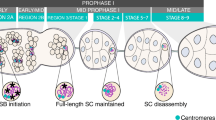
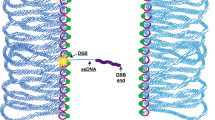
Abstract
Meiosis in Drosophila differs from the canonical type. Males lack synaptonemal complexes, chiasmata, and crossing-over. Only females have these classical traits of meiosis. However, during meiosis prophase I, female Drosophila lack the bouquet-like chromosome arrangement, an accessory mechanism for homologous chromosomes synapsis that is typical for the majority of eukaryotes. Instead, the pericentromeric heterochromatic regions of chromosomes are fused into the chromocenter. This leads to peculiarities in the pairing, synapsis, and segregation of chromosomes and to the so-called interchromosomal phenomena (effects). During late prophase I in females, chromosomes are packed in a karyosome, which is also characteristic of females in other animals with the nutrimental type of egg nutrition. The dissimilarities of meiosis in Drosophila from the classical scheme do not affect significantly its genetic consequences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anuradha, S. and Muniyappa, K., Molecular aspects of meiotic chromosome synapsis and recombination, Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol., 2005, vol. 79, pp. 49–132.
Anderson, L.K., Royer, S.M., Page, S.L., et al., Juxtaposition of C(2)M and the transverse filament protein C(3)G within the central region of Drosophila synaptonemal complex, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2005, vol. 102, pp. 4482–4487.
Arya, G.H., Lodico, M.J.P., Ahmad, O.I., et al., Molecular characterization of teflon, a gene required for meiotic autosome segregation in male Drosophila melanogaster, Genetics, 2006, vol. 174, pp. 125–134.
Baker, B.S. and Hall, J.S., Meiotic mutants: genetic control of meiotic recombination and chromosome segregation, in The Genetics and Biology of Drosophila, Ashburner, M. and Novitski, E.L., Eds., New York: Academic, 1976, vol. 1A, pp. 352–434.
Basheva, E.A., Borodin, P.M., and Bidau, C.J., General pattern of meiotic recombination in male dogs estimated by MLH1 and RAD51 immunolocalization, Chromosome Res., 2008, vol. 16, pp. 709–719.
Bickel, S.E., Wyman, D.W., Miyazaki, W.Y., et al., Identification of ORD, a Drosophila protein essential for sister chromatid cohesion, EMBO J., 1996, vol. 15, pp. 1451–1459.
Bogdanov, Yu.F., Dadashev, S.Ya., and Grishaeva, T.M., Comparative genomics and proteomics of Drosophila, Brenner’s nematode, and Arabidopsis: identification of functionally similar genes and proteins of meiotic chromosome synapsis, Russ. J. Genet., 2002, vol. 38, no. 8, pp. 908–917.
Bogdanov, Yu.F., Grishaeva, T.M., and Dadashev, S.Ya., Similarity of the domain structure of proteins as a basis for the conservation of meiosis, Int. Rev. Cytol., 2007, vol. 257, pp. 83–142.
Bridges, C.B., Sex in relation to chromosomes and genes, Am. Nat., 1925, vol. 59, pp. 127–137.
Bostock, C.J. and Sumner, A.T., The Eukaryotic Chromosome, Amsterdam: North Holland, 1978.
Büning, J., The Insect Ovary: Ultrastructure, Previtellogenic Growth and Evolution, New York: Chapman and Hall, 1994.
Cahoon, C.K. and Hawley, R.S., Flies get a head start on meiosis, PLoS Genet., 2013, vol. 9, p. e1004051.
Carotti, R.D., Marco, A.G., Andolfo, M., and Toti, L., Non-disjunction and heterochromatin in the meiosis of males of Drosophila melanogaster, Atti Accad. Naz. Lincei, Cl. Sci. Fis., Mat. Nat., Rend., 1973, vol. 53, pp. 192–197.
Carpenter, A.T.C., A meiotic mutant defective in distributive disjunction in Drosophila melanogaster, Genetics, 1973, vol. 73, pp. 393–428.
Carpenter, A.T.C., Electron microscopy of meiosis in Drosophila melanogaster females. I. Structure, arrangement and temporal change of the synaptonemal complex in wild type, Chromosoma, 1975a, vol. 51, pp. 157–182.
Carpenter, A.T.C., Electron microscopy of meiosis in Drosophila melanogaster females. II. The recombination nodule—a recombination-associated structure at pachytene?, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1975b, vol. 72, pp. 3186–3189.
Carpenter, A.T.C., Synaptonemal complexes and recombination nodules in wild-type Drosophila melanogaster females, Genetics, 1979, vol. 92, pp. 511–541.
Carpenter, A.T.C., EM autoradiographic evidence that DNA synthesis occurs at recombination nodules during meiosis in Drosophila melanogaster females, Chromosoma, 1981, vol. 83, pp. 59–80.
Carpenter, A.T.C. and Baker, B.S., Genic control of meiosis and some observations on the synaptonemal complex in Drosophila melanogaster, in Mechanisms in Recombination, Grell, R.F., Ed., New York: Springer-Verlag, 1974, pp. 365–375.
Christophorou, N., Rubin, T., and Huynh, J.-R., Synaptonemal complex components centromere pairing in premeiotic germ cells, PLoS Genet., 2013, vol. 9, p. e1004012.
Chua, P.R. and Roeder, G.S., Zip2, a meiosis-specific protein required for the initiation of chromosome synapsis, Cell, 1998, vol. 93, pp. 349–359.
Chubykin, V.L., Structure of chromocenter in oocytes, initiation of homologous pairing and regulation of crossover metabolism in Drosophila, Tsitologiya, 1995, vol. 37, pp. 481–490.
Chubykin, V.L., The role of the chromocenter in nonrandom meiotic segregation of nonhomologous chromosomes in Drosophila melanogaster females, Russ. J. Genet., 2001, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 205–212.
Chubykin, V.L., Chromocentral nature of interchromosome connections coorienting nonhomologous chromosomes in meiosis of Drosophila melanogaster females, Russ. J. Genet., 2009, vol. 45, no. 9, pp. 1027–1039.
Church, K. and Lin, H.-P.P., Kinetochore microtubules and chromosome movement during prometaphase in Drosophila melanogaster spermatocytes studied in life and with the electron microscope, Chromosoma, 1985, vol. 92, pp. 273–282.
Cline, T.W. and Meyer, B.J., Vive la difference: males vs females in flies vs worms, Annu. Rev. Genet., 1996, vol. 30, pp. 637–702.
Collins, K.A., Unruh, J.R., Slaughter, B.D., et al., Corolla is a novel protein that contributes to the architecture of the synaptonemal complex of Drosophila, Genetics, 2014, vol. 198, pp. 219–228.
Cooper, K.W., Meiotic conjunctive elements not involving chiasmata, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1964, vol. 52, pp. 1248–1255.
Cooper, K.W., Zimmering, S., and Krivshenko, J., Interchromosomal effects and segregation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1955, vol. 41, pp. 911–914.
Dävring, L. and Sunner, M., Female meiosis and embryonic mitosis in Drosophila melanogaster. I. Meiosis and fertilization, Hereditas, 1973, vol. 73, pp. 51–64.
Egel, R., Synaptonemal complex and crossing-over: structural support or interference?, Heredity (Edinburgh), 1978, vol. 41, pp. 233–237. FlyBase. https://doi.org/flybase.org/.
Funabiki, H., Hagan, I., Uzawa, S., and Yanagida, M., Cell cycle-dependent specific positioning and clustering of centromeres and telomeres in fission yeast, J. Cell Biol., 1993, vol. 121, pp. 961–976.
Grell, R.F., A new model for secondary nondisjunction: the role of distributive pairing, Genetics, 1962, vol. 47, pp. 1737–1754.
Grishaeva, T.M. and Bogdanov, Yu.F., A search for the Xchromosomal region that controls formation of the synaptonemal complex in Drosophila, Genetika, 1986, vol. 22, pp. 343–345.
Grishaeva, T.M. and Bogdanov, Yu.F., Dependence on genic balance for synaptonemal complex formation in Drosophila melanogaster, Genome, 1988, vol. 30, pp. 258–264.
Grishaeva, T.M. and Bogdanov, Yu.F., Genetic control of meiosis in Drosophila, Russ. J. Genet., 2000, vol. 36, no. 10, pp. 1089–1106.
Grishaeva, T.M. and Bogdanov, Yu.F., Conservation and variability of synaptonemal complex proteins in phylogenesis of eukaryotes, Int. J. Evol. Biol., 2014, vol. 2014, art. ID 856230.
Grishaeva, T.M., Dadashev, S.Ya., and Bogdanov, Yu.F., Gene CG17604 of Drosophila melanogaster predicted in silico may be the c(3)G gene, Drosophila Inf. Serv., 2001, vol. 84, pp. 84–88.
Gruzova, M.N., Some aspects of meiosis in oogenesis, in Tsitologiya i genetika meioza (Cytology and Genetics of Meiosis), Moscow: Nauka, 1975, pp. 113–137.
Gruzova, M.N., Zaichikova, Z.P., and Sokolov, I.I., Functional organization of the nucleus in oogenesis of Chrysopa perla L. (Insecta, Neuroptera), Chromosoma, 1972, vol. 37, pp. 353–386.
Halfer, C. and Barigozzi, C., Prophase synapses in somatic cells of Drosophila melanogaster, Chromosomes Today, 1973, vol. 4, pp. 181–185.
Hawley, R.S., How male flies do meiosis, Curr. Biol., 2002, vol. 12, pp. R660–R662.
Hawley, R.S., Solving a meiotic LEGO puzzle: transverse filaments and the assembly of the synaptonemal complex in Caenorhabditis elegans, Genetics, 2011, vol. 189, pp. 405–409.
Hawley, R.S., Irick, H., Haddox, D.A., et al., There are two mechanisms of achiasmate segregation in Drosophila females, one of which requires heterochromatic homology, Dev. Genet., 1992, vol. 13, pp. 440–467.
Hawley, R.S., McKim, K.S., and Arbel, T., Meiotic segregation in Drosophila melanogaster females: molecules, mechanisms, and myths, Ann. Rev. Genet., 1993, vol. 27, pp. 281–317.
Heidmann, D., Horn, S., Heidmann, S., et al., The Drosophila meiotic kleisin C(2)M functions before the meiotic divisions, Chromosoma, 2004, vol. 113, pp. 177–187.
Heiting, C., Synaptonemal complex: structure and function, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 1996, vol. 8, pp. 389–396.
Hollingsworth, N.M., Ponte, L., and Halsey, C., MSH5, a novel MutS homolog, facilitates meiotic reciprocal recombination between homologes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae but not mismatch repair, Genes Dev., 1995, vol. 9, pp. 1728–1739.
Hunter, N. and Borts, R.H., Mlh1 is unique among mismatch repair proteins in its ability to promote crossingover during meiosis, Genes Dev., 1997, vol. 11, pp. 1573–1582.
Huynh, J.-R. and St Johnston, D., The origin of asymmetry: early polarization of the Drosophila germline cyst and oocyte, Curr. Biol., 2004, vol. 14, pp. R438–R449.
Jang, J.K., Sherizen, D.E., Bhagat, R., Manheim, E.A., et al., Relationship of DNA double-strand breaks to synapses in Drosophila, J. Cell. Sci., 2003, vol. 116, pp. 3069–3077.
Joyce, E.F., Apotolopoulos, N., Beliveau, B.J., and Wu, C.T., Germline progenitors escape the wide-spread phenomenon of homolog pairing during Drosophila development, PLoS Genet., 2013, vol. 9, p. e1004013.
Kaufman, B.P., Somatic mitosis of Drosophila melanogaster, J. Morphol., 1934, vol. 56, pp. 125–156.
Koch, E.A., Smith, P.A., and King, R.C., The division and differentiation of Drosophila cystocytes, J. Morphol., 1967, vol. 121, pp. 55–70.
King, R.C., Ovarian Development in Drosophila melanogaster, New York: Academic, 1970a.
King, R.C., The meiotic behavior of the Drosophila oocyte, Int. Rev. Cytol., 1970b, vol. 28, pp. 125–168.
Lake, C.M. and Hawley, R.S., The molecular control of meiotic chromosomal behavior: events in early meiotic prophase in Drosophila oocytes, Annu. Rev. Physiol., 2012, vol. 74, pp. 425–451.
Lake, C.M., Nielsen, R.J., Guo, F., et al., Vilya, a component of the recombination nodule, is required for meiotic double-strand break formation in Drosophila, eLife, 2015, vol. 4, p. e08287.
Lima-de-Faria, A., Molecular Evolution and Organization of the Chromosome, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1983.
Litvinova, E.M., Reproduction biology of Drosophila, in Problemy genetiki v issledovaniyakh na drozofile (Problems of Genetics Studies of Drosophila), Novosibirsk: Nauka, 1977, pp. 19–61.
Liu, H., Jang, J.K., Kato, N., and McKim, K.S., mei-P22 encodes a chromosome-associated protein required for the initiation of meiotic recombination in Drosophila melanogaster, Genetics, 2002, vol. 162, pp. 245–258.
Lorenz, A., Estereicher, A., Kohli, J., and Loidl, J., Meiotic recombination proteins localize to linear elements in Schizosaccaromyces pombe, Chromosoma, 2006, vol. 115, pp. 330–340.
Lucchesi, J.C., Interchromosomal effects, in The Genetics and Biology of Drosophila, London: Academic, 1976, vol. 1A, pp. 315–329.
Lucchesi, J.C. and Suzuki, D.T., The interchromosomal control of recombination, Ann. Rev. Genet., 1968, vol. 2, pp. 53–86.
Manheim, E.A. and McKim, K.S., The synaptonemal complex component C(2)M regulates meiotic crossing over in Drosophila, Curr. Biol., 2003, vol. 13, pp. 276–285.
McKee, B.D., Habera, I., and Vrana, J.A., Evidence that intergenic spacer repeats of Drosophila melanogaster rRNA genes function as X-Y pairing sites in male meiosis, and a general model for achiasmatic pairing, Genetics, 1992, vol. 132, pp. 529–544.
McKim, K.S., Jang, J.K., and Manheim, E.A., Meiotic recombination and chromosome segregation in Drosophila females, Annu. Rev. Genet., 2002, vol. 36, pp. 205–232.
Meyer, G.F., Hess, O., and Beermann, W., Phasenspezifische Funktionsstrukturen in Spermatocytenkernen von Drosophila melanogaster und Ihre Abhängigkeit vom Y-Chromosom, Chromosoma, 1961, vol. 12, pp. 676–716.
Moens, P.B., Kolas, N., Tarsounas, M., and Spyropoulos, B., Interaction of recombination proteins RAD51/DMC1, RPA and BLM in mouse and rat synaptonemal complex associated recombination nodules, J. Exp. Bot., 2001, vol. 52, suppl., p. 101.
Monakhova, M.A., Centromeric ring in sexual cells of Chorthippus biguttules, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1973, vol. 213, pp. 205–208.
Moore, D.P., Miyazaki, W.Y., Tomkiel, J.E., and Orr-Weaver, T.L., Double or nothing: a Drosophila mutation affecting meiotic chromosome segregation in both females and males, Genetics, 1994, vol. 136, pp. 953–964.
Nokkala, S. and Puro, J., Cytological evidence for a chromocenter in Drosophila melanogaster oocytes, Hereditas, 1976, vol. 83, pp. 265–268.
Novitski, E., Evidence for the single phase pairing theory of meiosis, Genetics, 1975, vol. 79, pp. 63–71.
Novitsky, E. and Puro, J., A critique of theories of meiosis in the female of Drosophila melanogaster, Hereditas, 1978, vol. 89, pp. 51–67.
Oksala, T.A., The effect of autosomal inversion heterozygosity on crossing-over frequency in the X chromosome of D. melanogaster, Drosophila Inf. Serv., 1962, vol. 36, pp. 104–105.
Orr-Weaver, T.L., Meiosis in Drosophila: seeing is believing, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1995, vol. 92, pp. 10443–10449.
Page, S.L. and Hawley, R.S., c(3)G encodes a Drosophila synaptonemal complex protein, Genes Dev., 2001, vol. 15, pp. 3130–3143.
Page, S.L. and Hawley, R.S., Chromosome choreography: the meiotic ballet, Science, 2003, vol. 301, pp. 785–789.
Page, S.L. and Hawley, R.S., The genetics and molecular biology of the synaptonemal complex, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 2004, vol. 20, pp. 525–558.
Page, S.L., Khetani, R.S., Lake, C.M., et al., corona is required for higher-order assembly of transverse filaments into full-length synaptonemal complex in Drosophila oocytes, PLoS Genet., 2008, vol. 4, p. e1000194.
Penkina, M.V., Karpova, O.I., and Bogdanov, Yu.F., Synaptonemal complex proteins are specific proteins of meiotic chromosomes, Mol. Biol. (Moscow), 2002, vol. 36, pp. 397–407.
Prokof’eva-Bel’govskaya, A.A., Geterokhromnye raiony khromosom (Heterochromatic Regions of Chromosomes), Moscow: Nauka, 1986.
Rasmussen, S.W., Ultrastructural studies of spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster Meigen, Z. Zellforsch. Microsk. Anat., 1973, vol. 140, pp. 125–144.
Rasmussen, S.W., Studies on the development of synaptonemal complex in Drosophila melanogaster, C. R. Trav. Lab. Carlsberg, 1974, vol. 39, pp. 443–468.
Rasmussen, S.W. and Holm, P.B., Mechanics of meiosis, Hereditas, 1980, vol. 93, pp. 187–216.
Roeder, G.S., Meiotic chromosomes: it takes two to tango, Genes Dev., 1997, vol. 11, pp. 2600–2621.
Ross-Macdonald, P. and Roeder, G.S., Mutation of a meiosis-specific MutS homolog decreases crossing over but not mismatch correction, Cell, 1994, vol. 79, pp. 1069–1080.
Semenov, E.P. and Smirnov, A.F., Somatic conjugation of chromosomes in Drosophila melanogaster. Part 1. Conjugation of eu- and heterochromatin regions of chromosomes at different stages of the cell cycle, Genetika, 1979, vol. 15, pp. 2156–2167.
Smith, P.A. and King, R.C., Genetic control of synaptonemal complexes in Drosophila melanogaster, Genetics, 1968, vol. 60, pp. 335–351.
Spradling, A., Developmental genetics of oogenesis, in The Development of Drosophila melanogaster, Bate, M. and Martinez-Arias, A., Eds., New York: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press, 1993, vol. 1, pp. 1–70.
Suzuki, D.T., Interchromosomal effect on crossing over in Drosophila melanogaster. II. The reexamination of X chromosome inversion effects, Genetics, 1963, vol. 48, pp. 1605–1617.
Takeo, S., Swanson, S.K., Nandanan, K., et al., Shaggy/glycogen synthase kinase 3β and phosphorylation of Sarah/regulator of calcineurin are essential for completion of Drosophila female meiosis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2012, vol. 109, pp. 6382–6389.
Tanneti, N.S., Landy, K., Joyce, E.F., and McKim, K.S., A pathway for synapsis initiation during zygotene in Drosophila oocytes, Curr. Biol., 2011, vol. 21, pp. 1852–1857.
Vazquez, J., Belmont, A.S., and Sedat, J.W., The dynamics of homologous chromosome pairing during male Drosophila meiosis, Curr. Biol., 2002, vol. 12, pp. 1473–1483.
Yamomoto, M., Interchromosomal effects of heterochromatic deletions on recombination in Drosophila melanogaster, Genetics, 1979, vol. 93, pp. 437–448.
Zickler, D. and Kleckner, N., Meiotic chromosomes: integrating structure and function, Ann. Rev. Genet., 1999, vol. 33, pp. 603–754.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © T.M. Grishaeva, Yu.F. Bogdanov, 2018, published in Uspekhi Sovremennoi Biologii, 2018, Vol. 138, No. 1, pp. 68–82.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grishaeva, T.M., Bogdanov, Y.F. Peculiarities of Meiosis in Drosophila: A Classical Object of Genetics Has Nonstandard Meiosis. Biol Bull Rev 8, 279–291 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079086418040047
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079086418040047