Abstract
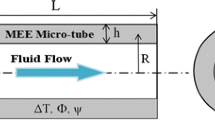
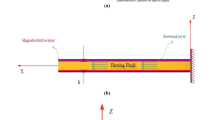
The main goal of this paper is to investigate the size-dependent nonlinear vibration and stability response of fluid-conveying sandwich micro-pipes exploiting magnetorheological elastomer (MRE) as a smart core. Considering the geometrical nonlinearity, based on von-Karman assumption, Euler–Bernoulli theory is employed for mathematical formulation of the problem. Additionally, modified couple stress theory (MCST) is utilized as a size-dependent theory to reach an accurate model. Kerwin assumption is taken into account, and Hamiltonian’s approach is hired to derive the coupled and nonlinear governing equations and boundary conditions of the system. For solution procedure, differential quadrature method (DQM) is used to discretize the governing equations and corresponding boundary conditions. Thereafter, the obtained algebraic nonlinear equations and boundary conditions are solved numerically to acquire the nonlinear eigenvalues of the system which could be analyzed to discuss the stability and critical flow velocity of the system. In numerical analysis, a detailed examination is conducted to elucidate the exact influences of the main intrinsic characteristics of MRE core (i.e., magnetic intensity and MRE core thickness) on vibrational response of the system. Accordingly, the main effects of the MRE layer on vibrational properties including frequency, loss factor, critical flow velocity and stability region for both cantilever and clamped–clamped pipes are investigated. The results reveal the substantial effect of the MRE core on the vibrational characteristics and stability of the system. The boosting effect of the MRE core layer on the stability of the system was disclosed. The results declare that, in addition to the magnetic intensity as a controlling parameter, the MRE core thickness is another important factor in vibration and stability characteristics of the system. Totally, the research reveals that the fabulous properties of the MRE layers could be considered and exploited in designing the fluid-conveying micro-pipes to obtain an efficient, smart and adaptive system response.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Wang, C. Bai, H. Zhang, Nonlinear vibrations of fluid-conveying FG cylindrical shells with piezoelectric actuator layer and subjected to external and piezoelectric parametric excitations. Compos. Struct. 248, 112437 (2020)
A. Amiri, R. Talebitooti, L. Li, Wave propagation in viscous-fluid-conveying piezoelectric nanotubes considering surface stress effects and Knudsen number based on nonlocal strain gradient theory. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 133(7), 252 (2018)
A. Amiri, R. Vesal, R. Talebitooti, Flexoelectric and surface effects on size-dependent flow-induced vibration and instability analysis of fluid-conveying nanotubes based on flexoelectricity beam model. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 156, 474–485 (2019)
R.B. Vemuluri, V. Rajamohan, P.E. Sudhagar, Structural optimization of tapered composite sandwich plates partially treated with magnetorheological elastomers. Compos. Struct. 200, 258–276 (2018)
S. Bornassi, H.M. Navazi, Torsional vibration analysis of a rotating tapered sandwich beam with magnetorheological elastomer core. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 29(11), 2406–2423 (2018)
H. Akhavan, M. Ghadiri, A. Zajkani, A new model for the cantilever MEMS actuator in magnetorheological elastomer cored sandwich form considering the fringing field and Casimir effects. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 121, 551–561 (2019)
A. GhorbanpourArani, H. BabaAkbarZarei, M. Eskandari, P. Pourmousa, Vibration behavior of visco-elastically coupled sandwich beams with magnetorheological core and three-phase carbon nanotubes/fiber/polymer composite facesheets subjected to external magnetic field. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 21(7), 2194–2218 (2019)
R. Selvaraj, M. Ramamoorthy, Dynamic analysis of laminated composite sandwich beam containing carbon nanotubes reinforced magnetorheological elastomer. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636220905253
Q. Sun, J.-X. Zhou, L. Zhang, An adaptive beam model and dynamic characteristics of magnetorheological materials. J. Sound Vib. 261(3), 465–481 (2003)
F. de Souza Eloy, G.F. Gomes, A.C. Ancelotti Jr., S.S. da Cunha Jr., A.J.F. Bombard, D.M. Junqueira, A numerical-experimental dynamic analysis of composite sandwich beam with magnetorheological elastomer honeycomb core. Compos. Struct. 209, 242–257 (2019)
H. Li, W. Wang, X. Wang, Q. Han, J. Liu, Z. Qin, J. Xiong, Z. Guan, A nonlinear analytical model of composite plate structure with an MRE function layer considering internal magnetic and temperature fields. Compos. Sci. Technol. 200, 108445 (2020)
H. Dai, L. Wang, Q. Ni, Dynamics of a fluid-conveying pipe composed of two different materials. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 73, 67–76 (2013)
Y.Q. Wang, Y.H. Wan, J.W. Zu, Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of functionally graded sandwich thin nanoshells conveying fluid incorporating surface stress influence. Thin Wall. Struct. 135, 537–547 (2019)
A.-R. AsghariArdalani, A. Amiri, R. Talebitooti, M.S. Safizadeh, On wave dispersion characteristics of fluid-conveying smart nanotubes considering surface elasticity and flexoelectricity approach. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. C-J Mech. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406220965611
A.E. Mamaghani, S. Khadem, S. Bab, Vibration control of a pipe conveying fluid under external periodic excitation using a nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dyn. 86(3), 1761–1795 (2016)
F. Liang, X.-D. Yang, Y.-J. Qian, W. Zhang, Transverse free vibration and stability analysis of spinning pipes conveying fluid. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 137, 195–204 (2018)
A. Amiri, A. Masoumi, R. Talebitooti, Flutter and bifurcation instability analysis of fluid-conveying micro-pipes sandwiched by magnetostrictive smart layers under thermal and magnetic field. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 16, 569–588 (2020)
H.-C. Li, L.-L. Ke, Size-dependent vibration and dynamic stability of AFG microbeams immersed in fluid. Thin Wall. Struct. 161, 107432 (2021)
Y. Wang, Y. Wei, Internal resonance analysis of a fluid-conveying tube resting on a nonlinear elastic foundation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 135(4), 1–38 (2020)
X. Zhu, Z. Lu, Z. Wang, L. Xue, A. Ebrahimi-Mamaghani, Vibration of spinning functionally graded nanotubes conveying fluid. Eng. Comput. 2020, 1–22 (2020)
F. Zheng, Y. Lu, A. Ebrahimi-Mamaghani, Dynamical stability of embedded spinning axially graded micro and nanotubes conveying fluid. Waves Random Complex Media 2020, 1–39 (2020)
M. Tang, Q. Ni, L. Wang, Y. Luo, Y. Wang, Nonlinear modeling and size-dependent vibration analysis of curved microtubes conveying fluid based on modified couple stress theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 84, 1–10 (2014)
A. Amiri, I. Pournaki, E. Jafarzadeh, R. Shabani, G. Rezazadeh, Vibration and instability of fluid-conveyed smart micro-tubes based on magneto-electro-elasticity beam model. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 20(2), 38 (2016)
S. Ahangar, G. Rezazadeh, R. Shabani, G. Ahmadi, A. Toloei, On the stability of a microbeam conveying fluid considering modified couple stress theory. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 7(4), 327 (2011)
L. Wang, H. Liu, Q. Ni, Y. Wu, Flexural vibrations of microscale pipes conveying fluid by considering the size effects of micro-flow and micro-structure. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 71, 92–101 (2013)
A. Setoodeh, S. Afrahim, Nonlinear dynamic analysis of FG micro-pipes conveying fluid based on strain gradient theory. Compos. Struct. 116, 128–135 (2014)
A.G. Arani, E. Haghparast, M.H. Rarani, Z.K. Maraghi, Strain gradient shell model for nonlinear vibration analysis of visco-elastically coupled Boron Nitride nano-tube reinforced composite micro-tubes conveying viscous fluid. Comput. Mater. Sci. 96, 448–458 (2015)
B. Abbasnejad, R. Shabani, G. Rezazadeh, Stability analysis of a piezoelectrically actuated micro-pipe conveying fluid. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 19(3), 577–584 (2015)
B. Abbasnejad, G. Rezazadeh, R. Shabani, Stability analysis of a capacitive fgm micro-beam using modified couple stress theory. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 26(4), 427–440 (2013)
F. Yang, A. Chong, D.C.C. Lam, P. Tong, Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 39(10), 2731–2743 (2002)
G. Zhou, Q. Wang, Study on the adjustable rigidity of magnetorheological-elastomer-based sandwich beams. Smart Mater. Struct. 15(1), 59 (2005)
Z. Ying, Y. Ni, Micro-vibration response of a stochastically excited sandwich beam with a magnetorheological elastomer core and mass. Smart Mater. Struct. 18(9), 095005 (2009)
B. Nayak, S. Dwivedy, K. Murthy, Dynamic analysis of magnetorheological elastomer-based sandwich beam with conductive skins under various boundary conditions. J. Sound Vib. 330(9), 1837–1859 (2011)
S. Aguib, A. Nour, H. Zahloul, G. Bossis, Y. Chevalier, P. Lançon, Dynamic behavior analysis of a magnetorheological elastomer sandwich plate. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 87, 118–136 (2014)
V.R. Babu, R. Vasudevan, Dynamic analysis of tapered laminated composite magnetorheological elastomer (MRE) sandwich plates. Smart Mater. Struct. 25(3), 035006 (2016)
S. Aguib, A. Nour, B. Benkoussas, I. Tawfiq, T. Djedid, N. Chikh, Numerical simulation of the nonlinear static behavior of composite sandwich beams with a magnetorheological elastomer core. Compos. Struct. 139, 111–119 (2016)
H. Navazi, S. Bornassi, H. Haddadpour, Vibration analysis of a rotating magnetorheological tapered sandwich beam. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 122, 308–317 (2017)
M. Hoseinzadeh, J. Rezaeepazhand, Dynamic stability enhancement of laminated composite sandwich plates using smart elastomer layer. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636218819158
S. Bornassi, H. Navazi, H. Haddadpour, Aeroelastic instability analysis of a turbomachinery cascade with magnetorheological elastomer based adaptive blades. Thin Wall. Struct. 130, 71–84 (2018)
R.B. Vemuluri, V. Rajamohan, A.B. Arumugam, Dynamic characterization of tapered laminated composite sandwich plates partially treated with magnetorheological elastomer. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 20(3), 308–350 (2018)
C. Wu, Q. Zhang, X. Fan, Y. Song, Q. Zheng, Smart magnetorheological elastomer peristaltic pump. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 30(7), 1084–1093 (2019)
S. Aguib, A. Nour, T. Djedid, G. Bossis, N. Chikh, Forced transverse vibration of composite sandwich beam with magnetorheological elastomer core. J. Mech. Sci. Technol 30(1), 15–24 (2016)
M. Rambausek, K. Danas, Bifurcation of magnetorheological film–substrate elastomers subjected to biaxial pre-compression and transverse magnetic fields. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 128, 103608 (2020)
A.G. Arani, T. Soleymani, Size-dependent vibration analysis of a rotating MR sandwich beam with varying cross section in supersonic airflow. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 151, 288–299 (2019)
M. Asgari, M.A. Kouchakzadeh, Aeroelastic characteristics of magneto-rheological fluid sandwich beams in supersonic airflow. Compos. Struct. 143, 93–102 (2016)
E.M. Kerwin Jr., Damping of flexural waves by a constrained viscoelastic layer. J. Acoust. Soc. 31(7), 952–962 (1959)
M. Rokn-Abadi, M. Yousefi, H. Haddadpour, M. Sadeghmanesh, Dynamic stability analysis of a sandwich beam with magnetorheological elastomer core subjected to a follower force. Acta Mech. 231(9), 3715–3727 (2020)
M. Fakhari, N. Saeedi, A. Amiri, Size-dependent vibration and instability of magneto-electro-elastic nano-scale pipes containing an internal flow with slip boundary condition. Int. J. Eng. 29(7), 995–1004 (2016)
L.-L. Ke, Y.-S. Wang, Z.-D. Wang, Nonlinear vibration of the piezoelectric nanobeams based on the nonlocal theory. Compos. Struct. 94(6), 2038–2047 (2012)
A. Masoumi, A. Amiri, R. Vesal, G. Rezazadeh, Nonlinear static pull-in instability analysis of smart nano-switch considering flexoelectric and surface effects via DQM. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. C-J Mech. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406221997481
L. Yin, Q. Qian, L. Wang, Strain gradient beam model for dynamics of microscale pipes conveying fluid. Appl. Math. Model. 35(6), 2864–2873 (2011)
M. Hosseini, R. Bahaadini, Size dependent stability analysis of cantilever micro-pipes conveying fluid based on modified strain gradient theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 101, 1–13 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amiri, A., Talebitooti, R. Vibration and stability analysis of fluid-conveying sandwich micro-pipe with magnetorheological elastomer core, considering modified couple stress theory and geometrical nonlinearity. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136, 1109 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-02117-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-02117-0