Abstract
Background
Insect body coloration often functions as camouflage to survive from predators or mate selection. Transportation of pigment precursors or related metabolites from cytoplasm to subcellular pigment granules is one of the key steps in insect pigmentation and usually executed via such transporter proteins as the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transmembrane transporters and small G-proteins (e.g. Rab protein). However, little is known about the copy numbers of pigment transporter genes in the butterfly genomes and about the roles of pigment transporters in the development of swallowtail butterflies.
Results
Here, we have identified 56 ABC transporters and 58 Rab members in the genome of swallowtail butterfly Papilio xuthus. This is the first case of genome-wide gene copy number identification of ABC transporters in swallowtail butterflies and Rab family in lepidopteran insects. Aiming to investigate the contribution of the five genes which are orthologous to well-studied pigment transporters (ABCG: white, scarlet, brown and ok; Rab: lightoid) of fruit fly or silkworm during the development of swallowtail butterflies, we performed CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing of these genes using P. xuthus as a model and sequenced the transcriptomes of their morphological mutants. Our results indicate that the disruption of each gene produced mutated phenotypes in the colors of larvae (cuticle, testis) and/or adult eyes in G0 individuals but have no effect on wing color. The transcriptomic data demonstrated that mutations induced by CRISPR/Cas9 can lead to the accumulation of abnormal transcripts and the decrease or dosage compensation of normal transcripts at gene expression level. Comparative transcriptomes revealed 606 ~ 772 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the mutants of four ABCG transporters and 1443 DEGs in the mutants of lightoid. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis showed that DEGs in ABCG transporter mutants enriched to the oxidoreductase activity, heme binding, iron ion binding process possibly related to the color display, and DEGs in lightoid mutants are enriched in glycoprotein binding and protein kinases.
Conclusions
Our data indicated these transporter proteins play an important role in body color of P. xuthus. Our study provides new insights into the function of ABC transporters and small G-proteins in the morphological development of butterflies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Butterflies display a diversity of body color among and within species in their different development stages, especially larvae and adults, serving diverse and crucial functions in sexual selection, predator avoidance, and thermoregulation [1]. Like other insects, the metabolites from three main pigmentation pathways (i.e., tyrosine-derived melanin, tryptophan-derived ommochromes and guanine-derived pteridines) and other related metabolites (i.e., uric acid etc.) mainly contribute to color pattern in butterflies [2, 3]. Tyrosine-derived melanin metabolites are well known to play central roles in body color of all kinds of insects [4]. Tryptophan-derived ommochromes and guanine-derived pteridine have been verified to contribute to eye color in many insects independently (e.g., flour beetle Tribolium casstaneum) [5,6,7,8,9], or jointly (e.g., fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, cotton ballworm Helicoverpa armigera, water strider Limnogonus franciscanus) [10,11,12,13,14]; they also play important roles in coloration of larval epidermis and wing etc. [15, 16]. In addition, the fourth pigment, i.e., papiliochrome, is unique to swallowtail butterflies (Papilionidae) and biosynthesized from one tyrosine-derived metabolite (N-β-alanyldopamine) and one tryptophan-derived metabolite (kynurenine) [17, 18]. In insects, pigments are biosynthesized in epidermal cells through a development process that includes pigment patterning and synthesis [18]. During the process, one of the key steps is the transportation of pigment precursors or related metabolites, which are usually executed via such transporter such as ATP-binding cassette (ABC) proteins, Rab proteins etc. [12, 19].
ABC family is one of the largest transporter families and present in all living organisms [20, 21]. They can be classified into seven subfamilies in human [22, 23] or eight subfamilies (A-H) in arthropods [24]. The majority of these ABC proteins function as primary-active transporters. For ABC transporters, ATP binding and hydrolyzing in the nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs) is a necessary process to transport a wide spectrum of substrates (e.g., amino acids, sugars, heavy metal ions and conjugates, peptides, lipids, polysaccharides, xenobiotic and chemotherapeutic drugs) via the integral transmembrane domains (TMDs) across lipid membranes [24, 25]. Notably, ABCG subfamily includes such well-studied ABC members as white, scarlet and brown in D. melanogaster, which are involved in the uptake of pigment precursors in ommochromes and pteridines pathways in the development of cells of Malpighian tubules and compound eyes [26,27,28,29]. The functional experiments from such a few non-dipteran insects as Lepidoptera (including a few moths and one nymphid African butterfly Bicyclus anynana), Coleoptera, Hemiptera, Orthoptera also confirmed the important roles of these ABCG members (especially white and scarlet) in pigmentation [8,9,10, 14, 30,31,32,33,34,35]. It is very interesting that no morphologically mutated phenotypes were observed in H. armigera of Lepidoptera after the brown gene was disrupted [10]. Nevertheless, another ABCG gene, ok, a paralog of brown, was identified in Lepidoptera (B. mori, H. armigera) and verified to play an important role in the development of larval epidermis or/and adult eyes [3, 10]. Another kind of notable transporter proteins are Rab proteins, which are small (21–25 kDa) monomeric GTPase/GTP-binding proteins and found in organisms ranging from yeast to humans with different gene copies [19]. They are known to be involved in intracellular vesicle transport [36]. Among 33 Rab genes identified in the genome of D. melanogaster, Rab32/RP1, encoded by gene lightoid, plays an important role in eye color via participating in biogenesis or degradation of pigment granules [37,38,39]. However, nothing is known for function of lightoid in other insects except for fruit fly and silkworm.
The experiments from Drosophila and other insects demonstrate the important roles of such transporter proteins as ABCG members and Rab proteins in pigmentations [12, 18, 19]. However, it is still not sure whether these findings hold for swallowtail butterflies (Papilionidae), the most historically significant group of butterflies (Papilionoidea) because of their phylogenetic basal position to all other butterflies and their morphological diversity. Moreover, it is not known how these transporter genes affect the expression profiling of other related genes. In addition, we aim to test if these transporters contribute to the biosynthesis of papiliochrome in swallowtail butterflies by transporting the precursor (kynurenine) of tryptophan-derived metabolites, as postulated in our previous work [2]. The swallowtail butterfly P. xuthus is an intriguing species commonly used in butterfly research because of both their enigmatically morphological changes in ontogeny and their well-studied biology as well as ease of breeding [2, 40,41,42]. Here, we systematically identified potential ABC transporters and Rab protein family in the genome of P. xuthus. Then, we investigate the contributions of five of them, which are orthologous to well-studied pigment transporters (ABCG: white, scarlet, brown and ok; Rab: lightoid) in fruit fly, in the development of P. xuthus via CRISPR/Cas9 technology which is widely used in insect [43]. Combining comparative transcriptomics of mutants and wild-types, we provide new insights into the function of ABC transporters and small G-proteins in the morphological development of swallowtail butterflies.
Results
Identification and phylogenetic analysis of ABC and Rab transporters in P. xuthus
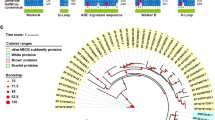
We comprehensively identified copy number of ABC gene family in the genome of the swallowtail butterfly P. xuthus. The genome has a total of 56 ABC transporters, which, like those of other insects, is classified into eight subfamilies (A-H) based on the multiple sequence alignment with those of D. melanogaster and B. mori (Fig. 1; Additional file 1: Table S1 and Table S2). Like that of most other insects, the most expanded subfamily in P. xuthus genome is ABCG (30% of total ABC, 17 members), and the next is ABCC (~ 21% of total), while the most expanded subfamily in other arthropods (e.g. Arachnida, Branchiopoda, Copepoda) and even in human is ABCC (Additional file 1: Table S1). These data suggest ABCG may play a more important role in the evolution of diverse insects. All ABC transporter genes of P. xuthus vary in length from 1841 bp (Px_01485_CG10226) to 33,147 bp (Px_12497_CG7627) and each of them possesses at least one nucleotide binding domain (NBD) (Additional file 1: Table S2). There are 21 full transporters (each full transporter including two NBDs and two transmembrane domains (TMDs)) in ABCA, ABCB and ABCC subfamilies, 28 half transporters (each half transporter including one NBD and one TMD) in ABCA, ABCB, ABCC, ABCD, ABCG, ABCH subfamilies, and seven atypical transporters (each only including 1 ~ 2 NBD but not TMD). ABCE and ABCF subfamilies contain atypical ABC transporters characterized by a pair of linked NBDs with no TMDs. In addition, three ABC genes (ABCA: Px_03164_CG32186; ABCB: Px_01485_CG10226; ABCG: Px_10205_CG11069) also show ABC domains with only one NBD (Additional file 1: Table S2). Seventeen members of ABCG span in five scaffolds with 2 to 5 genes in each, and 16 of them are typical half transporters, except one with a single NBD (Px_10205_CG11069) (Additional file 1: Table S2). Phylogenetic analysis indicates that the four pigmentation related genes (scarlet, white, brown and ok), which are all single-copy in P. xuthus, form a cluster among three species (P. xuthus, B. mori, and D. melanogaster) (Fig. 1).
Phylogenetic tree of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters of Papilio xuthus (Px), Bombyx mori (BGIBM) and Drosophila melanogaster (CG). The maximum likelihood tree was calculated on the basis of multiple alignments of the ABC transporter protein sequences. All ABCs were clustered into eight subfamilies (ABCA-H). The green pentagrams represent the genes belongs to the P. xuthus, the blue circles indicate the genes among B. mori, and the orange boxs show the genes in the genome of D. melanogaster. Four Px genes highlighted in grey in ABCG subfamily were selected to investigate their function in the development of P. xuthus via CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology
We identified 58 and 51 Rab members in the genomes of P. xuthus and B. mori, respectively (Additional file 1: Table S3), which are nearly twice as much as that in D. melanogaster (33) [38] and nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (29), but near to that in human (70) [44]. This is the first two cases of genome-wide identification of copy number of Rab gene in lepidopteran insects. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that both genomes showed an expansion of specific-lineage close to clades of Rab32 (lightoid) and Rab23 (Fig. 2). Both clades of Rab32 and Rab23 include single-copy orthologs within three investigated species. Among them, Px_17846_ltd, together with its ortholog of silkworm (BGIBMGA002711), is single-copy orthologous to lightoid of fruit fly (i.e. Rab32), which was found to be essential in eye development, autophagy and lipid storage via vesicle trafficking regulation in Drosophila [37, 39] and in silkworm’s response to bacterial challenge [45]. Rab23 is involved in the regulation of the number and planar polarization of the adult cuticular hairs in Drosophila [46] and lipid metabolism [39].
Phylogenetic tree of Rab family of Papilio xuthus (Px), Bombyx mori (BGIBM) and Drosophila melanogaster (CG). The green pentagrams represent the genes belongs to the P. xuthus, the blue circles indicate the genes among B. mori, and the orange boxs show the gene in the genome of D. melanogaster. Lightoid, highlighted in red in cluster D, was selected to investigate its function in the development of P. xuthus via CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology
Somatic mutations of four ABCG transporters and one Rab protein in P. xuthus
The experiments from Drosophila and other insects demonstrate the important roles of five genes (scarlet, white, brown, ok and lightoid) in pigmentations [12, 18, 19]. However, it is still not sure whether these findings hold for Papilionidae butterflies. To investigate the potential functions of these transporter proteins in swallowtails butterflies, we performed CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing for these five single-copy genes (white, scarlet, brown, ok and lightoid) using P. xuthus as a model (Tables 1 and 2; Figs. 3, 4, 5, 6; Additional file 1: Tables S4–5; Additional file 2: Fig. S1; Additional file 3: Fig. S2).
CRISPR/Cas9 disruption of white gene resulted in mosaic depigmented phenotypes in larval epidermis, testes and adult eyes of P. xuthus. a The fourth instar larva (L4). b The fifth instar larva (L5). c Testes of the fifth instar larva. d Adult eyes. Left panel: wild types; right panel: white mutants. The area with obviously morphological mutation in mutants and their corresponding part in wild-type were highlighted in red circle in the panels of (a) and (d) and in red square (b). Testes with obviously morphological mutation in mutants and their corresponding part in wild-type were highlighted in red arrow (c). Scale bars: 1 mm. The photo credit is provided by Zhiwei Dong
Scarlet mutants showed morphological mutation in adult eye color. a wild type of adult eyes. b G0 (the generation from injected eggs), mutant with white and black mosaic eyes. c G0 mutant with red and white mosaic eyes. d G2 (the second generation of G0 adults) mutant with white eyes. The photo credit is provided by Zhiwei Dong
Brown and ok mutants showed morphological mutation in the fifth instar larva (L5). a wild type of L5. b brown mutant of L5 (c) ok mutant of L5. The area with obviously morphological mutation in mutants and their corresponding part in wild-type were highlighted in red square. The photo credit is provided by Zhiwei Dong
Lightoid mutants showed morphological mutations in the fourth instar larvae (L4), the fifth instar larvae (L5) and the testis of L5. a L4. b L5. c Testes of L5. The area with obviously morphological mutation in mutants and their corresponding part in wild-type were highlighted in red circle (a) and red square (b). Testes with obviously morphological mutation in mutants and their corresponding part in wild-type were highlighted in red arrow (c). Scale bars: 1 mm. The photo credit is provided by Zhiwei Dong
Mutations in the white gene
We injected the mixed sgRNAs of three target sites (2nd exon: T_8165, T_8232; 3rd exon: T_8700) of white gene and Cas9 protein into eggs (Table 1; Additional file 1: Table S4). Compared with wild-types, the edited individuals showed some morphologically changes in both larvae and adults of G0 generation (directly developing from injected eggs) (Fig. 3). In details, the mosaic mutants of the fourth-instar larvae showed a disappearance of V-shaped white markings in their dorsal sides (Fig. 3a), which originally made them mimic to birds dropping to avoid predators. The fifth-instar larvae showed a translucent cuticle instead of green camouflage coloration in wild-types (Fig. 3b). We also observed that the testis of the fifth-instar larval mutants showed part or complete disappearance of white external sheath and red follicular epithelium (Fig. 3c). No changes in shape and color were observed in the pupa and adult wing (Additional file 2: Fig. S1B). Some of adults developed from larval mutants showed abnormal eyes with white and black mosaic color stripes instead of black eyes in wild-types (Fig. 3d).
Mutations in the scarlet gene
We injected the mixed sgRNA of two target sites (2nd exon: T_661, T_684) of scarlet gene and Cas9 protein into eggs (Table 1; Additional file 1: Table S4). No morphological changes were observed in the injected G0 larvae, but 36.36% (four individuals: three females and one male) emerged adults of G0 showed abnormal eyes with mosaic stripes of white and black/red-brown (Table 1 and Fig. 4b, c), but their wing pattern show no changes (Additional file 2: Fig. S1C). Because of the discordance of emergence time for male and female mutants, we made a cross of a wild-type female (Fwt) adult with G0 male adult mutant (MG0) of mosaic white and red-brown eye color and get six G1 adults, for which no morphological change was observed. We further made a cross between G1 female and male adults (FG1, MG1) to obtain four G2 adults (one female and three males), all of which showed the complete white eyes (Fig. 4d).
Mutations in the brown and ok genes
We injected the mixed sgRNA of two target sites (3rd exon: T_16066; 5th exon: T_15076) of brown gene and Cas9 protein into eggs (Table 1; Additional file 1: Table S4). We observed that 22.86% of the fifth-instar larvae of G0 showed a translucent cuticle (Table 1 and Fig. 5b), similar to that of white mutants. However, unlike those of white mutants, mutated fifth-instar larvae of brown have normal testis, and all mosaic G0 adults have normal black eyes and wing (Additional file 2: Fig. S1D). We also injected the mix sgRNA of two target sites (3rd exon: T_4354, T4454) of ok gene and Cas9 protein into eggs (Table 1; Additional file 1: Table S4). Similar to that of its close paralog brown mutants, G0 fifth-instar larvae of ok also showed a translucent cuticle (Fig. 5c), but normal testis and normal wing pattern (Additional file 2: Fig. S1E), and the mosaic G0 adults also have normal black eyes.
Mutations in the lightoid gene
We injected the mixed sgRNAs of four target sites (2nd exon: T_2307, T_2271; 3rd exon: T_3154, T3097) and Cas9 protein into eggs (Table 1; Additional file 1: Table S4). Like that of white disruption, we observed the disappearance of V-shape white markings in the fourth-instar larvae of G0 (Fig. 6a) and a translucent cuticle in their fifth-instar larvae (Table 1, Fig. 6b), but the adult wing pattern is unaffected (Additional file 2: Fig. S1F). Anatomy of these mutated fifth-instar larval testis also showed partially disappearance of white external sheath and red follicular epithelium (Table 1, Fig. 6c), just like that of white mutants. But unlike white mutants, no morphological changes were observed in G0 adults of lightoid developed from the fifth-instar larval mutants.
Genotyping of mutants
Genomic DNA was isolated from mutant adults/larvae, and PCR amplicons including the region of target sites were cloned and sequenced. The sequenced data validated that these five genes were disrupted in their corresponding mutants (Additional file 1: Table S5; Additional file 3: Fig. S2). All six G0 mutants of white (three 5th-instar larvae and three adults) showed the disruption (10–100% mutated rate) in all or part of target sites with numerous deletions (1–84 bp), inserts (1–30 bp) or substitutions in the targeted regions (Additional file 3: Fig. S2A). Four G2 adult mutants of scarlet showed a deletion of 8–11 bp in the target site T_684 in all clones (Additional file 3: Fig. S2B), suggesting that these G2 adults may be homozygous mutants of scarlet locus. All G0 larval mutants of brown were disrupted (mutated rate: 80–100%) in two target sites (T_15076 and T_16066) with numerous deletions (1–52 bp), inserts (2–21 bp) or substitutions (Additional file 3: Fig. S2C). All three larval mutants of ok were disrupted in target sites T_4354 and T_4454 with numerous deletions (2–25 bp), inserts (3–8 bp) or substitutions (Additional file 3: Fig. S2D). All three larval mutants of lightoid gene showed numerous deletions (1–24 bp), inserts (3–25 bp) or substitutions in all or part of target sites (T_3154, T_3097, T2307 and T_2271) (Additional file 3: Fig. S2E).
Transcriptome profiling of the mutants
To further investigate transcriptomic profiles involved with these pigment-related transporters, we dissected the epidermal tissues of the fifth-instar larval mutants induced by the disruption of white, brown, ok and lightoid genes and head tissues of adult mutants induced by the disruption of scarlet gene for transcriptomic sequencing. In total, 172 Gbp transcriptomic data and average 51 M reads per library were generated for 22 individuals (Additional file 1: Table S6), which are verified to be mutated at genomic DNA level. The average mapping depth of RNA reads in exon regions varied from 125× to 204× with the reads alignment ratio varying at 83.56–90.80% for both mutants and wild-types (Additional file 1: Table S7), suggesting that the transcriptomic data is adequate for transcriptomic analysis and identification of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between mutants and wild-types.
Variations in transcripts in mutants of five disrupted pigment transporting genes
The analysis of the transcriptomic sequencing depth indicate that most mutated individuals showed a deletion of several bases or reduced mapping depths in target regions than those of wild-types (Additional file 4: Fig. S3). Further analysis of nuclear variant calling (including SNPs and INDELs) for all the samples confirmed INDELs in the transcripts of most target regions, and also identified some SNP mutation in the regions of some targets (Additional file 1: Table S8). Specifically, a homozygous 8-bp deletion was identified at the region of target site T_684 in the transcripts of four investigated scarlet mutants of G2 (Additional file 1: Table S8; Additional file 4: Fig. S3B), as shown in PCR genotyping (Additional file 3: Fig. S2B). For G0 mutants of other four genes (white, brown, ok, and lightoid), a deletion of several bases or reduced mapping depths in target regions can be detected (Additional file 4: Fig. S3A, C, D, E). To further explore how the mutations introduced by CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing affect the expression of the genes, the expression level (Fragments per Kilobase Million, FPKM) of the exon involved with target sites were acquired by manually distinguishing the mutated reads and normal reads in the mutant samples (Fig. 7). Our data indicated that except T_16066 and T_15076 of brown, the exons of all other target sites showed a lower expression in mutated individuals than in wild-type individuals. Among them, the exons of most target sites (excl. T_8165 and T_8232 of white) showed a significantly (t-test, P-value < 0.05) decreased expression of normal transcript in mutated individuals than in wild-type individuals (Fig. 7a, b, d, e), suggesting that the normal transcripts were less transcribed after CRISPR/Cas9-induced mutations, thus leading to the down-expression of the five genes. For T_16066 and T_15076 of brown, they showed a slightly higher expression of normal transcripts in mutant samples than in wild-type samples (Fig. 7c), which may be caused by the dosage compensation [47]. In summary, these transcriptomic data demonstrated that mutations induced by CRISPR/Cas9 at genomic level can produce abnormal expression with accumulation of abnormal transcripts and decrease or dosage compensation of normal transcripts at transcriptomic level.
Expression level of the exons in which the target sites are located. a Px_03417_w (white). b Px_03415_st (scarlet). c Px_17845_w (brown). d Px_17844_st (ok), and (E) Px_17846_ltd (lightoid). Red, green and blue color indicates the expression level of normal transcripts in wild-types, normal transcripts in mutants and abnormal transcripts in mutants, respectively. The expression level is evaluated by FPKM (Fragments Per Kilobase of exon model per Million mapped reads). The number and marker above the line is the P-value, which is performed with t-test and are marked with * (less than 0.05) and ** (less than 0.01), respectively
Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and their functions analysis
Both the correlation analysis (Additional file 5: Fig. S4A) and the principle component analysis (PCA) (Additional file 5: Fig. S4B) based on transcriptomic data among individuals of mutants and wild-types showed that mutants and wild-types form two separate clusters, suggesting a high correlation of expression among mutants or wild-types. The number of DEGs among heads of G2 scarlet mutants and wild-types is 732 with half down-expressed (362) and another half up-expressed (370) (Fig. 8a). The epidermis of the fifth-instar larvae among mutants of white, brown, ok, and lightoid and their wild-types have 606, 772, 613 and 1443 DEGs, respectively (Fig. 8a). Among them, up-expressed DEGs of white (329), brown (399) and ok (337) mutants are a little more than their down-expressed DEGs, while lightoid mutants has about a three folds up-expressed number of DEGs (1097) than down-expressed (346). We found that mutants of scarlet, white, brown, ok and lightoid shared eight DEGs (three genes down-expressed in all mutants: Px_02773_Cyp6d4, Px_13524_CG10175, Px_15008_CG9701; four up-expressed in all mutants: Px_00724_unknow, Px_00828_amx, Px_02067_unknow, Px_03043_unknow; one up-expressed in scarlet mutants but down-expressed in other mutants: Px_03657_ImpL2) (Fig. 8b and Additional file 1: Table S9), suggesting some intersections in the expression profile of these transported-related genes. We found 10 DEGs shared in the mutants of all four ABC transporter and another 30 DEGs shared among the fifth-instar larval mutants of four gene white, brown, ok and lightoid (Additional file 1: Table S9).
Against annotated genes of P. xuthus genome with GO and KEGG annotation, we performed enrichment analysis on all DEGs of mutants. GO enrichment analysis show most DEGs in mutants of all five genes enriched in the molecular function categories and biological process (Fig. 9a, c and Additional file 6: Fig. S5A), though no shared patterns among them were identified in KEGG enrichment (Fig. 9b, d and Additional file 6: Fig. S5B). DEGs of four ABCG transporter (brown, ok, and white, scarlet) mutants shared four GO terms, including iron ion binding (GO: 0005506) and heme binding (GO: 0020037) and oxidoreductase activity (GO: 0016705) in molecular functions, and oxidation-reduction process (GO: 0055114) in biological process. DEGs of brown, ok, and white fifth-instar larval mutants enriched in the KEGG pathway of transporters. Most DEGs of lightoid were enriched in glycoprotein binding (GO: 0005515), and others enriched in protein kinase activity (GO:0004672), protein phosphorylation (GO:0006468) and signal transduction (GO:0007165); and the most conspicuous enriched KEGG pathways of lightoid are protein kinases, tight junction, focal adhesion, cytoskeleton proteins and amoebiasis. We also found some DEGs of scarlet mutants are specifically enriched in structural constituent of cuticle (GO:0042302), chitin binding (GO:0008061), chitin metabolic process (GO:0006030), lysozyme activity (GO:0003796), phosphatase activity (GO:0016791) in GO analysis, and in many KEGG pathways such as lipid biosynthesis, phenylalanine metabolism, tryptophan metabolism and amino acid related enzymes etc.
The functional enrichment of Gene Ontology (GO) term and KEGG pathway for the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) which were down and up expressed in the mutated groups. a and b represent the gene enrichment of GO term and KEGG pathway of down-regulated DEGs, separately. c and d represent the gene enrichment of GO term and KEGG pathway of up-regulated DEGs, separately
Discussion
We used CRISPR/Cas9-based mutagenesis to uncover the roles of four ABCGs (white, scarlet, ok, and brown) and one Rab member (lightoid) in the morphological development of swallowtails butterfly for the first time. Our experimental data demonstrated that all these genes contributed to morphological development of larvae (cuticle, testis) and/or adult eyes in swallowtail butterfly. White play a key role in the morphological development of both larvae (cuticle, testis) and adults (eye color), while other four transporters play an important role in larvae (cuticle: brown, ok, lightoid; testis: lightoid) or adult eye color (scarlet). Especially two genes (white, lightoid) were for the first time discovered to contribute larval testis. Combining the results from swallowtail butterfly and other insects, we found that all these transporters, though as orthologs or paralogs, show some lineage-specific phenotypes (Additional file 1: Table S10). Like in P. xuthus, white was found to contribute both adult eye color and larval cuticle by affecting tryptophan, guanine and uric acid transport in other lepidopteran insects including Satyrinae butterfly B. anynana [35], silkworm B. mori [9], and cotton bollworm H. armigera [10]. Nevertheless, it was reported to contribute only adult eye colors in other non-lepidopteran insects such as Diptera (Anopheles gambiae, A. albimanus, Aedes aegypti) [5, 48], Coleoptera (Harmonia axyridis, T. castaneum) [8, 49], Hemiptera (Nilaparvata lugens, Lygus hesperus, Limnogonus franciscanus) [32, 33], Orthoptera (Acheta domesticus), and in Crustacea Daphnia magna [31] (Additional file 1: Table S10). Lack of white protein was recessive embryonic lethal in H. armigera [10]. White and scarlet were verified to be heterodimer and function as a full transporter to transport tryptophan metabolites in ommochromes pathway in fruit fly [11, 26]. Thus, the mutant of both white and scarlet showed white eyes in D. melanogaster because of failure to transport either guanine or tryptophan into pigment cells [11, 28]. Especially, homologous disruption of scarlet in G2 adult result in white eyes, suggesting only ommochromes contributing to P. xuthus eye color, which is consistent with its function in silkworm [30]. The disruption of scarlet mainly displayed the mutated phenotype of adults’ eyes in insects including Lepidoptera (butterflies: P. xuthus (this study), B. anynana; moths: B. mori, H. armigera) and non-lepdopteras (Diptera: D. melanogaster; Coleoptera: T. castaneum, H. axyridis; Hemiptera: N. lugens, L. hesperus) [7, 9, 10, 28, 32,33,34,35, 49], and in crustacean (D. Magana) [31], but it also affect larval cuticle in one moth (H. armigera) [10]. The brown and white form heterodimer and transport the pteridines precursor into the pigment granules in the eye development of D. melanogaster [50]. It was reported that disruption of brown and white would affect the eye development of other two hemipteran insects (Lygus hesperus, Nilaparvata lugens) [32, 33]. However, it only affects larval development in butterfly (P. xuthus: larval cuticle) (this study) and in silkworm (acting as a riboflavin transporter in Malpighian tubule) [51]. Ok, a paralog of brown and identified only lepidopteran, can incorporate uric acid into the epidermis by forming heterodimers with white protein, and thus its mutants in moths show a translucent, oily-appearing epidermis in larval skin [3]. It showed effects on only larval cuticle of butterfly P. xuthus, but on both larval cuticle and adult eyes of another moth H. armigera [10]. Unlike in D. melanogaster, Rab-RP1 (lightoid) didn’t contribute to eye color of adult but only larval cuticle and testis in butterfly development. Rab-RP1 (lightoid) affected adult eye color by participating in biogenesis or degradation of pigment granules in Drosophila [36, 37]. In silkworm, BmRABRP (lightoid) mRNA and protein were found to be high expressed in the Malpighian tubule and fat body, respectively, and played an important role in the response to bacterial challenge [45]. Rab proteins are the largest branch of the Ras-like small GTPase superfamily. They vary between GTP- and GDP-bound states, which are facilitated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs), and function as molecular switches in transporting regulation of intracellular membrane trafficking in all eukaryotic cells [52]. Combining with our finding that Lepidopteran insects have an expansion of specific-lineage close to clades of Rab32 (lightoid) and Rab23 (Fig. 2), we speculate that Rab32 (lightoid) have gained new function, while other Rab copies may perform the transportation of pigment-related granules.
Unexpectedly, our experimental data demonstrated that all these genes didn’t contribute to wing color of swallowtail butterfly. These findings suggest that these investigated transporters, contrary to the postulated in previous works [2, 53], do not take part in transportation of the tryptophan-derived metabolite kynurenine, which is one of precursors in biosynthesis of papiliochrome [17]. Another possibility is that the five edited genes do have result in the reduced transportation of kynurenine but other genes may also transport kynurenine into wings and rescue the low concentration of kynurenine, finally leading to unchanged color in their wings. The current study investigated only some gene copies of pigment-related G subfamily of ABC transporters and the cluter_D group of Rab family (Figs. 1 and 2). Further experiments should be carried out to investigate the function of other transporters G subfamily of ABC transporters and the cluter_D group of Rab family, which may include the candidates to play a role in biosynthesis of papiliochrome.
Characterization of transcriptome can help explain the functional complexity of these genes. We noticed the mutants of all five genes have eight shared DEGs, suggesting some intersections in the expression profiles of these transported-related genes (Additional file 1: Table S9). Three down-expressed DGEs (Px_02773_Cyp6d4, Px_13524_CG10175, Px_15008_CG9701) in all five mutants are involved with detoxification. Px_02773_Cyp6d4 belongs to cytochrome P450 family, which is related to detoxification of such chemicals as pyrethroids but is not critical for the metabolism of vital endogenous substrates in fruit fly [54, 55]. However, our result suggests that the cyp6d4 gene is possibly involved in oxidation-reduction reaction of substances related to pigment metabolism and synthesis in butterfly P. xuthus. Px_13524_CG10175 is annotated as carboxylesterase, which is one of important detoxification systems [56,57,58,59]. Px_15008_CG9701 is annotated as lactase-phlorizin hydrolase, which plays important roles in locust detoxification [60, 61]. In Drosophila, kynurenine pathway is centrally related to toxicity because its intermediate 3-hydroxykynurenine (3-HK) can generate free radicals by auto-oxidation [62]. In insects, the ommochromes pathway is also the most important route for elimination of tryptophan metabolites, which are toxic in the presence of excessive quantities [63]. On the other hand, the 3-HK and kynurenine are also precursor of ommochromes pathway [64]. Thus, the pigmentation process may be one form of detoxification process. Among four up-expressed genes of DEGs in all mutants, three (Px_00724_unknow, Px_02067_unknow, Px_03043_unknow) show unknow function against fly Drosophila melanogaster annotation result; another one (Px_00828_amx) is annotated as TM2 domain-containing protein almondex, which is involved in several processes such as ectodermal cell fate determination, lateral inhibition, and positive regulation of notch signaling pathway [65]. In D. melanogaster, the almondex (amx) plays roles not only in the embryo but also in imaginal specification of the eyes [66]. Px_03657_ImpL2, the gene up-expressed in scarlet mutants but down-regulated in other mutants, is annotated as Neural/ectodermal development factor ecdysone-inducible gene L2 (ImpL2). In fruit fly, ImpL2 can reduce systemic insulin/IGF signaling and causes systemic organ wasting [67], extend the lifespan [68], and affected eye development by regulating one jak and one stat (stat92E) [69]. Our result confirm that ImpL2 are also related to eye development in butterfly. Ten DEGs and some enriched GO items were shared in the mutants of four ABCG members (white, scarlet, brown and ok) suggesting these homologs shared some common molecular basis in different developmental stages of different mutants (Additional file 1: Table S9). Among them, iron ion binding (GO: 0005506) and heme binding (GO: 0020037) may play an important role in color display [70, 71], while oxidoreductase activity (GO: 0016705) and oxidation-reduction process (GO: 0055114) may be related to the synthesis of related compounds [72,73,74]. Among shared DEGs, one gene (Px_10696_CG1640) was down-expressed in all four ABC mutants and annotated as amino transferases, which play important role on amino acid metabolism. One up-expressed DEG (Px_08852_Cpr56F) is annotated insect cuticle protein, which is important constituent of insect cuticle. Among four ABC mutants, scarlet is eye mutants of G2 adult and other three (white, brown, ok) are cuticle mutants of the fifth-instar larvae. We notice some differences of DEGs between eye mutants and larva mutants. One DEG (Px_03657_ImpL2, annotated as Neural/ectodermal development factor) shared in all five mutants and one DEG (Px_05180_Cyp9f2, annotated as Cytochrome P450) shared in four ABC transporter, showed up-expression only in scarlet mutants; on the other hand, similar genes were enriched in the pathway of transporters in the fifth-instar larval mutants of brown, ok, and white. Lightoid had similar larval phenotypes to those of white, brown and ok, but no shared GO and KEGG enrichment were identified among DEGs of lightoid and any other ABC transporters. In contrast, DEGs of lightoid mutant was related to glycoprotein binding, protein kinase activity and protein phosphorylation, signal transduction, tight junction, focal adhesion, cytoskeleton proteins, amoebiasis. Regardless of no shared function enrichment of DEGs among mutants of lightoid and other ABC transporter, 30 DEGs were identified to be shared among the fifth-instar larval mutants of four genes (lightoid, white, brown, and ok) (Additional file 1: Table S9). Among them, five P450 genes, one member of major facilitator superfamily is included among 17 down-expressed DEGs, while G-protein, laccase, ABCC and apterous are among 13 up-expressed DEGs. These results suggest that lightoid plays a role in signal transmission mainly through the phosphorylation cascade in the process of pigment transportation. Besides, our findings also provide some insights into genotyping-phenotyping sequencing profile in gene-editing study of especially non-model animals. In most cases, mosaic mutants may be used to check the function of genes in non-model animals because it is hard to get homozygous offspring of mutants. In such cases, we should remind that although the gene could be disrupted by high mutated rate at DNA level, different expression profiles of target gene could be observed. It is thought that after disrupted, genes will show decreased expression [2, 75,76,77]. Our results show that is not always the truth for mosaic mutants which include both disrupted and normal tissue. In this study, most mutants show a lower expression; however, although high mutated rates were observed for brown gene at DNA level (80–100%) (Additional file 1: Table S5), its mutants show even a little higher transcriptomic expression than wild-type (Fig. 7c), which is likely to be affected by the dosage compensation effect of gene. The similar phenomenon was also reported in mosaic mutants of homeobox gene abdominal B (Abd-B) disruption of one firefly [78]. These data provide evidence that a mosaic of phenotype change in mosaic mutants result from the fraction of abnormal transcript in altered tissues and normal transcripts in unaltered tissues.
Conclusions
For the first time, we comprehensively identified copy number of ABC family (56) and Rab family (58) in the genome of the swallowtail butterfly P. xuthus. We investigated the roles of four ABCGs (white, scarlet, brown, and ok) and one Rab gene (lightoid) in P. xuthus development using CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology. The results indicated that all these five genes play an important role in the morphological development of larvae (cuticle and/or testis) and/or adults’ eye color, but have no effect on wing color. Comparative transcriptomes of mutants and wild-types revealed some molecular mechanisms of these genes commonly or specifically underlying their phenotypic traits. Further functional verification on paralogs of ABCG and Rab, especially those members phylogenetic close to those here investigated functionally, may provide more evidence of body color in butterflies.
Methods
Gene identification, sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis
To identify genes encoding ABC transporters, BLASTP searches (E-value < 10− 5) were performed against P. xuthus genome [2] using the reported ABC protein sequences of D. melanogaster and B. mori [22, 79] as queries. The conserved nucleotide binding domain (NBD, PF00005.24) and transmembrane domain (TMD, PF00664.20) were scanned for putative ABC transporter genes using the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) HMMER v3.2.1 [80]. After removing redundancy, putative transporter genes with the best hit score were retained as candidate ABC genes. To assign the candidate ABC genes into different subfamilies, multiple alignments of the ABC transporter protein sequences were performed using MAFFT [81], and the poor aligned regions and partial gaps were removed with trim-AI (gt =0.5) [82]. Then, the alignments were subjected to a phylogenetic analysis using RAxML [83] based on the Maximum Likelihood (ML) method with settings “-f a -x 12345 -N 100 -p 12345 -m PROTGAMMAWAG”. The resulting trees were displayed and edited using interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3 [84]. The subfamily assignment of ABC proteins in each species was further confirmed using BLASTP analyses at the NCBI webserver (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast).
To identify Rab family in P. xuthus and B. mori genomes, respectively, BLASTP searches (E-value < 10− 5) were performed against the P. xuthus and B. mori genomes using the Rab protein sequences of D. melanogaster (http://flybase.org/). We filtered out the genes with identities lower than 30%. Two conserved domains (Ras: PF00071.19 and Roc: PF08477.10) were scanned by the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) HMMER v3.2.1 [85]. After removing redundancies, top hits for putative genes were retained. As the methods used in ABC transporter classification, we also performed sequence alignments and phylogenetic analysis with the same software and parameters, except for removing gaps (gt = 0.2).
CRISPR/Cas9 induced mutation
SgRNA design and synthesis
The sgRNA target sites were designed based on principle 5′-N20NGG-3′ (Additional file 1: Table S4) [86]. The dsDNA template for sgRNA production was generated according to our previously protocol [2, 75]. Recombinant Cas9 protein (PNA Bio Inc., CA, USA) were purchased directly.
Egg collection, microinjection, breeding and phenotyping
Eggs were collected within 30 min after lay and placed on a microscope slide and fixed by glue. Microinjection were performed with final concentrations of 1000 ng/μl Cas9 protein and 800–990 ng/μl sgRNA (Table 1) using a TransferManNK2 and FemtoJet microinjection system (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). All operations were finished within 2 h after lay. Approximately 245–485 eggs (Table 1) were injected for each gene and incubated at the condition with 25 °C, 12 h light/12 h darkness, 80% relative humidity and darkness for 4–6 days until hatching. Hatched larvae were transferred to host plant leaves (Zanthoxylum piperitum) for breeding and reared at 27 °C, 16 h light/25 °C, 8 h darkness and keep 80% relative humidity. The morphological changes were observed mainly from the fourth-instar larvae in order to avoiding the disturbance on early young larvae (first to third instar) which have similar morphology to the fourth-instar larvae. Pupae were transferred into plastic baskets before eclosion. Emerged adults were crossed via hand pairing, and then mated females were placed in net rooms with host plants for oviposition.
Genomic DNA extraction and mutagenesis detection
Part epidemic tissues of the fifth-instar larval mutants of four genes (white, brown, ok, lightoid) or the thorax and abdomen of adults (white, scarlet) and their corresponding wild types were dissected in phosphate buffer saline and then used to extract genomic DNA using TreliefTMAnimal Genomic DNA Kit (TsingKe, China) following the manufacturer’s protocols. The tissues of each individual were as a biological sample. At least three replicates were carried out for mutants of each gene. Except some adult mutants of white gene, part tissues of the same individual for the mutants and wild-types are also used for RNA extraction as described in the following part. Subsequently, primers flanking the target sites for each gene (Additional file 1: Table S4) were designed, and the PCR reaction were carried out using the 20 μl volumes, according to TransDirect PCR SuperMix (Trans, China). PCR products were TA-cloned into PMD19 vectors (Takara, Japan) and 10 clones were randomly picked up and sequenced for each individual. Sequence data were analyzed using SeqMan software (DNASTAR7.0) to determine the exact mutation type.
Transcriptome sequencing and data analysis
Part epidemic tissues of the fifth-instar larvae for the mutants of four genes (white, brown, ok, lightoid) and wild types or the head tissues of adult for mutant of scarlet gene and wild types were dissected for RNA extraction and sequencing. These individuals are the same as those used in genotyping above mentioned. The tissues of each individual were as a biological sample. At least three replicates were carried out for mutants of each gene and their wild-types, and total 22 samples from 22 individuals were included (Additional file 1: Table S6).
Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The 350 bp insert size paired-end libraries were generated using Illumina mRNA-Seq Prep Kit and were sequenced using Illumina HiSeq4000 sequencers with read length of PE150 at Novogene (Tianjin, China). After removing adapter sequences, about 6 Gbp raw reads were generated for each sample. The quality of the reads was evaluated using FastQC (https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/). We also filtered out those reads with more than 10% Ns or more than 30% low-quality bases (base quality < 20) using a custom Perl script. All cleaned reads were mapped back to the assembled genome of P. xuthus [2] using hisat2 [87] with the default parameters. After the reads were mapped, SortSam program of software Picard v2.18.9 (https://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/) was used to convert the sam file into bam file and sort according to the coordinate. HTSeq v0.11.2 [88], a python package used to analyze high-throughput sequencing data, were used to count the number of reads mapped on each gene. About the average depth of exons, we employed Samtools v1.3.1 [89, 90] to calculate the mapping depths of exonic regions and the average depth of the bases located in those exons was treated as the average mapping depth for exons. Then we manually count the number of the mutated reads which cover in the target sites for each sample, calculate the expression level (FPKM) of mutated transcripts and normal transcript in CRISPR-indued mutated individuals for exons with target sites. Further, t-test is used to test whether the expression level of normal transcripts is significantly decreased in CRISPR-induced mutant samples.
We also used a R package named DESeq2 [91] with the default pipeline to normalize the expression level to reduce the bias due to different amplification during PCR and calculate the expression level. Then clustering and principal component analysis (PCA) were done based on data that has suffered variance stabilizing transformation with vst function in DESeq2 [91]. Both the clustering and PCA showed clear separation between the unedited and edited individuals. Therefore, we used results function to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (|log2FC| ≥ 1 && FDR < 0.05). The GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of DEGs were then performed via InterProScan 5 [92] and BLASTP v2.4.0 [93] based on a custom R script with hypergeometric test, respectively. The P-values were corrected with Benjamini-Hochberg FDR. SNP calling analysis followed the process of hisat2/SortSam/MarkDuplicates (Picard)/Samtools/Bcftools v 1.3.1 [89, 90] . The genotypes with allele depth less than 5 (AD < 5) and genotype quality less than 20 (GQ < 20) were treated as missing genotypes. The mutations with missing genotypes in all mutant samples were removed. In addition, the mutations only identified in wild-type individuals also were removed because these mutations were not caused by CRISPR gene-editing.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or used in this study are included in this manuscript and the supplementary information files. The RNA sequencing data of mutants and wild-types used in this study have been deposited into NCBI database under BioProject Number PRJNA610787 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA610787). The genome assemblies and annotation of Papilio xuthus and Bombyx mori are available at NCBI database as BioProject ID PRJNA270384 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/?term=PRJNA270384) and PRJDA20217 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJDA20217), respectively. The reported ABC protein sequences (Fig. 1) and Rab protein sequences (Fig. 2) of D. melanogaster were downloaded from FlyBase (http://flybase.org/). The reported ABC protein sequences (Fig. 1) of B. mori were extracted from its genome. The conserved domains of ABC protein (PF00005.24: http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00005.24 and PF00664.20: http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00664.20) and Rab protein (PF00071.19: http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00071.19 and PF08477.10: http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF08477.10) are available at pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org/).
Abbreviations
- ABC:
-
ATP-binding cassette
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- FT:
-
Full transporter
- FPKM:
-
Fragments per kilobase million
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- HT:
-
Half transporter
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- ML:
-
Maximum likelihood
- NBDs:
-
Nucleotide-binding domains
- PCA:
-
Principle component analysis
- TMDs:
-
Transmembrane domains
References
Medina I, Vega‐Trejo R, Wallenius T, MRE S, Stuart-Fox D. From cryptic to colorful: Evolutionary decoupling of larval and adult color in butterflies. Evol Lett. 2019;4(1):34–43.
Li X, Fan D, Zhang W, Liu G, Zhang L, Zhao L, Fang X, Chen L, Dong Y, Chen Y, et al. Outbred genome sequencing and CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing in butterflies. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8212.
Wang L, Kiuchi T, Fujii T, Daimon T, Li M, Banno Y, Kikuta S, Kikawada T, Katsuma S, Shimada T. Mutation of a novel ABC transporter gene is responsible for the failure to incorporate uric acid in the epidermis of ok mutants of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;43(7):562–71.
True JR. Insect melanism: the molecules matter. Trends Ecol Evol. 2003;18(12):640–7.
Beard CB, Benedict MQ, Primus JP, Finnerty V, Collins FH. Eye pigments in wild-type and eye-color mutant strains of the African malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. The J Hered. 1995;86(5):375–80.
Sethuraman N, O'Brochta DA. The Drosophila melanogaster cinnabar gene is a cell autonomous genetic marker in Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol. 2005;42(4):716–8.
Broehan G, Kroeger T, Lorenzen M, Merzendorfer H. Functional analysis of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter gene family of Tribolium castaneum. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:6.
Grubbs N, Haas S, Beeman RW, Lorenzen MD. The ABCs of eye color in Tribolium castaneum: orthologs of the Drosophila white, scarlet, and brown genes. Genetics. 2015;199(3):749–59.
Komoto N, Quan GX, Sezutsu H, Tamura T. A single-base deletion in an ABC transporter gene causes white eyes, white eggs, and translucent larval skin in the silkworm w-3(oe) mutant. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;39(2):152–6.
Khan SA, Reichelt M, Heckel DG. Functional analysis of the ABCs of eye color in Helicoverpa armigera with CRISPR/Cas9-induced mutations. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40025.
Summers K, Howells A, Pyliotis N. Biology of eye pigmentation in insects. Adv Insect Physiol. 1982;16: Elsevier:119–66.
Lloyd V, Ramaswami M, Kramer H. Not just pretty eyes: Drosophila eye-colour mutations and lysosomal delivery. Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8(7):257–9.
Dong Y, Friedrich M. Nymphal RNAi: systemic RNAi mediated gene knockdown in juvenile grasshopper. BMC Biotechnol. 2005;5:25.
Vargas-Lowman A, Armisen D, Burguez Floriano CF, da Rocha Silva Cordeiro I, Viala S, Bouchet M, Bernard M, Le Bouquin A, Santos ME, Berlioz-Barbier A, et al. cooption of the pteridine biosynthesis pathway underlies the diversification of embryonic colors in water striders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(38):19046–54.
Linzen B. The tryptophan→ ommochrome pathway in insects. Adv Insect Physiol. 1974;10: Elsevier:117–246.
Harmsen R. The excretory role of pteridines in insects. Exp Biol. 1966;45(1):1–13.
Umebachi Y. Papiliochrome, a new pigment group of butterfly. Zool Sci. 1985;2(2):163–74.
Wittkopp PJ, Beldade P. Development and evolution of insect pigmentation: genetic mechanisms and the potential consequences of pleiotropy. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2009;20(1):65–71.
Bhuin T, Roy JK. Rab proteins: the key regulators of intracellular vesicle transport. Exp Cell Res. 2014;328(1):1–19.
Dassa E, Bouige P. The ABC of ABCS: a phylogenetic and functional classification of ABC systems in living organisms. Res Microbiol. 2001;152(3–4):211–29.
Holland I, Cole S, Kuchler K, Higgins C. ABC proteins: from bacteria to man academic press. London, UK: Elsevier; 2003.
Dean M, Rzhetsky A, Allikmets R. The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. Genome Res. 2001;11(7):1156–66.
Dean M, Hamon Y, Chimini G. The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. J Lipid Res. 2001;42(7):1007–17.
Dermauw W, Van Leeuwen T. The ABC gene family in arthropods: comparative genomics and role in insecticide transport and resistance. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014;45:89–110.
Wu C, Chakrabarty S, Jin MH, Liu KY, Xiao YT. Insect ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters: roles in xenobiotic detoxification and Bt insecticidal activity. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11):2829.
Ewart GD, Howells AJ. ABC transporters involved in transport of eye pigment precursors in Drosophila melanogaster. Methods Enzymol. 1998;292:213–24.
Ewart GD, Cannell D, Cox GB, Howells AJ. Mutational analysis of the traffic ATPase (ABC) transporters involved in uptake of eye pigment precursors in Drosophila melanogaster. Implications for structure-function relationships. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(14):10370–7.
Mackenzie SM, Brooker MR, Gill TR, Cox GB, Howells AJ, Ewart GD. Mutations in the white gene of Drosophila melanogaster affecting ABC transporters that determine eye colouration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1419(2):173–85.
Sullivan DT, Bell LA, Paton DR, Sullivan MC. Purine transport by Malpighian tubules of pteridine-deficient eye color mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Genet. 1979;17(5):565–73.
Tatematsu K, Yamamoto K, Uchino K, Narukawa J, Iizuka T, Banno Y, Katsuma S, Shimada T, Tamura T, Sezutsu H, et al. Positional cloning of silkworm white egg 2 (w-2) locus shows functional conservation and diversification of ABC transporters for pigmentation in insects. Genes Cells. 2011;16(4):331–42.
Ismail NIB, Kato Y, Matsuura T, Watanabe H. Generation of white-eyed Daphnia magna mutants lacking scarlet function. PLoS One. 2018;13(11).
Jiang Y, Lin X. Role of ABC transporters White, Scarlet and Brown in brown planthopper eye pigmentation. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2018;221-222:1–10.
Brent CS, Hull JJ. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of eye coloration genes in the western tarnished plant bug (Lygus hesperus knight). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2019;100(2):e21527.
Francikowski J, Krzyzowski M, Kochanska B, Potrzebska M, Baran B, Chajec L, Urbisz A, Malota K, Lozowski B, Kloc M, et al. Characterisation of white and yellow eye colour mutant strains of house cricket, Acheta domesticus. Plos One. 2019;14(5):e0216281.
Matsuoka Y, Monteiro A. Melanin pathway genes regulate color and morphology of butterfly wing scales. Cell Rep. 2018;24(1):56–65.
Fujikawa K, Satoh AK, Kawamura S, Ozaki K. Molecular and functional characterization of a unique Rab protein, RABRP1, containing the WDIAGQE sequence in a GTPase motif. Zool Sci. 2002;19(9):981–93 913.
Ma J, Plesken H, Treisman JE, Edelman-Novemsky I, Ren M. Lightoid and claret: a Rab GTPase and its putative guanine nucleotide exchange factor in biogenesis of Drosophila eye pigment granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(32):11652–7.
Zhang J, Schulze KL, Hiesinger PR, Suyama K, Wang S, Fish M, Acar M, Hoskins RA, Bellen HJ, Scott MP. Thirty-one flavors of Drosophila Rab proteins. Genetics. 2007;176(2):1307–22.
Wang C, Liu ZH, Huang X. Rab32 is important for autophagy and lipid storage in Drosophila. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32086.
Nishikawa H, Iijima T, Kajitani R, Yamaguchi J, Ando T, Suzuki Y, Sugano S, Fujiyama A, Kosugi S, Hirakawa H, et al. A genetic mechanism for female-limited Batesian mimicry in Papilio butterfly. Nature Genet. 2015;47(4):405–U169.
Futahashi R, Fujiwara H. Juvenile hormone regulates butterfly larval pattern switches. Science. 2008;319(5866):1061.
Futahashi R, Fujiwara H. Identification of stage-specific larval camouflage associated genes in the swallowtail butterfly, Papilio xuthus. Dev Genes Evol. 2008;218(9):491–504.
Chen L, Wang G, Zhu YN, Xiang H, Wang W. Advances and perspectives in the application of CRISPR/Cas9 in insects. Zool Res. 2016;37(4):220–8.
Pereira-Leal JB, Seabra MC. The mammalian Rab family of small GTPases: definition of family and subfamily sequence motifs suggests a mechanism for functional specificity in the Ras superfamily. J Mol Biol. 2000;301(4):1077–87.
Chen C, Eldein S, Zhou X, Sun Y, Gao J, Sun Y, Liu C, Wang L. Immune function of a Rab-related protein by modulating the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2018;97(1):e21434.
Pataki C, Matusek T, Kurucz E, Ando I, Jenny A, Mihaly J. Drosophila Rab23 is involved in the regulation of the number and planar polarization of the adult Cuticular Hairs. Genetics. 2010;184(4):1051–U1267.
McAnally AA, Yampolsky LY. Widespread transcriptional autosomal dosage compensation in Drosophila correlates with gene expression level. Genome Biol Evol. 2009;2:44–52.
Cornel AJ, Benedict MQ, Rafferty CS, Howells AJ, Collins FH. Transient expression of the Drosophila melanogaster cinnabar gene rescues eye color in the white eye (WE) strain of Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1997;27(12):993–7.
Tsuji T, Gotoh H, Morita S, Hirata J, Minakuchi Y, Yaginuma T, Toyoda A, Niimi T. Molecular characterization of eye pigmentation-related ABC transporter genes in the ladybird beetle Harmonia axyridis reveals striking gene duplication of the white gene. Zool Sci. 2018;35(3):260–7.
Dreesen TD, Johnson DH, Henikoff S. The brown protein of Drosophila melanogaster is similar to the white protein and to components of active transport complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988;8(12):5206–15.
Zhang H, Kiuchi T, Hirayama C, Katsuma S, Shimada T. Bombyx ortholog of the Drosophila eye color gene brown controls riboflavin transport in Malpighian tubules. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2018;92:65–72.
Li G, Marlin MC. Rab family of GTPases. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1298:1–15.
Ferguson LC, Jiggins CD. Shared and divergent expression domains on mimetic Heliconius wings. Evol Dev. 2009;11(5):498–512.
Giraudo M, Unnithan GC, Le Goff G, Feyereisen R. Regulation of cytochrome P450 expression in Drosophila: genomic insights. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2010;97(2):115–22.
Hardstone MC, Baker SA, Gao JW, Ewer J, Scott JG. Deletion of Cyp6d4 does not alter toxicity of insecticides to Drosophila melanogaster. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2006;84(3):236–42.
Zhang J, Ge P, Li D, Guo Y, Zhu KY, Ma E, Zhang J. Two homologous carboxylesterase genes from Locusta migratoria with different tissue expression patterns and roles in insecticide detoxification. J Insect Physiol. 2015;77:1–8.
Yu QY, Lu C, Li WL, Xiang ZH, Zhang Z. Annotation and expression of carboxylesterases in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. BMC Genomics. 2009;10:553.
Chen C, Liu Y, Shi X, Desneux N, Han P, Gao X. Elevated carboxylesterase activity contributes to the lambda-cyhalothrin insensitivity in quercetin fed Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner). PLoS One. 2017;12(8):e0183111.
Solé M, Sanchez-Hernandez JC. Elucidating the importance of mussel carboxylesterase activity as exposure biomarker of environmental contaminants of current concern: an in vitro study. Ecol Indic. 2018;85:432–9.
Qin X, Hao K, Ma J, Huang X, Tu X, Ali M, Pittendrigh BR, Cao G, Wang G, Nong X. Molecular ecological basis of grasshopper (Oedaleus asiaticus) phenotypic plasticity under environmental selection. Front Physiol. 2017;8:770.
Huang X, Lv S, Zhang Z, Chang BH. Phenotypic and transcriptomic response of the grasshopper Oedaleus asiaticus (Orthoptera: Acrididae) to toxic rutin. Front Physiol. 2020;11:52.
Campesan S, Green EW, Breda C, Sathyasaikumar KV, Muchowski PJ, Schwarcz R, Kyriacou CP, Giorgini F. The kynurenine pathway modulates neurodegeneration in a Drosophila model of Huntington's disease. Curr Biol : CB. 2011;21(11):961–6.
Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI. Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology. Oxford: Pergamon; 1985.
Figon F, Casas J. Ommochromes in invertebrates: biochemistry and cell biology. Biol Rev. 2019;94(1):156–83.
Michellod MA, Randsholt NB. Implication of the Drosophila beta-amyloid peptide binding-like protein AMX in notch signaling during early neurogenesis. Brain Res Bull. 2008;75(2–4):305–9.
Michellod MA, Forquignon F, Santamaria P, Randsholt NB. Differential requirements for the neurogenic gene almondex during Drosophila melanogaster development. Genesis. 2003;37(3):113–22.
Kwon Y, Song W, Droujinine IA, Hu YH, Asara JM, Perrimon N. Systemic organ wasting induced by localized expression of the secreted insulin/IGF antagonist ImpL2. Dev Cell. 2015;33(1):36–46.
Paik D, Jang YG, Lee YE, Lee YN, Yamamoto R, Gee HY, Yoo S, Bae E, Min KJ, Tatar M, et al. Misexpression screen delineates novel genes controlling Drosophila lifespan. Mech Ageing Dev. 2012;133(5):234–45.
Flaherty MS, Zavadil J, Ekas LA, Bach EA. Genome-wide expression profiling in the Drosophila eye reveals unexpected repression of notch signaling by the JAK/STAT pathway. Dev Dynam. 2009;238(9):2235–53.
Locke M, Nichol H. Iron economy in Insects: transport, metabolism, and storage. Annu Rev Entomol. 1992;37(1):195–215.
Tang X, Zhou B. Iron homeostasis in insects: insights from Drosophila studies. IUBMB Life. 2013;65(10):863–72.
Arakane Y, Muthukrishnan S, Beeman RW, Kanost MR, Kramer KJ. Laccase 2 is the phenoloxidase gene required for beetle cuticle tanning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(32):11337–42.
Arakane Y, Lomakin J, Beeman RW, Muthukrishnan S, Gehrke SH, Kanost MR, Kramer KJ. Molecular and functional analyses of amino acid decarboxylases involved in cuticle tanning in Tribolium castaneum. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(24):16584–94.
Andersen SO. Insect cuticular sclerotization: a review. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;40(3):166–78.
Li XY, Liu GC, Sheng WJ, Dong ZW, Chen L, Zhao RP, Wang W. Genome editing in the butterfly type-species Papilio machaon. Insect Sci. 2017;24(4):708–11.
Liu Z, Ling L, Xu J, Zeng B, Huang Y, Shang P, Tan A. MicroRNA-14 regulates larval development time in Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2018;93:57–65.
Zhang Z, Aslam AF, Liu X, Li M, Huang Y, Tan A. Functional analysis of Bombyx Wnt1 during embryogenesis using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. J Insect Physiol. 2015;79:73–9.
Zhang R, He J, Dong Z, Liu G, Yin Y, Zhang X, Li Q, Ren Y, Yang Y, Liu W. Genomic and experimental data provide new insights into luciferin biosynthesis and bioluminescence evolution in fireflies. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1–19.
Liu S, Zhou S, Tian L, Guo E, Luan Y, Zhang J, Li S. Genome-wide identification and characterization of ATP-binding cassette transporters in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. BMC Genomics. 2011;12:491.
Potter SC, Luciani A, Eddy SR, Park Y, Lopez R, Finn RD. HMMER web server: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(W1):W200–w204.
Kuraku S, Zmasek CM, Nishimura O, Katoh K. Aleaves facilitates on-demand exploration of metazoan gene family trees on MAFFT sequence alignment server with enhanced interactivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(W1):W22–8.
Capella-Gutiérrez S, Silla-Martínez JM. Gabaldón T: trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(15):1972–3.
Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(9):1312–3.
Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(W1):W242–5.
Finn RD, Clements J, Arndt W, Miller BL, Wheeler TJ, Schreiber F, Bateman A, Eddy SR. HMMER web server: 2015 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(W1):W30–8.
Bassett AR, Tibbit C, Ponting CP, Liu JL. Highly efficient targeted mutagenesis of Drosophila with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Cell Rep. 2014;6(6):1178–9.
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods. 2015;12(4):357–60.
Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W. HTSeq--a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(2):166–9.
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R. Genome project data processing S: the sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(16):2078–9.
Li H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2011;27(21):2987–93.
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15(12):550.
Jones P, Binns D, Chang HY, Fraser M, Li W, McAnulla C, McWilliam H, Maslen J, Mitchell A, Nuka G, et al. InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(9):1236–40.
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden TL. BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009;10:421.
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their careful reading of our manuscript and their many insightful comments and suggestions.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31621062) (to WW), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (“Light of West China” (to LXY); the Strategic Priority Research Program (No. XDB13000000, to WW)). The funding body played no role in study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation or manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL, WW designed and managed the project. GL, RZ, ZD, JH performed the experiments. GL, RZ, ZD, ZC, JH, WTW bred the butterflies. WL, JH carried out the bioinformatics analysis. GL, WL, XL, JH, RZ, LC wrote the draft manuscript. XL, WW supervised and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1
Gene numbers in the subfamilies of ABC transporter in the genomes of Papilio xuthus, other 31 insects, other five arthropods and human. Table S2. Details of the 56 ABC transporters identified in the genome of Papilio xuthus. Table S3. Details of the Rab families identified in the genome of Papilio xuthus and Bombyx mori. Table S4. The target of the CRISPR-edited locus and primer for genotyping sequences. Table S5. Mutation rate among different individual mutants and their mutated clones across different target sites. Table S6. The information of RNA sequencing and data for samples. Table S7. The mapping information of RNA reads for all samples. Table S8. The mutations in the target regions from transcriptomics data. Table S9. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the mutants of five edited genes (brown, ok, scarlet, white, lightoid) and their wild-types. Table S10. Summary on functions of five genes experimentally verified in this study and previously published.
Additional file 2: Fig. S1
. No phenotypic changes were observed in wings of mutated adults of five genes induced by CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing. (A) wild type; (B) white mutant; (C) scarlet mutant; (D) brown mutant; (E) ok mutant; (F) lightoid mutant. Note that in the panels of B, C and E, incomplete shapes of hindwings were produced during flying; the photos of panels A, B, C, and F were taken based on live butterflies, while those of panels D and E were taken based on dried specimens. The photo credit is provided by Zhiwei Dong.
Additional file 3: Fig. S2
. Sequence analysis for CRISPR/Cas9 mutations. (A) Knockout of three targets in three white mutants of fifth instar larva and of two targets in three white mutants of adult. (B) Knockout of two target in four scarlet mutants. (C) Knockout of two target in three mutants in brown gene. (D) Knockout of two target in three ok mutants. (E) Knockout of four target in three lightoid mutants. The above line (intron) and boxes (exon) denote gene structure and the arrow denotes transcribed direction for each gene. The regions of target sites in each exon were labeled in red. Letters in blue indicate target sequences, letters underlined indicate protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM) region, and letters in red indicate insert and substitution bases. Numbers before semicolon in brackets on the right of the sequence mean the clone number exhibiting the same mutation pattern, and numbers after the semicolon mean the length (bp) of the insertion, deletion and substitution, respectively. NA, not applicable because mutation type did not appear in the sequenced clones. WT represents wild-type.
Additional file 4: Fig. S3
. The structure of five genes and the distribution of transcriptomic sequencing depths in their disrupted exons of mutated and wild-type individuals. (A) - (E) represent the detail information of Px_03417_w (white), Px_03415_st (scarlet), Px_17845_w (brown), Px_17844_st (ok), and Px_17846_ltd (lightoid), respectively. On the below, the structure of genes was plotted in proportion of its true length with exons in light blue blocks and target region of CRISRP in red blocks. Arrows denotes gene direction. The line chart on the top show the distribution of transcriptomic sequencing in target sites (light red and light blue blocks) and flanking regions. The light red lines and light blue lines denote mutated and wild-type individuals, respectively.
Additional file 5: Fig. S4
. The heatmap and the principle component analysis (PCA) analysis of gene expression in mutated and wild-type individuals. (A) The heatmaps. (B) The PCA analysis.
Additional file 6: Fig. S5
. The functional enrichment of GO term (A) and KEGG (B) pathway for all differentially expressed gene (DEGs). The different shapes represent different knocked out genes: circle, square, diamond, regular triangle, inverted triangle, indicate Px_17845_w (brown), Px_17846_ltd (lightoid), Px_03415_st (scarlet), Px_17844_st (ok), and Px_03417_w (white), respectively.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Liu, W., Zhao, R. et al. Genome-wide identification and gene-editing of pigment transporter genes in the swallowtail butterfly Papilio xuthus. BMC Genomics 22, 120 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07400-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07400-z