Abstract
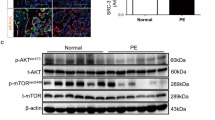
Preeclampsia (PE) is currently thought to be characterized by oxidative stress which may lead to endothelial dysfunction. The normal function of vascular endothelium is essential to vascular homeostasis. Previous studies have shown that steroid receptor coactivator 3 (SRC-3) interacts with estrogen receptors (ERs) which are involved in the vasoprotective effects of estrogen and is also associated with cell migration, invasion, and inflammation; however, its role in PE remains unclear. The main purpose of this study is to identify the role of SRC-3 in the function of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) during the development of PE. Our study demonstrated that the expression of SRC-3 was significantly decreased in PE placentas compared to normal placentas. Additionally, lentivirus short hairpin RNA against SRC-3 and hypoxia/reoxygenation treatments attenuated migration and tube formation abilities and enhanced HUVEC apoptosis. Furthermore, we detected possible downstream in the PI3K/Akt/ mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signal pathway activity, which is involved in SRC-3-mediated HUVEC function. Our data suggest that oxidative stress plays a crucial role in controlling SRC-3 expression, which influences the migration and tube formation abilities of endothelial cells through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. This action may then result in PE pathogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steegers EA, von Dadelszen P, Duvekot JJ, Pijnenborg R. Preeclampsia. Lancet. 2010;376(9741):631–644.
Abalos E, Cuesta C, Grosso AL, Chou D, Say L. Global and regional estimates of preeclampsia and eclampsia: a systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013;170(1): 1–7.
Walsh SW. Maternal-placental interactions of oxidative stress and antioxidants in preeclampsia. Semin Reprod Endocrinol. 1998; 16(1):93–104.
Burton GJ, Jauniaux E. Oxidative stress. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;25(3):287–299.
Suen CS, Berrodin TJ, Mastroeni R, Cheskis BJ, Lyttle CR, Frail DE. A transcriptional coactivator, steroid receptor coactivator-3, selectively augments steroid receptor transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(42):27645–27653.
Anzick SL, Kononen J, Walker RL, et al. AIB1, a novel estrogen receptor co-activator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1997;277(5328):965–968.
Yoshida H, Liu J, Samuel S, Cheng W, Rosen D, Naora H. Steroid receptor coactivator-3, a homolog of taiman that controls cell migration in the Drosophila ovary, regulates migration of human ovarian cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2005; 245(1–2):77–85.
Xu FP, Xie D, Wen JM, et al. SRC-3/AIB1 protein and gene amplification levels in human esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 2007 8;245(1–2):69–74.
Mo P, Zhou Q, Guan L, et al. Amplified in breast cancer 1 pro-motes colorectal cancer progression through enhancing notch sig-naling. Oncogene. 2015;34(30):3935–3945.
Cai D, Shames DS, Raso MG, et al. Steroid receptor coactivator-3 expression in lung cancer and its role in the regulation of cancer cell survival and proliferation. Cancer Res. 2010;70(16): 6477–6485.
Bai J, Uehara Y, Montell DJ. Regulation of invasive cell behavior by taiman, a Drosophila protein related to AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast cancer. Cell. 2000;103(7): 1047–1058.
Lahusen T, Fereshteh M, Oh A, Wellstein A, Riegel AT. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine phosphorylation and signaling controlled by a nuclear receptor coactivator, amplified in breast cancer 1. Cancer Res. 2007;67(15):7256–7265.
Fereshteh MP, Tilli MT, Kim SE, et al. The nuclear receptor coactivator amplified in breast cancer-1 is required for Neu (ErbB2/HER2) activation, signaling, and mammary tumorigenesis in mice. Cancer Res. 2008;68(10):3697–3706.
Oh A, List HJ, Reiter R, et al. The nuclear receptor coactivator AIB1 mediates insulin-like growth factor I-induced phenotypic changes in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64(22): 8299–8308.
Al-Otaiby M, Tassi E, Schmidt MO, et al. Role of the nuclear receptor coactivator AIB1/SRC-3 in angiogenesis and wound healing. Am J Pathol. 2012;180(4):1474–1484.
Yuan Y, Liao L, Tulis DA, Xu J. Steroid receptor coactivator-3 is required for inhibition of neointima formation by estrogen. Circulation. 2002;105(22):2653–2659.
Roberts JM., Taylor RN, Goldfien A. Clinical and biochemical evidence of endothelial cell dysfunction in the pregnancy syndrome preeclampsia. Am J Hypertens. 1991;4(8):700–708.
Roberts JM, Taylor RN, Musci TJ, Rogers GM, Hubel CA, McLaughlin MK. Preeclampsia. An endothelial cell disorder. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989;161(5):1200–1204.
Hung TH, Skepper JN, Burton GJ. In vitro ischemia-reperfusion injury in term human placenta as a model for oxidative stress in pathological pregnancies. Am J Pathol. 2001;159(3):1031–1043.
Cudmore M, Ahmad S, Al-Ani B, et al. Negative regulation of soluble Flt-1 and soluble endoglin release by heme oxygenase-1. Circulation. 2001; 15(13): 1789–1797.
Qiu Q, Yang M, Tsang BK, Gruslin A. EGF-induced trophoblast secretion of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 involves activation of both PI3 K and MAPK signalling pathways. Reproduction. 2004;128(3): 355–363.
Jia RZ, Ding GC, Gu CM, Huang T, Rui C, Wang YX, Lu Q. CDX2 enhances HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cell invasion by altering the expression of matrix metalloproteinases. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34(3):628–636.
Cudmore MJ, Ahmad S, Sissaoui S, et al. Loss of Akt activity increases circulating soluble endoglin release in preeclampsia: identification of inter-dependency between Akt-1 and heme oxy-genase-1. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(9):1150–1158.
Ying H, Furuya F, Willingham MC, Xu J, O’Malley BW, Cheng SY. Dual functions of the steroid hormone receptor coactivator 3 in modulating resistance to thyroid hormone. Mol Cell Biol. 2005; 25(17):7687–7895.
Torres-Arzayus MI, Font de Mora J, Yuan J, et al. High tumor incidence and activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in transgenic mice define AIB1 as an oncogene. Cancer Cell. 2004;6(3):263–274.
Leach RE, Kilburn BA, Petkova A, Romero R, Armant DR. Diminished survival of human cytotrophoblast cells exposed to hypoxia/reoxygenation injury and associated reduction of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198(4):471.el-471.e8.
Hung TH, Burton GJ. Hypoxia and reoxygenation: a possible mechanism for placental oxidative stress in preeclampsia. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;45(3): 189–200.
Millauer B, Wizigmann-Voos S, Schnurch H, et al. High affinity VEGF binding and developmental expression suggest Flk-1 as a major regulator of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Cell. 1993; 72(6):835–846.
Quinn TP, Peters KG, De Vries C, Ferrara N, Williams LT. Fetal liver kinase 1 is a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor and is selectively expressed in vascular endothelium. Proc Natl AcadSci USA. 1993;90(16):7533–7537.
Plate KH, Breier G, Millauer B, Ullrich A, Risau W. Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and its cognate receptors in a rat glioma model of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 1993;53(23):5822–5827.
Koch S, Claesson-Welsh L. Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012;2(7):a006502.
Cook-Mills JM, Marchese ME, Abdala-Valencia H. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression and signaling during disease: regulation by reactive oxygen species and antioxidants. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(6):1607–1638.
Lee YW, Kuhn H, Hennig B, Neish AS, Toborek M. IL-4-induced oxidative stress upregulates VCAM-1 gene expression in human endothelial cells. JMol Cell Cardiol. 2001;33(1):83–94.
Sanchez-Aranguren LC, Prada CE, Riano-Medina CE, Lopez M. Endothelial dysfunction and preeclampsia: role of oxidative stress. Front Physiol. 2014;5:372.
Lash GE, Naruse K, Innes BA, Robson SC, Searle RF, Bulmer JN. Secretion of angiogenic growth factors by villous cytotrophoblast and extravillous trophoblast in early human pregnancy. Placenta. 2010;31(6):545–548.
Kim SC, Park MN, Lee YJ, Joo JK, An BS. Interaction of steroid receptor coactivators and estrogen receptors in the human placenta. J Mol Endocrinol. 2016;56(3):239–247.
Douglas NC, Tang H, Gomez R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) functions to promote uterine decidual angiogenesis during early pregnancy in the mouse. Endocrinology. 2009;150(8):3845–3854.
Meric-Bernstam F, Akcakanat A, Chen H, et al. PIK3CA/ PTEN mutations and Akt activation as markers of sensitivity to allosteric mTOR Inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(6): 1777–1789.
Zhou G, Hashimoto Y, Kwak I, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ. Role of the steroid receptor coactivator SRC-3 in cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(21):7742–7755.
Mendelsohn ME, Karas RH. The protective effects of estrogen on the cardiovascular system. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(23): 1801–1811.
Chen Z, Yuhanna IS, Galcheva-Gargova Z, Karas RH, Mendel-sohn ME, Shaul PW. ERa mediates the nongenomic activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by estrogen. J Clin Invest. 1999; 103(3):401–406.
Bakir S, Mori T, Durand J, Chen YF, Thompson JA, Oparil S. Estrogen-induced vaso-protection is ER dependent: evidence from the balloon-injured rat carotid artery model. Circulation. 2000;101(20):2342–2344.
Jobe SO, Tyler CT, Magness RR. Aberrant synthesis, metabolism, and plasma accumulation of circulating estrogens and estrogen metabolites in preeclampsia implications for vascular dysfunction. Hypertension. 2013;61(2):480–487.
Schiessl B, Mylonas I, Hantschmann P, et al. Expression of endothelial NO synthase, inducible NO synthase, and estrogen receptors alpha and beta in placental tissue of normal, preeclamptic, and intrauterine growth-restricted pregnancies. J Histochem Cytochem. 2005;53(12):1441–1449.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Y., Shan, N., Tan, B. et al. SRC-3 Plays a Critical Role in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells by Regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway in Preeclampsia. Reprod. Sci. 25, 748–758 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719117725818
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719117725818