Abstract
Sulfuric acid lignin (SAL) is a byproduct of the acid saccharification of lignocellulosic materials for bio-fuel generation. The recalcitrant and highly complex structure of SAL significantly limits its industrial use, making it a useless industrial waste. In a previous study, we proposed a hydrothermal reaction for SAL that can convert it into water-soluble compounds (HSALs), which considerably expanded its industrial use scenario. In this study, we converted this water-soluble HSAL into two ionic modifications with applications as flocculants and dispersants. Firstly, the introduction of a carboxy group was carried out with bromoacetic acid. In the carboxymethylated HSAL (C-HSAL), the carboxymethyl groups content was as high as 3.66 mmol/g. Dispersibility tests using gypsum paste showed that C-HSAL exhibited a dispersibility almost equivalent to that of commercial lignosulfonate. Furthermore, another investigation was conducted synthesizing cationized HSAL derivatives by the reaction with glycidyl trimethylammonium chloride (GTA). Dye removal tests were performed with the obtained lignin-based flocculants using three organic dyes. The results showed ideal dye removal ratios for the GTA-HSALs (higher than 90% for all dyes tested), thereby suggesting that they have a huge potential as core molecules to develop high-efficient dye flocculants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Climate change caused by the excessive use of fossil fuels has attracted great attention [1]. Bio-fuel generation by the biorefining industry is a renewable and environmentally friendly energy source [2,3,4]. However, in the acid-hydrolysis-based saccharification of woody materials using concentrated sulfuric acid as catalyst, large quantities of sulfuric acid lignin (SAL) are generated, becoming a major industrial by-product. SAL shows an extremely low reactivity and it is insoluble in water or organic solvents, due to its highly complex recalcitrant structure [5, 6]. To overcome this barrier to its industrial use and perform carbon recycling, many attempts have been made to convert SAL into new raw materials suitable for chemicals production, using phenolization [7], Mannich reaction [8], and polyester conversion by ɛ-caprolactone [9], among other reactions. Those works have shown that SAL has a good chemical modification potential, but the complexity of these processes and their high total production cost makes it difficult to use them in large-scale industrial applications. In our previous report we proposed a simple and low-cost method using a hydrothermal reaction to convert SAL into water-soluble compounds (HSAL) [10]. Further analysis of the structural characteristics of HSAL shows demethylation, depolymerization, the introduction of phenolic hydroxyls, and parts of aromatic ring were slightly broken while recondensation reactions of sulfuric acid lignin occurred simultaneously during the hydrothermal reaction.
On the other hand, various kinds of dyes are used as colorants in the textile, leather, paper, plastic, and food process industries which caused a huge pollution to the aquatic environment such as lakes and rivers, resulting a lasting ecological disaster [11, 12] Currently, the inorganic flocculants like ferric salt, aluminum salt, and magnesium salt are most widely used. But the relation between residual aluminum flocculants and Alzheimer make those flocculants as another terrible environmental burden [13]. Thence, develop an environmental friendly and high-efficient dry flocculant become a top priority. Additionally, the aromatic backbones, with hydroxyl groups and molecular weight around 4–17 kDa [14], of the water-soluble HSALs show great potential as matrix molecules for synthesizing effective flocculants for binding and precipitating ionic substances in water [15].
Furthermore, the most widely available lignin-based material is lignosulfonate which is obtained from spent sulfite-pulping liquors; [16] it has excellent dispersing properties [17], and it is utilized as a superplasticizer in concrete and gypsum [18, 19] Its superior dispersion characteristics are mainly attributed to its water-soluble anionic-polyelectrolyte structure [20, 21] Thus, the conversion of HSALs into lignosulfonate-like materials should be an effective way to facilitate their industrial use [22].
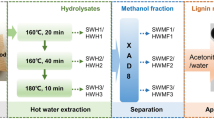
Herein, we now report two kinds of ionic modifications following the above-mentioned research. Figure 1 schematically shows the schemes used to convert HSALs into two principal ionized compounds:
-
(a)
HSAL cationization (Fig. 1a). The water-soluble cationic HSAL (GTA-HSAL) was synthesized by HSAL reaction with glycidyl trimethylammonium chloride (GTA). Elemental analysis was carried out to estimate the conversion of cationic groups attached to HSAL and dye removal tests were performed using three organic dyes.
-
(b)
HSAL anionization (Fig. 1b). The water-soluble carboxymethylated anionic HSAL (C-HSAL) was synthesized by HSAL carboxymethylation carried out with bromoacetic acid. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, elemental analysis, and carboxylic acid group quantification was performed on C-HSAL, as well as dispersibility tests with gypsum to compare it to commercial lignosulfonate.
Experimental
Materials
Remazol Brilliant Blue R (RBB) and Direct Red 23 (DR) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC, USA. Acid Black 1 (AB) was purchased from Kanto Chemical Co., Inc., Japan. GTA was purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., Japan. Bromoacetic acid was purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., Japan.
Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) chips were ground into powder (approximately 60–80 mesh) and subjected to extractives removal in a Soxhlet extractor followed by the Klason method to obtain SAL.
HSAL preparation
A mixture containing 500 mg of SAL, 500 mg of alkali (NaOH), and 15 mL of water was sealed in a stainless-steel tube with an inner volume of 50 cm3 and heated at 280 °C for 2 h. Immediately afterwards, the tube was cooled to room temperature by immersion in a water bath. The reaction mixture was filtered using a 1G3 filter (Sekiya, Tokyo, Japan) to obtain the liquid form of the hydrothermally treated SAL (HSAL) which was collected and dialyzed to remove inorganic reagents using a cellulose tube with a 3500 molecular weight cutoff (Tubing TM 3500; Bio-Design, Carmel, NY, USA). The reaction products were lyophilized to obtain the HSAL [9].
Synthesis of cationic lignin derivatives (GTA-HSAL)
GTA is a cationizing agent and conducted here for HSAL modification. According to the previous study, HSAL was first dissolved in 0.5 N NaOH, and various quantities of GTA were added to the solution [12]. After heating at 50 °C for 3 h, the reaction mixture was dialyzed using the above-detailed cellulose tube. The reaction products were lyophilized to obtain GTA-HSAL. The cationic ion N-(2-hydroxypropyl)-3-trimethylammonium attached to the HSAL structure was determined by nitrogen content measurement.
HSAL carboxymethylation
In previous studies [14], we found that HSAL showed a high content of phenolic hydroxyl groups. Based on this structural characteristic, the introduction of a carboxyl group by carboxymethylation with halogenoacetic acid was performed as follows. 400 mg of HSAL and 0.16 g of NaOH were dissolved in 50 mL of 80% aqueous methanol followed by the slow addition of bromoacetic acid (114 mg/day, reaction time was settled from 3 to 10 days) and stirring at 60 °C. After the reaction, 2 M HCl was slowly added to the reaction mixture to adjust its pH to 3. The mixture was dialyzed with the above-detailed cellulose tube to remove excess reagents. The reaction products were collected and lyophilized to yield C-HSAL.
FT-IR spectroscopy
The analyses of HSAL and C-HSALs were performed by FT-IR spectroscopy (8400 s, SHIMADZU, Kyoto, Japan). The region between 2000 and 400 cm−1 was recorded, with a resolution of 4 cm−1 and 32 scans. Each test sample was prepared according to the potassium bromide method.
Elemental analysis
The elemental analysis of HSAL-based compounds was conducted by CHN coder MT-6 (YANACO Co., Ltd., Kyoto, Japan). Each sample was measured at least three times.
Measurement of the carboxyl group content
Carboxyl group content of C-HSALs was performed by dissolving a 30 mg sample of each C-HSALs in 0.5 N NaOH and titrating it with 0.25 N HCl.
GTA-HSAL dye removal test
Dye removal tests were carried out with three kinds of organic dyes: RBB, DR, and AB (Additional file 1: Figure S1) at room temperature (25 °C) [15]. Each dye was dissolved in water (100 mg/L) and 7 mL of the solution was placed in a test tube together with a volume of the GTA-HSAL solution containing the desired amount of nitrogen, calculated from the results of the nitrogen elemental analysis. After continuous shaking for 10 s, the mixed solution was left stationary for 10 min followed by centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 10 min. The absorbance of the supernatant was measured in an UV–Vis spectrophotometer (V-530, JASCO, Japan). The UV–Vis spectra wavelengths of RBB, DR, and AB were 593, 506, and 618 nm, respectively. The remaining dye concentration in the supernatant was calculated from the calibration curve of each dye. The dye removal efficiency was calculated based on the following equation:
where C0 and C means the dye concentrations in the supernatant before and after the dye removal test, respectively. All the dye removal tests were conducted three times.
Evaluation of dispersibility
Dispersibility tests were conducted with gypsum and compared with commercial lignosulfonate (LS) as follows (Additional file 1: Figure S2) [19]. A 110 g sample of gypsum paste was dissolved in 88 mL of water at 20 °C. After addition of the requisite quantity of the samples (C-HSALs or LS), the solution was stirred for 15 s and the resultant gypsum paste was poured into a ring-shaped container (diameter = 50 mm, height = 50 mm) set on a glass plate. After being left stationary for 10 s, the ring-shaped container was removed to allow the gypsum paste to spread out on the glass plate. The final diameter (ϕfinal) was measured, and the flow value was defined with the following equation:
where ϕin is the initial diameter (50 mm). The dispersibility test for each sample was carried out at least three times.
Results and discussion
Characterization of GTA-HSAL
In our previous study, the structural characteristics analysis results of HSAL clearly show a noticeable increasing of phenolic hydroxyl content. Meanwhile, GTA was conducted here to substituting those phenolic hydroxyls with N-(2-hydroxypropyl)-3-trimethylammonium and synthesis a cationic HSAL derivative (GTA-HSAL).
The elemental analyses of the GTA-HSALs are shown in Table 1. Comparing GTA-HSAL with HSAL, the differences in nitrogen content are attributed to the N-(2-hydroxypropyl)-3-trimethylammonium, the cationizing agent used for HSAL modification, attached to its structure. An increase in the nitrogen content is observed at higher GTA additions. The highest nitrogen content is 6.98% for the 15 mL GTA addition, which indicated GTA cationic ion attached to each lignin phenylpropane base unit of HSAL.
Dye removal property on GTA-HSAL
In our previous study [23], kraft lignin was conducted to prepare the mordant for rosin sizing by introduction of amino group. Results shown that the reaction product failed to exhibit any mordant characteristic. The efficiency of a mordant is well known to be mainly due to its molecular weight, charge density and molecular geometric structures. The nitrogen content of the reaction product was sufficient; however, the molecular weight was lower leading to the low mordant efficient. Based on this conclusion, we believe that kraft lignin and soda lignin have no possibility to convert into flocculants with high efficiency.
In this study, the dye-flocculating properties of GTA-HSAL were evaluated using three types of anionic dyes: RBB, DR, and AB. GTA-HSAL was added to the dye solutions to start-up dye flocculation. The dye removal efficiency was evaluated by measuring the dye concentration in the supernatant liquid of the mixed solution.
The resultant dye removal efficiencies, based on the molar ratio between cationic quaternary amino groups in the GTA-HSAL and the three dyes, RBB, DR, and AB, are summarized in Fig. 2. GTA-HSAL presents ideal dye removal at certain nitrogen-to-dye molar ratios. For RBB, the best removal efficiency (99.05%) is at 4.16 N of GTA-HSAL/-SO3 of dye (mol/mol). If the nitrogen-to-dye molar ratio was higher than this optimum, the dye removal efficiency drastically decreased, due, probably, to their positive conversion in the solution. For DR, GTA-HSAL shows the highest removal efficiency (98.08%) at a lower nitrogen-to-dye molar ratio than for the other dyes and demonstrates wide-range applicability. In the case of AB, the general trend is similar to that for RBB and DR but with the lowest best-dye removal-efficiency nitrogen-to-dye molar ratio (93.4%).
From these results, we can conclude that GTA is an efficient cationizing agent for converting HSAL into GTA-HSAL. Furthermore, the dye removal tests showed that GTA-HSAL had an ideal removal efficiency for these three organic dyes. The molecular weight of the cationic lignin-based flocculants should have an important role for achieving high efficiency. The skeletal structure of HSAL is a hydrophobic phenylpropane unit with a higher phenolic hydroxyl content (4.77%) [14] which enhanced the addition of the N-(2-hydroxypropyl)-3-trimethylammonium (cationic ion) to HSAL in the GTA treatment.
Based on these results, we can conclude that the cationic ion introduced to the phenolic hydroxyl would be the key factor for GTA-HSAL showing ideal removal efficiencies for these three organic dyes. The anionic dyes and the flocculants are mixed in the solution and, due to the electrostatic coupling; the molecules neutralize and decrease their water solubility due to flocculation. Then the hydrophobic interaction between the neutralized molecules forms larger agglomerates. On the other hand, if the nitrogen-to-dye molar ratio is too high, the inner cationic site will not carry out the electrostatic coupling because of steric hindrance, causing the dye removal efficiency to drastically decrease. We hypothesize the flocculation behavior between GTA-HSAL and anionic dyes to be as depicted in Fig. 3.
HSAL carboxymethylation (CHSAL)
The introduction of a carboxyl group by carboxymethylation with halogenoacetic acid was conducted according to a previous study [24]. As in the latest report [14], a higher phenolic hydroxyl content was observed after the hydrothermal reaction with SAL. Halogenoacetic acid reacted with the phenolic hydroxyl groups and introduced carboxymethyl groups; 80% aqueous methanol was applied as the reaction solvent; the reaction conditions and C-HSALs properties are shown in Table 2. The increase in the quantity of the reagent and the prolongation of the reaction time resulted in an increase in the number of introduced carboxymethyl groups (from 1.66 to 3.66 mmol/g).
Table 3 presents the elemental analyses results of HSAL and C-HSALs. HSAL had an oxygen elemental content higher than that of the C-HSALs, and, among C-HSALs, it decreased with an increase in reagent quantity and reaction time. The comparison of the oxygen contents of the HSAL and C-HSALs indicate that carboxymethyl groups were introduced during the carboxymethylation of HSAL. This result is consistent with the comparison results of the carboxyl group between HSAL and C-HSALs.
The FT-IR spectra of HSAL and C-HSALs are shown in Fig. 4. Comparing C-HSAL with HSAL, we find that the 1760–1690 cm−1 (C=O stretch), 1440–1395 cm−1 (O–H bend), and 1320–1210 cm−1 (C–O stretch) peaks are increasing which suggests the introduction of the carboxymethyl group into HSAL by the carboxymethylation with halogenoacetic acid.
C-HSAL dispersibility
Dispersant is a very practical engineering additive which applied into the gypsum wallboard slurry to reduce the amount of water used which allows lower energy use and help achieve improved efficiency. According to our previous study [19], the molecular weight of lignosulfonates also influenced dispersibility. Results shown clearly that the dispersion effect and the molecular weight of the dispersant matrix molecules are also highly positively correlated. From the result, we believe that it is difficult to obtain dispersants with high efficiency from kraft lignin and soda lignin because of their low molecular weight.
In this experiment, the dispersibility of the C-HSALs was determined by the fluidity of gypsum paste in the presence of the additives and measured with small-scale testing equipment [21]. Figure 5 shows the dispersion efficiencies of all the prepared water-soluble C-HSALs derivatives at 0.1% dosage. This suggests that C-HSAL possesses a high efficiency (the average flow value of C-HSAL #10 is 146.74 while the blank shows 105.76) and a dispersibility almost equivalent to that of commercial lignosulfonate (average flow value 155.61). Among the three C-HSALs, the dispersion efficiency increases with a higher carboxymethyl group into HSAL: the average flow values of C-HSAL #3 and #10 are 123.49 to 146.74, respectively, while their carboxymethyl contents are 1.66 and 3.66 mmol/g, respectively.
It has been found that the efficiency of a dispersant is significantly affected by its molecular weight and related to its steric repulsive force. Further research indicates that the steric repulsive force had a greater effect than the electrostatic repulsive force on the fluidity of cement paste [18]. In this study, the molecular weights of C-HSALs (approximately 4–10 kDa) were higher than that of LS (around 5.8 kDa), and this suggests that the difference in molecular weights may be one of the reasons for the efficiency differences of the prepared polymers. Concerning these points, we hypothesize the dispersion behavior between C-HSAL and gypsum paste to be as shown in Fig. 6.
Conclusions
-
1.
Dye removal tests were performed using three kinds of organic dyes and GTA-HSAL-based flocculants. We ideal dye removal ratios by GTA-HSALs, higher than 90% for all dyes tested, which suggested that they have a huge potential as core molecules to develop high efficiency dye flocculants.
-
2.
The carboxymethylation with bromoacetic acid was carried out. Dispersibility tests using gypsum paste showed that the C-HSALs have dispersibilities almost equivalent to that of commercial lignosulfonate.
-
3.
From these results, we believe that HSAL has potential, with some chemical modifications, to produce raw materials for various industrial uses.
Abbreviations
- SAL:
-
sulfuric acid lignin
- HSAL:
-
hydrothermal treated SAL
- C-HSAL:
-
carboxymethylated HSAL
- GTA:
-
glycidyl trimethylammonium chloride
- GTA-HSAL:
-
HSAL reacted with GTA
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- RBB:
-
Remazol Brilliant Blue R
- DR:
-
Direct Red 23
- AB:
-
Acid Black 1
- LS:
-
lignosulfonate
References
Oreskes N (2004) The scientific consensus on climate change. Science 306:1686
Ren J, An D, Liang H, Dong L, Gao Z, Geng Y, Zhu Q, Song S, Zhao W (2016) Life cycle energy and CO2 emission optimization for biofuel supply chain planning under uncertainties. Energy 103:151–166
Wang B, Wang Q, Wei YM, Li ZP (2018) Role of renewable energy in China’s energy security and climate change mitigation: an index decomposition analysis. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 90:187–194
Wheeler J, Caballero JA, Ruiz-Femenia R, Guillén-Gosálbez G, Mele FD (2017) MINLP-based Analytic Hierarchy Process to simplify multi-objective problems: application to the design of biofuels supply chains using on field surveys. Comput Chem Eng 102:64–80
Yasuda S, Terashima N (1983) Chemical structure of sulfuric acid lignin VI Physical and chemical properties of sulfuric acid lignin. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 29:795–800
Yasuda S, Hamaguchi E, Matsushita Y, Goto H, Imai T (1998) Ready chemical conversion of acid hydrolysis lignin into water-soluble lignosulfonate II: hydroxymethylation and subsequent sulfonation of phenolized lignin model compounds. J Wood Sci 44:116–124
Matsushita Y, Sano H, Imai M, Imai T, Fukushima K (2007) Phenolization of hardwood sulfuric acid lignin and comparison of the behavior of the syringyl and guaiacyl units in lignin. J Wood Sci 53:67–70
Matsushita Y, Yasuda S (2003) Reactivity of a condensed-type lignin model compound in the Mannich reaction and preparation of cationic surfactant from sulfuric acid lignin. J Wood Sci. 49:166–171
Matsushita Y, Inomata T, Takagi Y, Hasegawa T, Fukushima K (2011) Conversion of sulfuric acid lignin generated during bioethanol production from lignocellulosic materials into polyesters with Ɛ-caprolactone. J Wood Sci 57:214–218
Matsushita Y, Inomata T, Hasegawa T, Fukushima K (2009) Bioresource Technology Solubilization and functionalization of sulfuric acid lignin generated during bioethanol production from woody biomass. Bioresour Technol 100:1024–1026
Yagub MT, Sen TK, Afroze S, Ang HM (2014) Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 209:172–184
Wahlström R, Kalliola A, Heikkinen J, Kyllönen H, Tamminen T (2017) Lignin cationization with glycidyltrimethylammonium chloride aiming at water purification applications. Ind Crop Prod 104:188–194
Saeed S, Khan S, Saeed S, Khan R (2015) Removal of dyes from textile waste water using adsorption by activated carbon of rice husk. Int J Inno Sci Res 17:191–196
Liu Q, Matsushita Y, Aoki D, Yagami S, Fukushima K (2018) Effects of hydrothermal reaction of sulfuric acid lignin from Cryptomeria japonica for industrial utilization. Bioresource 13:7805–7825
Kajihara M, Aoki D, Matsushita Y, Fukushima K (2018) Synthesis and characterization of lignin-based cationic dye-flocculant. J Appl Polym Sci 135:1–8
Huang C, Ma J, Zhang W, Huang G, Yong Q (2018) Preparation of lignosulfonates from biorefinery lignins by sulfomethylation and their application as a water reducer for concrete. Polymers 10:841
Zhou M, Qiu X, Yang D, Lou H (2006) Properties of different molecular weight sodium lignosulfonate fractions as dispersant of coal-water slurry. J Dispersion Sci Technol 27:851–856
Li Z, Pang Y, Lou H, Qiu X (2009) Influence of lignosulfonates on the properties of dimethomorph water-dispersible granules. BioResources 4(2):589–601
Matsushita Y, Yasuda S (2005) Preparation and evaluation of lignosulfonates as a dispersant for gypsum paste from acid hydrolysis lignin. Bioresour Technol 96:465–470
Yang D, Qiu X, Pang Y, Zhou M (2008) Physicochemical properties of calcium lignosulfonate with different molecular weights as dispersant in aqueous suspension. J Disper Sci Technol 29:1296–1303
Konduri MKR, Fatehi P (2018) Designing anionic lignin-based dispersant for kaolin suspensions. Colloids Surf A 538:639–650
Cerrutti BM, Souza CS, Castellancd A, Ruggiero R, Frollini E (2012) Carboxymethyl lignin as stabilizing agent in aqueous ceramic suspensions. Ind Crop Prod 36:108–115
Matsushita Y, Yasuda S (2003) Preparation and evaluation of mordants for neutral rosin size emulsion from lignin. Kami-pa-gi-kyō-shi 57:882–892
Konduria MK, Kong F, Fatehi P (2015) Production of carboxymethylated lignin and its application as a dispersant. Eur Polymer J 70:371–383
Authors’ contributions
QL mainly planed and performed the almost experiments and analyzed all data obtained in this research. QL was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. YM also planed this research and also analyzed all data obtained in this research. TM is a corresponding author. DA and KF also analyzed the data obtained from flocculant and dispersibility test. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI (No. 17H03842) and China Scholarship Council program (CSC 201708050043).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its additional files.
Funding
Not applicable.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Chemical structure of three dyes for dye removal test. Figure S2. Schematic procedure for evaluation of dispersibility test.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Matsushita, Y., Aoki, D. et al. Industrial utilizations of water-soluble sulfuric acid lignin prepared by hydrothermal treatment as flocculant and dispersant. J Wood Sci 65, 18 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s10086-019-1797-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s10086-019-1797-1