Abstract
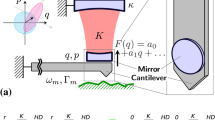
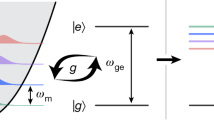
The electromechanical coupling in the nanomechanical detection experiment is important as people forever pursue the higher sensitivity. In this work, we have studied theoretically the electromechanical coupling effect on the sensitivity of nanomechanical motion with the mixing current detection method under monostable and bistable regime, respectively. To obtain the sensitivity, the response function, the shot noise and the backaction noise with the coupling in the nanomechanical system consists of the oscillator coupled to a quantum dot are present. It is found that for the monostable state, the higher coupling means higher sensitivity. Both the contributions of shot noise and the backaction noise to the sensitivity are the decreasing function of the coupling. Once the system enters the bistability regime, the telegraph noise dominates instead of the resonance frequency noise, that due to the electron hopping in the bistable regime contributes more noise for the detection, its value is 3 orders of magnitude larger than the contribution of shot noise. As a result, one could find that there is a optimal value of the coupling corresponding to the phase transition point where the sensitivity is the best. Our results provide the pioneer and useful approach for the detection experiment.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Authors’ comment: This is a theoretical study and no experimental data.]
References
A. Benyamini, A. Hamo, S.V. Kusminskiy, F. von Oppen, S. Ilani, Nat. Phys. 10, 151 (2014)
M. Ganzhorn, W. Wernsdorfer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 175502 (2012)
X.K.L. Ekinci, M.L. Roukes, Appl. Phys. Lett 84, 4469 (2004)
J. Moser, J. Güttinger, A. Eichler, M.J. Esplandiu, D.E. Liu, M.I. Dykman, A. Bachtold, Nat. Nano. 8, 493 (2013)
B. Lassagne, D. Garcia-Sanchez, A. Aguasca, A. Bachtold, Nano Lett. 8, 3735 (2008)
V. Puller, B. Lounis, F. Pistolesi, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 125501 (2013)
V. Sazonova, Y. Yaish, H. Üstünel, D. Roundy, T.A. Arias, P.L. McEuen, Nature 431, 284 (2004)
J. Moser, A. Eichler, J. Güttinger, M.I. Dykman, A. Bachtold, Nat. Nano 9, 1007 (2014)
F. Pistolesi, R. Shekhter, Phys. Rev. B 92, 035423 (2015)
Y.M. Blanter, O. Usmani, a Y. V. Nazarov, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 136802 (2004)
Y.M. Blanter, O. Usmani, a Y. V. Nazarov, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 049904 (2005)
A.D. Armour, M.P. Blencowe, Y. Zhang, Phys. Rev. B 69, 125313 (2004)
C.B. Doiron, W. Belzig, C. Bruder, Phys. Rev. B 74, 205336 (2006)
R. Avriller, B. Murr, F. Pistolesi, Phys. Rev. B 97, 155414 (2018)
F. Pistolesi, Phys. Rev. A 97, 063833 (2018)
D. Mozyrsky, M.B. Hastings, I. Martin, Phys. Rev. B 73, 035104 (2006)
J. Koch, F. von Oppen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 206804 (2005)
F. Pistolesi, Phys. Rev. B 76 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.76.165317
F. Pistolesi, Y.M. Blanter, I. Martin, Phys. Rev. B 78, 085127 (2008)
F. Pistolesi, J. Low Temp. Phys. 154, 199 (2009)
S. Zippilli, G. Morigi, A. Bachtold, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 096804 (2009)
P. Stadler, W. Belzig, G. Rastelli, Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 047201 (2014)
N.M. Chtchelkatchev, W. Belzig, C. Bruder, Phys. Rev. B 70, 193305 (2004)
I. Mahboob, K. Nishiguchi, A. Fujiwara, H. Yamaguchi, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 127202 (2013)
I. Mahboob, H. Okamoto, K. Onomitsu, H. Yamaguchi, Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 167203 (2014)
R. Micchi, G.and Avriller, F. Pistolesi, Phys. Rev. Lett. 115 (2015), https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.206802
G. Micchi, R. Avriller, F. Pistolesi, Phys. Rev. B 94, 125417 (2016)
O. Usmani, Y.M. Blanter, Y.V. Nazarov, Phys. Rev. B 75, 195312 (2007)
B. Lassagne, Y. Tarakanov, J. Kinaret, D. Garcia-Sanchez, A. Bachtold, Science 325, 1107 (2009)
Y. Wang, F. Pistolesi, Phys. Rev. B 95, 035410 (2017)
Y. Wang, G. Micchi, F. Pistolesi, J. Phys. Cond. Matter 29, 465304 (2017)
M. Poggio, M.P. Jura, C.L. Degen, M.A. Topinka, H.J. Mamin, D. Goldhaber-Gordon, D. Rugar, Nat. Phys. 4, 635 (2008)
A.A. Clerk, Phys. Rev. B 70, 245306 (2004)
M.P. Blencowe, M.N. Wybourne, Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 3845 (2000)
Y.M. Blanter, M. Büttiker, Phys. Rep. 336, 1 (2000)
J. Brüggemann, G. Weick, F. Pistolesi, F. von Oppen, Phys. Rev. B 85, 125441 (2012)
A.A. Clerk, M.H. Devoret, S.M. Girvin, F. Marquardt, R.J. Schoelkopf, Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 1155 (2010)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Sailing Plan Project of Yibin University (No. 2021QH08). We thank G. Bary and Lin Li for careful read and useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yue Wang contributed to the conception of the study, Futi Liu performed the numerical calculations and wrote the manuscript, Duohui Huang gave the analysis of the results and corrected the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Liu, F. & Huang, D. Electromechanical coupling effect in the detection of nanomechanical motion . Eur. Phys. J. B 94, 107 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-021-00114-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/s10051-021-00114-x