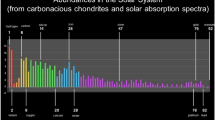
Abstract.
Given the limited space in this contribution, it is not possible to go into the details of the exciting astrophysical topic of stellar evolution and nucleosynthesis. It is attempted to emphasize the basics of this basic concept of the hydrostatic evolution of stars as they are driven by the interplay between gravity and nuclear energy generation, which is expressed by the virial theorem. In the case of massive stars roughly above \( 8 {\rm M}_{\odot}\), the breakdown of the hydrostatic evolution, due to the lack of nuclear energy generation, leads to gravitational collapse followed either by a successful supernova explosion, leaving a neutron star behind, or by a black hole, which is the ultimate end stage. The stars of masses in the lower mass range end their evolution as white dwarfs. The nucleosynthesis process in stars is a complex task. Most of the elements and their isotopes, especially the heavy elements, are produced in an explosive environment, or in the late stages of the asymptotic giant branch stars. The present paper will concentrate mainly on the evolutionary aspects, due to the to limited space given here.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Iben Jr., A. Renzini, Phys. Rep. 105, 329 (1984)
M.F. El Eid, Astron. Astrophys. 285, 915 (1994)
K. Nomoto, M. Hashimoto, Phys. Rep. 163, 13 (1988)
J. Jose, G. Hallabi, M.F. El Eid, Astron. Astrophys. 593, A54 (2016)
V. Bromm et al., Nature 459, 49B (2009)
W.W. Ober, M.F. El Eid, K.J. Fricke, Astron. Astrophys. 119, 61 (1983)
A. Heger, S.E. Woosley, Astrophys. J. 567, 532 (2002)
V. Bromm et al., Nature 459, 29 (2009)
Gal-Yam et al., Nature 462, 579 (2009)
R. Kippenhahn, A. Wegert, Stellar Structure and Evolution (Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1990)
F.J. Roger, C.A. Iglesias, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 79, 507 (1992)
O. Straniero et al., ASP Conf. Ser. 497, 259 (2015)
F. Herwig et al., Astron. Astrophys. 324, L81 (1997)
L. Deng, D.R. Xiong, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 386, 1979 (2008)
B. Freytag et al., Astron. Astrophys. 313, 497 (1996)
B.W. Carroll, D.A. Ostile, An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics (Pearson, New York, 2007)
B. Paczynski, M. Rozyczka, Acta Astron. 25, 213 (1977)
M.F. El Eid, L.-S. The, B.S. Meyer, Space Sci. Rev. 147, 1 (2009)
F. Herwig, Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 43, 435 (2005)
M. Busso et al., Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 37, 239 (1999)
C. Sneden, J.J. Cowan, R. Gallino, Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 46, 241 (2008)
S. Jones et al., Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 455, 3848 (2015)
G.M. Halabi, M.F. El Eid, A. Champgane, Astrophys. J. 761, 10 (2012)
M. Salaris, S. Cassisi, Evolituon of Stars and Stellar populations (Wiley:Chichester West Sussex, UL, 2008)
A.-J. Lai, Y. Li, Res. Astron. Astophys. 11, 1351 (2011)
R.J. de Boer, arXiv:1709.03144v1 (2107)
M. Kunz et al., Astrophys. J. 567, 643 (2002)
M. Angulo et al., Nucl. Phys. A 656, 3 (1999)
G. Imbtriani et al., Astrophys. J. 558, 903 (2001)
G.R. Caughlan et al., At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 32, 197 (1985)
G.R. Caughlan et al., At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 40, 283 (1985)
L.-S. The, M.F. El Eid, B.S. Meyer, Astrophys. J. 655, 1058 (2007)
F.K. Thielemann et al., Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 67, 253 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Eid, M.F. Comments on stellar evolution. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 133, 372 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12236-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12236-2