Abstract
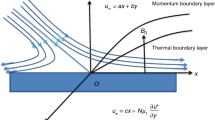
The inherent irreversibility in boundary-layer flow of a radiating water/functionalized carbon nanotubes nanofluid over a convectively heated moving wedge and a horizontal/vertical plates is examined. The water-based nanofluid contains two types of carbon nanotubes, namely SWCNTs and MWCNTs. Using a suitable similarity transformation, the model partial differential equations are reduced to ordinary differential equations along with the corresponding boundary conditions. Solutions are obtained for the nanofluid velocity and temperature profiles analytically via optimal homotopy asymptotic method and numerically via shooting method with Runge–Kutta–Fehlberg integration scheme. Entropy generation analysis is conducted based on second law of thermodynamic, and the Bejan number is determined. Results are presented in graphical and tabular forms in order to scrutinize the effects of various geometrical, dynamical and thermophysical parameters on velocity, temperature, skin friction, Nusselt number, entropy generation rate and Bejan number. Generally, it is found that the entropy production can be minimized by reducing the convection through boundaries, moving the obstacle at the same velocity and direction as the flow (λoptimal = 1) and controlling the penetration of viscous dissipation, while increasing nanoparticles rate and thermal radiation has influence to increase the entropy generation. In addition, horizontal plate corresponding to the wedge angle value m = 0 is the optimum geometry to reduce entropy production.















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
11 August 2020
After publication of the article, mistakes were found.
Abbreviations
- FCNT:
-
Functionalized carbon nanotube
- SWCNT:
-
Single-wall carbon nanotube
- MWCNT:
-
Multi-wall carbon nanotube
- RKF:
-
Runge–Kutta–Fehlberg method
- OHAM:
-
Optimal homotopy asymptotic method
- HC:
-
Heat convection
- TR:
-
Thermal radiation
- HTI:
-
Heat transfer irreversibility
- FFI:
-
Fluid friction irreversibility
References
V.M. Falkner, S.W. Skan, Some approximate solutions of the boundary-layer equations. Philos. Mag. 12, 865–896 (1931)
K.A. Yih, Uniform suction/blowing effect on forced convection about a wedge: uniform heat flux. Acta Mech. 128(3/4), 173–181 (1998)
M.K. Nayak, A.K. Hakeem, O.D. Makinde, Time varying chemically reactive magneto-hydrodynamic non-linear Falkner–Skan flow over a permeable stretching/shrinking wedge: Buongiorno model. J. Nanofluids 8(3), 467–476 (2019)
F. Mabood, S.M. Ibrahim, M.M. Rashidi, M.S. Shadloo, G. Lorenzini, Non-uniform heat source/sink and Soret effects on MHD non-Darcian convective flow past a stretching sheet in a micropolar fluid with radiation. Int. J. Heat. Mass Transf. 93, 674–682 (2016)
B. Mahanthesh, O.D. Makinde, B.J. Gireesha, K.L. Krupalakshmi, I.L. Animasaun, Two-phase flow of dusty Casson fluid with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux and heat source past a cone, wedge and plate. Defect Diffus. Forum 387, 625–639 (2018)
A.V. Kuznetsov, D.A. Nield, Boundary layer treatment of forced convection over a wedge with an attached porous substrate. J. Porous Media 9(7), 683–694 (2006)
B.L. Kuo, Heat transfer analysis for the Falkner–Skan wedge flow by the differential transformation method. Int. J. Heat. Mass Transf. 48(23/24), 5036–5046 (2005)
S.U.S. Choi, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, in Proceedings of ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, San Francisco, USA, ASME, FED 231/MD, vol. 66 (1995), pp. 99–105
R. Haq, I. Rashid, Z.H. Khan, Effects of aligned magnetic field and CNTs in two different base fluids over a moving slip surface. J. Mol. Liq. 243, 682–688 (2017)
N.A. Che Sidik, M.N.A.W.M. Yazid, S. Samion, A review on the use of carbon nanotubes nanofluid for energy harvesting system. Int. J. Heat. Mass Transf. 111, 782–794 (2017)
Y.H. Hung, H.J. Gu, Multiwalled carbon nanotube nanofluids used for heat dissipation in hybrid green energy systems. J. Nanomater. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/196074
N.A. Yacob, A. Ishak, I. Pop, Falkner–Skan problem for a static or moving wedge in nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 50, 133–139 (2011)
M. Khan, M. Azam, On unsteady Falkner–Skan flow of MHD Carreau nanofluid past a static/moving wedge with convective surface condition. J. Mol. Liq. 230, 48–58 (2017)
M. Hashim, A. Khan, Hamid, Numerical investigation on time-dependent flow of Williamson nanofluid along with heat and mass transfer characteristics past a wedge geometry. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 118, 480–491 (2018)
M. Khan, A. Ahmed, J. Ahmed, Transient flow of magnetized Maxwell nanofluid: Buongiorno model perspective of Cattaneo–Christov theory. Appl. Math. Mech. 41(4), 655–666 (2020)
M. Azam, T. Xu, A. Shakoor, M. Khan, Effects of Arrhenius activation energy in development of covalent bonding in axisymmetric flow of radiative-cross nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 113, Article No. 104547 (2020)
A. Hashim, M. Hamid, Khan, Multiple solutions for MHD transient flow of Williamson nanofluids with convective heat transport. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 103, 126–137 (2019)
A. Hamid, A. Hashim, A. Hafeez, M. Khan, A.S. Alshomrami, M. Alghamdi, Heat transport features of magnetic water–graphene oxide nanofluid flow with thermal radiation: stability test. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 76, 434–441 (2019)
A. Bejan, Entropy Generation Minimization (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1996)
O.D. Makinde, W.A. Khan, A. Aziz, On inherent irreversibility in Sakiadis flow of nanofluids. Int. J. Exergy 2, 159–174 (2013)
F.A. Soomro, R.U. Haq, Z.H. Khan, Numerical study of entropy generation in MHD water-based carbon nanotubes along an inclined permeable surface. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132(10), 412 (2017)
J. Qing, M.M. Bhatti, M.A. Abbas, M.M. Rashidi, M.E. Ali, Entropy generation on MHD Casson nanofluid flow over a porous stretching/shrinking surface. Entropy 18(4), 123 (2016)
M. Ishaq, A. Gohar, Z. Shah, S. Islam, S. Muhammad, Entropy generation on nanofluid thin film flow of Eyring–Powell fluid with thermal radiation and MHD effect on an unsteady porous stretching sheet. Entropy 20(6), 412 (2018)
M.I. Afridi, M. Qasim, N.A. Khan, O.D. Makinde, Minimization of entropy generation in MHD mixed convection flow with energy dissipation and Joule heating: utilization of Sparrow–Quack–Boerner local non-similarity method. Defect Diffus. Forum 387, 63–77 (2018)
M.I. Afridi, M. Qasim, O.D. Makinde, Second law analysis of boundary layer flow with variable fluid properties. ASME J. Heat Transf. 10, 104505 (2017)
O.D. Makinde, A.S. Eegunjobi, Entropy analysis in MHD flow with heat source and thermal radiation past a stretching sheet in a porous medium. Defect Diffus. Forum 387, 364–372 (2018)
A. Malvandi, D.D. Ganji, F. Hedayati, E. Yousefi Rad, An analytical study on entropy generation of nanofluids over a flat plate. Alex. Eng. J. 52(4), 595–604 (2013)
F. Hedayati, A. Malvandi, D.D. Ganji, Second-law analysis of fluid flow over an isothermal moving wedge. Alex. Eng. J. 53(1), 1–9 (2014)
H. Berrehal, Thermodynamics second law analysis for MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer caused by a moving wedge. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 33(6), 2949–2955 (2019)
A. Bejan, A study of entropy generation in fundamental convective heat transfer. J. Heat Transf. 101, 718–725 (1979)
A.S. Butt, S. Munawar, A. Ali, A. Mehmood, Entropy generation in the Blasius flow under thermal radiation. Phys. Scr. 85(3), 035008 (2012)
R.D. Ene, V. Marinca, Approximate solutions for steady boundary layer MHD viscous flow and radiative heat transfer over an exponentially porous stretching sheet. Appl. Math. Comput. 269, 389–401 (2015)
H. Berrehal, A. Maougal, Entropy generation analysis for multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) suspended nanofluid flow over wedge with thermal radiation and convective boundary condition. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 33(1), 459–464 (2019)
H. Berrehal, A. Maougal, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, On the analytic solution of magneto-hydrodynamic (MHD) flow by a moving wedge in porous medium. Defect Diffus. Forum 389, 128–137 (2018)
T. Watanabe, Thermal boundary layers over a wedge with uniform suction or injection in forced flow. Acta Mech. 83, 119–126 (1990)
K.A. Yih, Uniform suction/blowing effect on forced convection about a wedge: uniform heat flux. Acta Mech. 128, 173–181 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berrehal, H., Mabood, F. & Makinde, O.D. Entropy-optimized radiating water/FCNTs nanofluid boundary-layer flow with convective condition. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 535 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00536-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-020-00536-z