Abstract
Background
The Drosophila central nervous system (CNS) is a convenient model system for the study of the molecular mechanisms of conserved neurobiological processes. The manipulation of gene activity in specific cell types and subtypes of the Drosophila CNS is frequently achieved by employing the binary Gal4/UAS system. However, many Gal4 driver lines available from the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center (BDSC) and commonly used in Drosophila neurobiology are still not well characterized. Among these are three lines with Gal4 driven by the elav promoter (BDSC #8760, #8765, and #458), one line with Gal4 driven by the repo promoter (BDSC #7415), and the 69B-Gal4 line (BDSC #1774). For most of these lines, the exact insertion sites of the transgenes and the detailed expression patterns of Gal4 are not known. This study is aimed at filling these gaps.
Results
We have mapped the genomic location of the Gal4-bearing P-elements carried by the BDSC lines #8760, #8765, #458, #7415, and #1774. In addition, for each of these lines, we have analyzed the Gal4-driven GFP expression pattern in the third instar larval CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs. Localizations of the endogenous Elav and Repo proteins were used as markers of neuronal and glial cells, respectively.
Conclusions
We provide a mini-atlas of the spatial activity of Gal4 drivers that are widely used for the expression of UAS–target genes in the Drosophila CNS. The data will be helpful for planning experiments with these drivers and for the correct interpretation of the results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Genetic and molecular studies in Drosophila can provide valuable insight into the pathogenesis of human diseases, due to the high conservation of key molecular mechanisms underlying biological processes in metazoans, and to the fact that about 77% human disease genes have orthologues in Drosophila [1]. Thus, targeted expression of mutant human disease genes in Drosophila can recapitulate relevant aspects of the pathology [2, 3]. Such expression is frequently achieved by employing the binary Gal4/UAS system, which allows the control of the activity of the gene of interest in a spatiotemporal-restricted manner [4]. The specificity of Gal4 expression allows cellular resolution that is particularly important for studies on the nervous system, in which there is a need to manipulate the activity of small sets of neurons or glia cells [5,6,7,8].
Anatomically, the Drosophila larval CNS comprises the brain and the ventral nerve cord (VNC), which are the equivalents of the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, respectively. The brain is composed of two main regions, the optic lobes located at the lateral surface of the brain hemispheres and the medially-located central brain [9]. Histologically, the CNS can be subdivided into the neuronal cell cortex, where all neuronal cell bodies reside, and the neuropil, where axons and dendrites project to form neural circuits [10]. Currently, a lot of different Gal4 drivers are available for targeted expression of reporter genes in distinct CNS cell types and subtypes. The choice of the proper driver for each experiment is crucial, since it can influence the results and their interpretation. However, for several widely-used Gal4 driver lines, the exact genomic location of the Gal4-bearing transgene and the precise pattern of Gal4 expression are still unknown. This information could be very useful (i) to learn whether the insertion of the Gal4 transgene disrupts the expression of an endogenous gene potentially relevant for the analysis undertaken and (ii) for combining the driver with other transgenes or mutations, so as to construct the desired genotype. Thus, we decided to identify the insertion sites of the transgenes and characterize Gal4 expression patterns in larval CNS for the following five commonly used CNS-specific driver lines available from BDSC: #8760, #8765, #458, #7415, and #1774.
In three lines, the Gal4 expression seems to be primarily under the control of the regulatory sequences of the embryonic lethal, abnormal vision (elav) gene, which is active in postmitotic neurons throughout development [11,12,13]. The lines #8760 and #8765 carry the P{Gal4-elav.L} element [14] somewhere on the third and second chromosomes, respectively. This P-element-based transposon contains a 3.5-kb genomic fragment including the elav promoter region [15] upstream of the Gal4 coding sequence. In line #458, an enhancer-trap Gal4 construct, P{GawB} [16], is inserted in the promoter of the elav gene (X:523350; here and afterwards, coordinates are from Release 6 of the D. melanogaster genome assembly [17]); this insertion is also known as the elavC155 allele [18]. Some differences between patterns/strength of activity of these drivers were previously described in epithelial tissues and embryonic CNS [19, 20]. Gal4 drivers from all the three lines are used to drive the expression of different genes and RNAi constructs in neuronal cells in CNS [21, 22].
In line #7415, the P{Gal4} element, presumably an enhancer-trap Gal4 construct, is inserted somewhere in the reversed polarity (repo) locus (3R:18236194..18239604; the insertion is referred to as Gal4repo) and the Gal4 expression pattern matches that of the endogenous Repo protein [23], which is specifically expressed in glia during development [24]. Contrary to the elav-Gal4 drivers, no activity of Gal4repo was detected in larval epithelial tissues [19]; the highest level of repo expression in the larval CNS was observed in the optic lobes [24]. The Gal4repo driver is commonly used to manipulate gene expression in glial cells in the CNS [25, 26].
Line #1774 carries the P{GawB} element inserted somewhere on the third chromosome. This insertion is known as 69B or 69B-Gal4 [16] and it drives expression of the reporter genes semi-ubiquitously. In third instar larvae, 69B-Gal4 activity was detected in the CNS, imaginal discs, ring gland, epidermis and testes [16, 27,28,29]. In the CNS, the expression of 69B-Gal4 seems to be restricted to non-glial cells [30].
Our previous experience indicates that transgenic Drosophila lines often carry more transposon constructs than commonly assumed, and that these insertions can potentially influence the experimental outcome [31]. In the present study, we identified the precise genomic locations of the Gal4 transgenes in lines #8760, #8765, #7415, and #1774, and confirmed the previous mapping of elavC155 in line #458. We also carefully characterized the expression pattern of a UAS-GFP reporter gene induced by the Gal4 drivers of these five lines in the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs of third instar larvae. We found that the enhancer-trap Gal4 drivers from lines #458 and #7415 elicit the expression patterns highly comparable to those of the endogenous Elav and Repo proteins, respectively. In contrast, the elav-Gal4 drivers from lines #8760 and #8765 match the Elav expression pattern only partially. In addition, our data support the view that the 69B-Gal4 driver is primarily active in non-glial cell types.
Results
Molecular characterization of the chromosomes bearing the Gal4 drivers
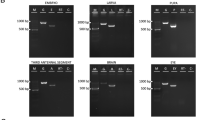
We first evaluated the number of P-element-based constructs harbored by the chromosomes Chr3#8760, Chr2#8765, ChrX#458, Chr3#7415, and Chr3#1774 bearing the Gal4 drivers in the five BDSC lines. To do that, we replaced all chromosomes (except the ones bearing the Gal4 constructs) in the original BDSC stocks with those from yw; KrIf-1/CyO; TM3, Sb1/TM6, Tb1 flies. Next, we performed qPCR analysis using genomic DNA from such fly lines with pairs of primers specific to the 5′ and 3′ P-element ends [31]. Notably, the minimal functional 5′ P-element end of 140 bp [32], present in the P{GawB} transposon and likely in P{Gal4} transposon, cannot be detected by these primers. qPCR indicates that there is only one P-element construct in each of the following chromosomes: Chr3#8760, Chr2#8765, ChrX#458, and Chr3#7415 (Fig. 1). However, Chr3#1774 seems to carry not only the P{GawB} construct but also another unexpected transposon possessing a long 5′ P-element end (Fig. 1).
Copy numbers of P-element ends in different fly lines as measured by qPCR. One copy of P-element ends corresponds to a single transgene in the heterozygous flies. As expected, no P-element ends were detected in yw; KrIf-1/CyO; TM3, Sb1/TM6, Tb1 flies. In the BDSC lines #8760, #8765, #458, #7415, and #1774, all chromosomes except those carrying P-element insertions (based on the annotations of these lines available at BDSC website) were replaced by chromosomes from the line yw; KrIf-1/CyO; TM3, Sb1/TM6, Tb1 before qPCR analysis: #8760 (yw; KrIf-1/CyO; Chr3#8760/TM3, Sb1); #8765 (yw; Chr2#8765/KrIf-1; TM3, Sb1/TM6, Tb1); #458 (ChrX#458/yw; KrIf-1/CyO; TM3, Sb1/TM6, Tb1); #7415 (yw; KrIf-1/CyO; Chr3#7415/TM3, Sb1); #1774 (yw; KrIf-1/CyO; Chr3#1774/TM3, Sb1). In line #1774, two P-element transgenes were detected. The experiment was done in three replicates. Error bars represent standard errors
Next, we used an inverse PCR approach [33] to identify the insertion sites of the P-element constructs present in Chr3#8760, Chr2#8765, ChrX#458, Chr3#7415, and Chr3#1774 (Fig. 2). In Chr3#8760, the P{Gal4-elav.L} construct is inserted within an mdg3 retrotransposon (at DNA sequence position 731–738, GenBank accession number X95908.1), which in turn is imbedded in the second/third intron of the CG16779 gene (immediately after position 3R:9478115). In Chr2#8765, the insertion site of the P{Gal4-elav.L} construct is in the promoter region of the l(2)01289 gene (2R:6740727–6740734). In ChrX#458, the P{GawB} construct is inserted in the promoter region of the elav gene (X:523343–523350), confirming the description of this line (https://flybase.org/reports/FBrf0211983). In Chr3#7415, the P{Gal4} construct is inserted in the repo gene promoter (3R:18236035–18236042). Notably, in ChrX#458 and Chr3#7415, the orientation of the Gal4 coding sequence matches that of the elav and repo genes. In Chr3#1774, the insertion site of P{GawB} element is in the promoter region of the corto gene (3R:5087163–5087170), but the orientation of the Gal4 coding sequence is opposite to the orientation of this gene. In addition, this chromosome carries an internally truncated P-element sequence of ~ 1.1 kb (corresponding to positions 3152–2931 and 1138–246 of GenBank accession number AB331393.1) inserted in the distal antenna-related (danr) gene promoter region (3R:25138044–25138051). The presence and location of all transposons was verified by PCR with primers specific to the P-element ends and genomic sequences flanking the insertion sites (Additional file 1: Table S1).
Insertion sites of P-element constructs found in the BDSC lines #8760, #8765, #458, #7415, and #1774. Thick horizontal black lines show segments of chromosomes flanking the insertion sites of P-element constructs. Genes on the forward and reverse strands are shown in magenta and blue, respectively. Coding sequences, UTRs and introns are represented as wide bars, narrow bars and lines, respectively. Grey triangles represent the 5′ and 3′ P-element ends, as well as the 5′ and 3′ long terminal repeats of the mdg3 retrotransposon. Note that there are two types of 5′ P-element ends in the transposons: the “standard” ends of 585 bp and short ends of 140 bp, the latter are indicated by red asterisks. All P-element transgenes and the mdg3 retrotransposon are not shown to scale. LTR, long terminal repeat
Expression patterns of the Gal4 drivers
To reveal spatial activity of the Gal4 drivers carried by Chr3#8760, Chr2#8765, ChrX#458, Chr3#7415, and Chr3#1774 in the larval CNS and eye imaginal discs, we used a UAS-GFP reporter. Flies carrying the Gal4 drivers were crossed to UAS-GFP flies and the tissues dissected from the resulting progeny were immunostained with anti-Elav or anti-Repo antibodies and analyzed by confocal microscopy. GFP with a nuclear localization signal [34] was used because Elav and Repo are nuclear proteins [12, 35].
In the larval CNS, the expression pattern of elav-Gal4 from lines #8760 and #8765 overlaps only partially with Elav immunostaining. The degree of colocalization of the GFP and Elav signals is higher in the VNC than in the central brain or the optic lobes (Fig. 3a-b, d-e; Additional files 2 and 3: Figures S1 and S2). We also observed ectopic GFP expression in the neuropil and nerve roots (Fig. 3b, e). In the eye imaginal discs, the endogenous Elav protein is expressed in photoreceptor neurons and therefore marks the developing eye area posterior to the morphogenetic furrow [36]. We found that the elav-driven expression of Gal4 in lines #8760 and #8765 does not fully reproduce the pattern of Elav immunostaining, as the GFP signals occupy a narrower area compared to the Elav signal (Fig. 3c, f; Additional file 4: Figure S3).
Comparison of GFP expression patterns elicited by the elav-Gal4 drivers of the BDSC lines #8760, #8765, and #458 with the Elav immunostaining pattern in the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs from third-instar larvae. Maximum intensity projections of confocal images of tissues stained with anti-Elav antibodies and showing GFP expression in the CNS and eye-antennal discs driven by Chr3#8760 (a-c), Chr3#8765 (d-f) or Chr3#458 (g-i). a, d, g The GFP and Elav patterns overlap only partially in the central brain and optic lobes. b, e Colocalization of the GFP and Elav signals in the VNC. Note the ectopic GFP expression in the neuropil (arrows) and in nerve roots (arrowheads). c, f In the eye imaginal discs, the pattern of the GFP expression is narrower compared to anti-Elav antibody staining. h Substantial colocalization of the GFP and Elav signals in the VNC. i In the eye imaginal discs, the patterns of GFP and Elav expression seem largely overlap. CB, central brain; OL, optic lobe; ED, eye imaginal disc; VNC, ventral nerve cord. Scale bars: a, d, g, 200 μm; b, c, e, f, h, i, 100 μm
Also, in the CNS from line #458 bearing the elavC155 allele, the overlapping of the GFP and Elav signals is only partial. Signal colocalization is evident in the VNC but there is no ectopic GFP expression in the neuropil (Fig. 3g, h; Additional file 5: Figure S4). In the eye imaginal discs of elavC155 larvae, the GFP expression pattern is almost completely overlapping the Elav immunostaining (Fig. 3i; Additional files 4 and 5: Figures S3 and S4).
In the optic lobes and eye imaginal discs, the GFP expression pattern directed by the Gal4repodriver of line #7415 is almost coincidental with the localization of the Repo protein (Fig. 4; Additional file 6: Figure S5). However, in both the VNC and central brain, the GFP and Repo localization patterns are slightly different (Fig. 4i-l; Additional file 6: Figure S5).
Comparison of GFP expression patterns controlled by the Gal4repo driver from the BDSC line #7415 with the Repo expression pattern in the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs from third-instar larvae. Maximum intensity projections of confocal images of tissues stained with anti-Repo antibodies are shown. a-d Substantial overlap between the GFP and Repo signals in the CNS and eye imaginal discs. e-h Perfect colocalizations of the GFP and Repo signals in the eye imaginal disc and optic stalk. i-l Colocalization of the GFP and Repo expression patterns in the VNC. m-p Overlapping of the GFP and Repo signals in the central brain and optic lobes; note that the GFP expression pattern seems to be broader than the Repo immunostaining pattern. CB, central brain; OL, optic lobe; ED, eye imaginal disc; VNC, ventral nerve cord. Scale bars: a-d, 200 μm; e-p, 100 μm
To characterize the expression pattern of the 69B-Gal4 driver of line #1774, we compared the GFP localization elicited by this driver with the distribution of the Elav and Repo proteins in larval CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs. The GFP and Elav signals substantially colocalize in the VNC and eye imaginal discs, but colocalization is limited in the central brain and the optic lobes. In addition, the 69B-Gal4 driver is heavily expressed in the antennal disc, where Elav is not present (Fig. 5; Additional file 7: Figure S6). A comparison between the 69B-Gal4 and Repo expression patterns revealed that individual Repo-positive cells in the central brain, optic lobes and optic stalk also express GFP. In the eye-antennal disc, Repo is expressed only in the posterior part of the eye disc, where it partially overlaps with the GFP signal (Fig. 6; Additional file 8: Figure S7). Altogether, these results suggest that the 69B-Gal4 driver is mainly active in neuronal cells, although it is also expressed in other cell types, including imaginal disc cells and small subsets of glial cells.
Comparison of GFP expression patterns elicited by the 69B-Gal4 driver from the BDSC line #1774 with the Elav immunostaining pattern in the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs from third-instar larvae. Maximum intensity projections of confocal images of tissues stained with anti-Elav antibodies are shown. a-d Overlapping of the GFP expression pattern and the Elav localization in the CNS and eye imaginal discs. e-h In the eye-antennal disc, the Elav staining is largely coincident with the GFP signal, but the GFP expression is much broader than that of the Elav protein and includes the anterior area of the eye disc and the antennal disc. i-l Partial colocalization of the GFP and Elav expression patterns in the VNC. m-p Partial overlap between the GFP and Elav signals in the central brain and optic lobes. Note that GFP is expressed only in subset of Elav-positive cells in the VNC. CB, central brain; OL, optic lobe; ED, eye imaginal disc; a, anterior part of the disc; p, posterior part of the disc; VNC, ventral nerve cord. Scale bars: a-d, 200 μm; e-p, 100 μm
Comparison of GFP expression patterns elicited by 69B-Gal4 driver from the BDSC line #1774 with the Repo expression pattern in the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs from third-instar larvae. Maximum intensity projections of confocal images of tissues stained with anti-Repo antibodies are shown. a-d In the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs, the GFP expression pattern overlaps with that of Repo just in individual groups of cells (arrowheads). e-h In the eye-antennal imaginal discs, the broad GFP expression pattern overlaps with the Repo protein expression pattern only in the optic stalk and in the posterior part of the eye disc. i-l The GFP and Repo expression patterns in the VNC are not overlapping. m-p The GFP and Repo signals minimally overlap in the central brain and optic lobes; cells showing both signals are indicated by arrowheads. CB, central brain; OL, optic lobe; ED, eye imaginal disc; a, anterior part of the disc; p, posterior part of the disc; VNC, ventral nerve cord. Scale bars: a-d, 200 μm; e-p, 100 μm
Discussion
The accessibility of the CNS of Drosophila third instar larvae and its similarities to the developing mammalian nervous system make it a very attractive model system. Here, we have characterized five transgenic fly lines carrying commonly used Gal4 drivers for neurobiological studies. Specifically, we identified the genomic insertion sites of the Gal4 transgenes and visualized the Gal4 activity patterns using a UAS-GFP reporter. These patterns were compared to the localization of the Elav and Repo proteins that are believed to be specific for neuronal and glial cell types, respectively.
In lines #8760 and #8765, the functions of the CG16779 and l(2)01289 genes might be compromised by the insertion of the elav-Gal4 construct. Information on these genes and their expression profiles is currently scarce. However, both genes were found to regulate Drosophila lifespan [37, 38], suggesting some caution in the interpretation the longevity experiments, in which the elav-Gal4 drivers were used [39,40,41]. In addition, the CG16779 gene is predicted to encode a factor involved in regulation of Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), which is responsible for the synthesis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine [42]. In line #1774, P-element insertions resulted in mutations in the corto and danr genes. The corto gene encodes an Enhancer of Trithorax and Polycomb (ETP) protein, which might be involved in the maintenance of gene expression patterns throughout development [43]. In the CNS of third instar larvae, the expression of corto was detected in the optic lobes and the VNC [44]. The danr gene encodes a putative transcription factor, which is involved in the retinal determination network during eye development [45, 46]. Lastly, it is not clear whether the insertions of the enhancer-trap Gal4 constructs in the lines #458 and #7415 somehow affect the expression of the elav and repo genes, respectively. Nevertheless, all these Gal4 driver lines, with the exception of #8765, are homozygous or hemizygous viable.
The partial overlap of Gal4 expression from lines #8760 and #8765 with the localization of the Elav protein in the CNS and eye imaginal discs, as well as ectopic Gal4 expression in the neuropil, are not so surprising. This finding is probably related to the absence of important regulatory sequences controlling the expression pattern of the endogenous elav gene within the P{Gal4-elav.L} transposon. Particularly, it was recently reported that the elav gene is ubiquitously transcribed and post-transcriptionally repressed in non-neural tissues via its 3′ UTR sequence [47], which is absent in the P{Gal4-elav.L} construct. At the same time, the influence of the genomic location on the activity of the elav-Gal4 construct in lines #8760 and #8765 seems to be negligible, as both drivers elicit almost identical Gal4 expression patterns.
More interesting are the observations made for the enhancer-trap Gal4 drivers elavC155 and Gal4repo that were expected to mimic the expression patterns of the genes, in which they are integrated. These drivers do indeed show substantial, but not complete, overlap between the Gal4 expression and Elav and Repo immunostaining, respectively. This indicates that some regulatory signals, that normally control the activity of the elav and repo genes, became inactive or improperly functional upon the insertion of the transgenes. The presence of the P-transposase promoter and the mini-white reporter gene in the P{GawB} and P{Gal4} elements might be responsible for the phenomenon.
The unique expression pattern of 69B-Gal4 driver is most likely the result of interactions of the P-transposase promoter located upstream of the Gal4 coding sequence in the P{GawB} construct with the enhancers and some other regulatory elements from the corto locus.
Conclusions
Most of the currently available Gal4 drivers used in Drosophila neurobiology elicit expression patterns that only partially overlap those of the endogenous proteins. Transgenes encoding Gal4 under the control of promoters of particular genes may lack important regulatory elements that are normally located either outside the genes or in their exon-intron sequences. In addition, expression of such Gal4 transgenes may depend on their genomic location. The enhancer-trap Gal4 constructs, although showing expression patterns similar to those of the genes in which they are integrated, also seem to lack some regulatory expression signals. Thus, a perfect copying of the endogenous protein expression patterns by Gal4 drivers appears to be a very complex task. To accomplish this task, it would be necessary to identify all factors affecting the activity of the gene studied. Until this is achieved, all available information on the expression patterns of Gal4 drivers, should be taken into account in both experimental design and the interpretation of the results.
Methods
Fly stocks
Flies were raised and crossed on standard cornmeal agar media at 25 °C. The fly stocks carrying driver constructs used in this study were obtained from the BDSC (Bloomington, IN, USA; https://bdsc.indiana.edu/): #8760 (w*; P{w+mC = Gal4-elav.L}3); #8765 (P{w+mC = Gal4-elav.L}2/CyO); #458 (P{w+mW.hs = GawB}elavC155); #7415 (w1118; P{w+m* = Gal4}repo/TM3, Sb1); #1774 (w*; P{w+mW.hs = GawB}69B); #4775 (w1118; P{w+mC = UAS-GFP.nls}14). Line yw; KrIf-1/CyO; TM3, Sb1/TM6, Tb1 was provided by the “Molecular and Cellular Biology” core facility of the IMCB SB RAS.
Genomic DNA extraction and determination of P-element transgene copy number
Genomic DNA was isolated from 30 to 50 flies according to the protocol reported earlier [48]. For detection of P-element-based transgene copy number by qPCR, we used the reference plasmid pP5′-Vps36-759bp-P3′ described previously [31]. The following three primer pairs were used: Vps36-realtime-F and Vps36-realtime-R specific for the Vps36 gene, qP5-F1 and qP5-R1 for the 5′ P-element end, and qP3-F1 and qP3-R1 for the 3′ P-element end (for primer sequences, see [31]). Importantly, primers qP5-F1 and qP5-R1 can detect only the “standard” 5′ P-element end of 585 bp in length, but not the minimal functional 5′ P-element end of 140 bp in length that is present in enhancer-trap Gal4 transposons. qPCR was performed with 100 ng of genomic DNA or 5 pg of the reference plasmid pP5′-Vps36-759bp-P3′, 400 nM of each primer in a 25-μl reaction mixture using the HS-qPCR SYBR Blue Master Mix (Biolabmix), and the CFX96 Touch Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad) under the following conditions: incubation at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 39 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s. Data analysis was performed using CFX Manager™ Software v3.0 (Bio-Rad). The 5′ and 3′ P-element copy numbers per diploid genome were calculated according to [31].
Mapping P-element transgene insertion sites
Mapping of P-element transgene insertion sites was done by inverse-PCR [33] according to “Inverse PCR & Cycle Sequencing of P Element Insertions for STS Generation” protocol of E.J. Rehm (Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project; www.fruitfly.org/about/methods/inverse.pcr.html) with the following modifications. One microgram of genomic DNA was digested with HhaI (New England Biolabs) or Kzo9I (SibEnzyme) or MspI (SibEnzyme) or SalI (New England Biolabs) restriction enzyme for 6 h at 37 °C in a volume of 50 μl. Restriction fragments were circularized by incubation with T4 DNA ligase (Thermo Scientific) and then purified using Microcon Ultracel YM-30 centrifugal filter (Millipore), followed by elution of DNA in 40 μl of nuclease-free water. Five microliters of each sample was used as a template for PCR amplification of fragments containing the P-element end (5′ or 3′) and flanking genomic DNA. PCR reactions were performed using Phusion® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (New England Biolabs) and the following two primer pairs: Plac1 and Plac4 specific for the 5′ P-element end of 585 bp (but not of 140 bp) in length, and Pry1 and Pry2 specific for the 3′ P-element end (for primer sequences, see Additional file 1: Table S1). The gel-purified PCR products were cloned into pBluescript II SK+ vector (Promega) for subsequent sequencing using universal primers pBS-F1 (5′-cagggttttcccagtcacgac-3′) and pBS-R1 (5′-ggctttacactttatgcttcc-3′).
PCR genotyping
PCR was performed using Hot-Start Taq DNA polymerase (Biolabmix) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Details of primer pairs used for genotyping all P-element transposons are provided in Additional file 1: Table S1. The PCR products were analyzed on 1% agarose gel along with an appropriate DNA marker.
Immunofluorescence staining and confocal microscopy
The CNS and attached eye-antennal imaginal discs were dissected from third instar larvae. For direct GFP detection (without GFP immunostaining) and antibody staining, tissues were fixed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 4% formaldehyde (Merck), and then washed 3 times (5 min each) with 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS. The primary monoclonal rat anti-Elav (DSHB #7E8A10) and monoclonal mouse anti-Repo (DSHB #8D12) antibodies were used at concentration 1 μg/ml. They were detected by goat anti-rat IgG antibodies conjugated to AlexaFluor568 (1:800; Invitrogen #A-11077) and by goat anti-mouse IgG antibodies conjugated to AlexaFluor568 (1:800; Invitrogen #A-11031). Finally, tissues were stained with 0.4 μg/ml DAPI dissolved in PBS. All samples were imaged at the same settings using confocal microscope LSM 710 (Carl Zeiss) with 10×/0.45 plan-apo and 20×/0.8 plan-apo lenses. Optical sections were combined using the LSM Image Browser version 4.2 software (Carl Zeiss).
Availability of data and materials
All materials are available upon request.
Abbreviations
- BDSC:
-
Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center
- CB:
-
Central brain
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DSHB:
-
Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank
- Elav:
-
Embryonic lethal, abnormal vision
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- LTR:
-
Long terminal repeats
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- Repo:
-
Reverse polarity
- VNC:
-
Ventral nerve code
- UAS:
-
Upstream activation sequence
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
References
Reiter LT, Potocki L, Chien S, Gribskov M, Bier E. A systematic analysis of human disease-associated gene sequences in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Res. 2001;11(6):1114–25.
Xu Z, Tito AJ, Rui Y-N, Zhang S. Studying polyglutamine diseases in Drosophila. Exp Neurol. 2015;274(Pt A):25–41.
McGurk L, Berson A, Bonini NM. Drosophila as an in vivo model for human neurodegenerative disease. Genetics. 2015;201(2):377–402.
Duffy JB. GAL4 system in Drosophila: a fly geneticist's Swiss army knife. Genesis. 2002;34(1–2):1–15.
Venken KJT, Simpson JH, Bellen HJ. Genetic manipulation of genes and cells in the nervous system of the fruit fly. Neuron. 2011;72(2):202–30.
Griffith LC. Identifying behavioral circuits in Drosophila melanogaster: moving targets in a flying insect. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2012;22(4):609–14.
Jenett A, Rubin GM, Ngo T-TB, Shepherd D, Murphy C, Dionne H, Pfeiffer BD, Cavallaro A, Hall D, Jeter J, et al. A GAL4-driver line resource for Drosophila neurobiology. Cell Rep. 2012;2(4):991–1001.
Manning L, Heckscher ES, Purice MD, Roberts J, Bennett AL, Kroll JR, Pollard JL, Strader ME, Lupton JR, Dyukareva AV, et al. A resource for manipulating gene expression and analyzing cis-regulatory modules in the Drosophila CNS. Cell Rep. 2012;2(4):1002–13.
Sousa-Nunes R, Cheng LY, Gould AP. Regulating neural proliferation in the Drosophila CNS. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010;20(1):50–7.
Freeman MR. Drosophila central nervous system glia. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(11):a020552.
Robinow S, White K. The locus elav of Drosophila melanogaster is expressed in neurons at all developmental stages. Dev Biol. 1988;126(2):294–303.
Robinow S, White K. Characterization and spatial distribution of the ELAV protein during Drosophila melanogaster development. J Neurobiol. 1991;22(5):443–61.
Berger C, Renner S, Lüer K, Technau GM. The commonly used marker ELAV is transiently expressed in neuroblasts and glial cells in the Drosophila embryonic CNS. Dev Dyn. 2007;236(12):3562–8.
Luo L, Liao YJ, Jan LY, Jan YN. Distinct morphogenetic functions of similar small GTPases: Drosophila Drac1 is involved in axonal outgrowth and myoblast fusion. Genes Dev. 1994;8(15):1787–802.
Yao K-M, White K. Neural specificity of elav expression: defining a Drosophila promoter for directing expression to the nervous system. J Neurochem. 1994;63(1):41–51.
Brand AH, Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 1993;118(2):401–15.
Hoskins RA, Carlson JW, Wan KH, Park S, Mendez I, Galle SE, Booth BW, Pfeiffer BD, George RA, Svirskas R, et al. The Release 6 reference sequence of the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Genome Res. 2015;25(3):445–58.
Lin DM, Goodman CS. Ectopic and increased expression of Fasciclin II alters motoneuron growth cone guidance. Neuron. 1994;13(3):507–23.
Casas-Tintó S, Arnés M, Ferrús A. Drosophila enhancer-Gal4 lines show ectopic expression during development. R Soc Open Sci. 2017;4(3):170039.
Kim MD, Kolodziej P, Chiba A. Growth cone pathfinding and filopodial dynamics are mediated separately by Cdc42 activation. J Neurosci. 2002;22(5):1794–806.
Liu J, Li T, Yang D, Ma R, Moran TH, Smith WW. Synphilin-1 alters metabolic homeostasis in a novel Drosophila obesity model. Int J Obes. 2012;36(12):1529–36.
Kang J, Shin S, Perrimon N, Shen J. An evolutionarily conserved role of Presenilin in neuronal protection in the aging Drosophila brain. Genetics. 2017;206(3):1479–93.
Sepp KJ, Schulte J, Auld VJ. Peripheral glia direct axon guidance across the CNS/PNS transition zone. Dev Biol. 2001;238(1):47–63.
Xiong W-C, Okano H, Patel NH, Blendy JA, Montell C. repo encodes a glial-specific homeo domain protein required in the Drosophila nervous system. Genes Dev. 1994;8(8):981–94.
Ren Q, Awasaki T, Wang Y-C, Huang Y-F, Lee T. Lineage-guided Notch-dependent gliogenesis by Drosophila multi-potent progenitors. Development. 2018;145(11):dev160127.
Tamura T, Sone M, Yamashita M, Wanker EE, Okazawa H. Glial cell lineage expression of mutant ataxin-1 and huntingtin induces developmental and late-onset neuronal pathologies in Drosophila models. PLoS One. 2009;4(1):e4262.
Rimmington G, Dalby B, Glover DM. Expression of N-terminally truncated cyclin B in the Drosophila larval brain leads to mitotic delay at late anaphase. J Cell Sci. 1994;107(Pt 10):2729–38.
Huang X, Suyama K, Buchanan J, Zhu AJ, Scott MP. A Drosophila model of the Niemann-pick type C lysosome storage disease: dnpc1a is required for molting and sterol homeostasis. Development. 2005;132(22):5115–24.
Loveall BJ, Deitcher DL. The essential role of bursicon during Drosophila development. BMC Dev Biol. 2010;10:92.
Palgi M, Greco D, Lindström R, Auvinen P, Heino TI. Gene expression analysis of Drosophilaa Manf mutants reveals perturbations in membrane traffic and major metabolic changes. BMC Genomics. 2012;13:134.
Ogienko AA, Yarinich LA, Fedorova EV, Lebedev MO, Andreyeva EN, Pindyurin AV, Baricheva EM. New slbo-Gal4 driver lines for the analysis of border cell migration during Drosophila oogenesis. Chromosoma. 2018;127(4):475–87.
Mullins MC, Rio DC, Rubin GM. Cis-acting DNA sequence requirements for P-element transposition. Genes Dev. 1989;3(5):729–38.
Ochman H, Gerber AS, Hartl DL. Genetic applications of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics. 1988;120(3):621–3.
Shiga Y, Tanaka-Matakatsu M, Hayashi S. A nuclear GFP/β-galactosidase fusion protein as a marker for morphogenesis in living Drosophila. Develop Growth Differ. 1996;38(1):99–106.
Halter DA, Urban J, Rickert C, Ner SS, Ito K, Travers AA, Technau GM. The homeobox gene repo is required for the differentiation and maintenance of glia function in the embryonic nervous system of Drosophila melanogaster. Development. 1995;121(2):317–32.
Fan Y, Wang S, Hernandez J, Yenigun VB, Hertlein G, Fogarty CE, Lindblad JL, Bergmann A. Genetic models of apoptosis-induced proliferation decipher activation of JNK and identify a requirement of EGFR signaling for tissue regenerative responses in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(1):e1004131.
Nakayama M, Ishibashi T, Ishikawa HO, Sato H, Usui T, Okuda T, Yashiro H, Ishikawa H, Taikou Y, Minami A, et al. A gain-of-function screen to identify genes that reduce lifespan in the adult of Drosophila melanogaster. BMC Genet. 2014;15:46.
Rival T, Page RM, Chandraratna DS, Sendall TJ, Ryder E, Liu B, Lewis H, Rosahl T, Hider R, Camargo LM, et al. Fenton chemistry and oxidative stress mediate the toxicity of the β-amyloid peptide in a Drosophila model of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurosci. 2009;29(7):1335–47.
Balan V, Miller GS, Kaplun L, Balan K, Chong Z-Z, Li F, Kaplun A, VanBerkum MFA, Arking R, Freeman DC, et al. Life span extension and neuronal cell protection by Drosophila nicotinamidase. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(41):27810–9.
Morrow G, Samson M, Michaud S, Tanguay RM. Overexpression of the small mitochondrial Hsp22 extends Drosophila life span and increases resistance to oxidative stress. FASEB J. 2004;18(3):598–9.
Slade FA, Staveley BE. Arm-Gal4 inheritance influences development and lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(4):12788–96.
Konstantinides N, Kapuralin K, Fadil C, Barboza L, Satija R, Desplan C. Phenotypic convergence: distinct transcription factors regulate common terminal features. Cell. 2018;174(3):622–35.
Salvaing J, Nagel AC, Mouchel-Vielh E, Bloyer S, Maier D, Preiss A, Peronnet F. The enhancer of Trithorax and Polycomb Corto interacts with Cyclin G in Drosophila. PLoS One. 2008;3(2):e1658.
Harvie PD, Filippova M, Bryant PJ. Genes expressed in the ring gland, the major endocrine organ of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1998;149(1):217–31.
Curtiss J, Burnett M, Mlodzik M. distal antenna and distal antenna-related function in the retinal determination network during eye development in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 2007;306(2):685–702.
Hoang CQ, Burnett ME, Curtiss J. Drosophila CtBP regulates proliferation and differentiation of eye precursors and complexes with Eyeless, Dachshund, Dan, and Danr during eye and antennal development. Dev Dyn. 2010;239(9):2367–85.
Sanfilippo P, Smibert P, Duan H, Lai EC. Neural specificity of the RNA-binding protein Elav is achieved by post-transcriptional repression in non-neural tissues. Development. 2016;143(23):4474–85.
Pindyurin AV. Genome-wide cell type-specific mapping of in vivo chromatin protein binding using an FLP-inducible DamID system in Drosophila. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1654:99–124.
Acknowledgments
We thank Maurizio Gatti for critical reading of the manuscript. Microscopy analysis and DNA sequencing were carried out at the “Molecular and Cellular Biology” core facility of the IMCB SB RAS.
About this supplement
This article has been published as part of BMC Genetics Volume 21 Supplement 1, 2020: Selected Topics in “Systems Biology and Bioinformatics” - 2019: genetics. The full contents of the supplement are available online at https://bmcgenet.biomedcentral.com/articles/supplements/volume-21-supplement-1.
Funding
This work was mainly supported by the Russian Science Foundation grant 18–74-00050 and in part of qPCR experiments by a project of the Fundamental Scientific Research Program of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (0310–2019-0005). Publication costs are funded by the Russian Science Foundation grant 18–74-00050. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: AVP. Performed the experiments: ENA, AAO, ESO, ALO. Analyzed the data: ENA, AAO, ESO, AVP. Wrote the paper: AAO, ESO, ENA, AVP. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1.
Primers used for PCR verification of transposon insertion sites and details of PCR products.
Additional file 2: Figure S1.
Representative series of z-stack confocal images of the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs from a third-instar larva expressing GFP under the control of the elav-Gal4 driver from the BDSC line #8760. The tissues are stained with anti-Elav antibodies.
Additional file 3: Figure S2.
Representative series of z-stack confocal images of the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs from a third-instar larva expressing GFP under the control of the elav-Gal4 driver from the BDSC line #8765. The tissues are stained with anti-Elav antibodies.
Additional file 4: Figure S3.
Comparison of GFP expression patterns elicited by the Gal4 drivers from the BDSC lines #8760, #8765, and #458 with the Elav immunostaining pattern in the eye-antennal imaginal discs from third-instar larvae. CB, central brain; OL, optic lobe. Scale bar: 100 μm.
Additional file 5: Figure S4.
Representative series of z-stack confocal images of the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs from a third-instar larva expressing GFP under the control of the elavC155 driver from the BDSC line #458. The tissues are stained with anti-Elav antibodies.
Additional file 6: Figure S5.
Representative series of z-stack confocal images of the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs from a third-instar larva expressing GFP under the control of the Gal4repo driver from the BDSC line #7415. The tissues are stained with anti-Repo antibodies.
Additional file 7: Figure S6.
Representative series of z-stack confocal images of the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs from a third-instar larva expressing GFP under the control of the 69B-Gal4 driver from the BDSC line #1774. The tissues are stained with anti-Elav antibodies.
Additional file 8: Figure S7.
Representative series of z-stack confocal images of the CNS and eye-antennal imaginal discs from a third-instar larva expressing GFP under the control of the 69B-Gal4 driver from the BDSC line #1774. The tissues are stained with anti-Repo antibodies.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Ogienko, A.A., Andreyeva, E.N., Omelina, E.S. et al. Molecular and cytological analysis of widely-used Gal4 driver lines for Drosophila neurobiology. BMC Genet 21 (Suppl 1), 96 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-020-00895-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-020-00895-7