et al. The constitutive expression of a chrysanthemum ERF transcription factor influences flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Biotechnol. 2019;61(1):20–31.
Duan Y, Li S, Chen Z, Zheng L, Diao Z, Zhou Y, et al. Dwarf and deformed flower 1, encoding an F-box protein, is critical for vegetative and floral development in rice (Oryza sativa L.). the. Plant J. 2012;72(5):829–42.
Lehti-Shiu MD, Uygun S, Moghe GD, Panchy N, Fang L, Hufnagel DE, et al. Molecular evidence for functional divergence and decay of a transcription factor derived from whole-genome duplication in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 2015;168(4):1717–34.
Jung JH, Lee S, Yun J, Lee M, Park CM. The miR172 target TOE3 represses AGAMOUS expression during Arabidopsis floral patterning. Plant Sci. 2014;215:29–38.
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT, Salzberg SL. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT. StringTie and Ballgown Nature Protoc. 2016;11(9):1650–67.
Danecek P, Bonfield JK, Liddle J, Marshall J, Ohan V, Pollard MO, et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience. 2021;10(2):giab008.
Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W. featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(7):923–30.
Robinson MD, Oshlack A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010;11(3):R25.
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant. 2020;13(8):1194–202.
Yue J, Liu J, Tang W, Wu YQ, Tang X, Li W, et al. Kiwifruit genome database (KGD): a comprehensive resource for kiwifruit genomics. Hortic Res. 2020;7(1):117.
Perez-Rodriguez P, Riano-Pachon DM, Correa LGG, Rensing SA, Kersten B, Mueller-Roeber B. PInTFDB: updated content and new features of the plant transcription factor database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:D822–7.
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, et al. Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007;23(21):2947–8.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol. 2018;35(6):1547–9.
Zhuang J, Chen JM, Yao QH, Xiong F, Sun CC, Zhou XR, et al. Discovery and expression profile analysis of AP2/ERF family genes from Triticum aestivum. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38(2):745–53.
Bailey TL, Johnson J, Grant CE, Noble WS. The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(W1):W39–49.
Lescot M, Dehais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, et al. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(1):325–7.
Ginestet C. ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. J Res. 2011;174:245–6.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070377).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XY planned and designed the research. GH prepared the samples. QJ and ZW analyzed the data. QJ wrote the manuscript. XY revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors declare that all methods and materials were carried out in accordance with relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and legislation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
The protein sequences and coding sequences of the AP2/ERF gene family in A. eriantha and A. chinensis.
Additional file 2: Table S2.
The detailed information of exited AP2 domain in listed AP2/ERF genes in this study.
Additional file 3: Table S3.
The basic information of AP2/ERF gene family in A. eriantha and A. chinensis.
Additional file 4: Table S4.
The gene structures of AP2/ERF gene family in A. eriantha and A. chinensis.
Additional file 5: Table S5.
The amino acid sequence of motif and annotation in AeAP2/ERF proteins
Additional file 6: Fig. S1.
Distributions of all cis-elements in AP2/ERF genes in A. eriantha.
Additional file 7: Table S6.
Cis-elements in the promoters of putative AP2/ERF genes in A. eriantha.
Additional file 8: Table S7.
The results of Ka/Ks calculations of AP2/ERF homologous gene pairs between A. eriantha and A. chinensis.
Additional file 9: Fig. S2.
The expression heatmap of duplicated gene pairs in A. eriantha. Each line represents one duplicated gene pair.
Additional file 10: Table S8.
Summary of the raw sequencing data and mapping rate of A. eriantha.
Additional file 11: Table S9.
The TPM values of different flower developments in RNA-seq of A. eriantha.
Additional file 12: Table S10.
Primer sequences of AP2/ERF genes in A. eriantha for qRT-PCR.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Q., Wang, Z., Hu, G. et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of AP2/ERF gene superfamily during flower development in Actinidia eriantha. BMC Genomics 23, 650 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08871-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08871-4