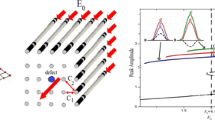
Abstract
The existence, dynamics and switching of bright and dark spatial soliton in coupled active cavities array above lasing threshold in presence of population inversion are studied here. Different types of discrete cavity soliton lasers are introduced and their stability is analyzed, together with the comparison of population inversion effects on bright and dark solitons. The effects of injection time, intensity, width, and phase difference of switching beam are analyzed to perform a successful ON/OFF switching.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Chen, T. Lv, A. Zheng, Y. Han, Controlled switching of discrete solitons in periodically poled lithium niobate waveguide arrays. Appl. Opt. 25(8), 1663 (2013)
T.R.O. Melvina, A.R. Champneysa, P.G. Kevrekidisb, J. Cuevasc, Travelling solitary waves in the discrete Schrodinger equation with saturable nonlinearity: existence, stability and dynamics. Elsevier Phys. D 237, 551–567 (2008)
K. Staliunas, O. Egorov, Y.S. Kivshar, F. Lederer, Bloch cavity solitons in nonlinear resonators with intracavity photonic crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 153903 (2008)
O.A. Egorov, F. Lederer, Spontaneously walking discrete cavity solitons. Opt. Lett. 38(7), 1010 (2013)
O. Egorov, F. Lederer, K. Staliunas, Subdiffractive discrete cavity solitons. Opt. Lett. 32(15), 2106 (2007)
B.H. Khiaban, K.M. Aghdami, R. Kheradmand, Switchable discrete cavity solitons in 2D waveguide structure with defect. Eur. Phys. J. D 69, 53 (2015)
K.M. Aghdami, M. Golshani, R. Kheradmand, Two-dimensional discrete cavity solitons: switching and all-optical gates. IEEE Photonics J. 4(4), 1147 (2012)
A. Kanshu, C.E. Ruter, D. Kip, J. Cuevas, P.G. Kevrekidis, Dark lattice solitons in one-dimensional waveguide arrays with defocusing saturable nonlinearity and alternating couplings. Eur. Phys. J. D 66, 182 (2012)
A. Motahharynia, K.M. Aghdami, R. Kheradmand, Modeling of population inversion in coupled active lasing cavities: aspects of the stability analysis. Chaos Solitons Fractals 118, 106–111 (2019)
K.J. Vahala, X. Yi, Q. Yang, Physics and applications of counter propagating solitons in microcavities. In: SPIE LASE (California, San Francisco, 2019)
B. Apter, N. Lapshina, A. Handelman, G. Rosenman, Light waveguiding in bioinspired peptide nanostructures. J. Pep. Sci. 25, 3164 (2019)
M. Eslami, S.Z. Gandomani, F. Prati, H. Tajalli, R. Kheradmand, Ultra low-energy switch based on a cavity soliton laser with pump modulation. J. Opt. 19, 015502 (2017)
O. Egorov, U. Peschel, F. Lederer, Mobility of discrete cavity solitons. Phys. Rev. E 72, 066603 (2005)
O. Egorov, U. Peschel, and F. Lederer, Discrete quadratic cavity solitons. Phys. Rev. E 71, 056612 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.71.056612
M. Bache, F. Prati, G. Tissoni, R. Kheradmand, L.A. Lugiato, I. Protsenko, M. Brambilla, Cavity soliton laser based on VCSEL with saturable absorber. Appl. Phys. 81, 913–920 (2005)
J.E. Prilepsky, A.V. Yulin, M. Johansson, S.A. Derevyanko, Discrete solitons in coupled active lasing cavities. OSA, 2012
M. Golshani, S. Weimann, Kh. Jafari, M. Khazaei Nezhad, A. Langari, A. R. Bahrampour, T. Eichelkraut, S. M. Mahdavi, and A. Szameit Impact of loss on the wave dynamics in photonic waveguide lattices. arXiv[physics.optics] 1408.5740v2, 2014
Z. Shi, J. Xue, Z. Xing, Y. Li, H. Li, Discrete multipole dark solitons in saturable nonlinearity media with parity-time symmetric lattices. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132, 79 (2017)
A.V. Yulin, A. Aladyshkina, A.S. Shalin, Motion of dissipative optical fronts under the action of an oscillating pump. Phys. Rev. E 94, 022205 (2016)
A.G. Ardakani, Wave propagation through photonic waveguide lattices in the presence of optical gain and loss. Appl. Opt. 55(13), 3589 (2016)
R. Kheradmand, K.M. Aghdami, K. Talouneh, The switching of dark and bright soliton in 1D discrete cavity laser. Chaos Solitons Fractals 91, 511–515 (2016)
Oleg A. Egorov, Falk Lederer, Yuri S. Kivshar, How does an inclined holding beam affect discrete modulational instability and solitons in nonlinear cavities? OSA 15(7), 4149 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motahharynia, A., Aghdami, K.M. & Kheradmand, R. The study of discrete cavity soliton lasers in presence of population inversion. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 135, 2 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-019-00017-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-019-00017-y