Abstract
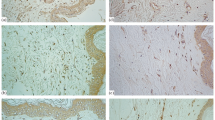
The goal of this research was to study the content of lamin B receptors in human dermal fibroblasts during different age periods (from a 20-week pregnancy to the age of 85) in correlation with their proliferative activity. Lamin B receptors and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) were identified in skin sections by indirect immunohistochemistry. Our results have shown that an increase in the share of fibroblasts with positive staining for the lamin B receptors and an increase in the expression level of lamin B receptors in fibroblast nuclei are observed during the period from age zero to 20 years of age as compared with other age periods. The total fibroblast count, including positively PCNA-stained dermal fibroblasts, decreased most significantly from the age of 20. The increase in the content of lamin B receptors in dermal fibroblasts, which is observed from birth until the age of 20, can be considered one of the triggering moments leading to the agedependent decrease in counts of human dermal fibroblasts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Golubtsova, N.N., Filippov, F.N., and Gunin, A.G., Lamin B1 and lamin B2 in human skin in the process of aging, Adv. Gerontol., 2016, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 275–281.
Golubtsova, N.N., Filippov, F.N., and Gunin, A.G., Lamin A and lamin-associated polypeptide 2 (LAP-2) in human skin fibroblasts in the process of aging, Adv. Gerontol., 2017, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 60–67.
Arai, R., En, A., Ukekawa, R., et al., Aberrant localization of lamin B receptor (LBR) in cellular senescence in human cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2016, vol. 473, no. 4, pp. 1078–1083.
Barton, L.J., Soshnev, A.A., and Geyer, P.K., Networking in the nucleus: a spotlight on LEM-domain proteins, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 2015, vol. 34, pp. 1–8.
Butin-Israeli, V., Adam, S.A., Jain, N., et al., Role of lamin B1 in chromatin instability, Mol. Cell Biol., 2015, vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 884–898.
Freund, A., Laberge, R.M., Demaria, M., et al., Lamin B1 loss is a senescence-associated biomarker, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2012, vol. 23, pp. 2066–2075.
Gunin, A.G., Kornilova, N.K., Vasilieva, O.V., and Petrov, V.V., Age-related changes in proliferation, the numbers of mast cells, eosinophils, CD45 positive cells in human dermis, J. Gerontol., Ser. A., 2011, vol. 66, no. 4, pp. 385–392.
Gunin, A.G., Petrov, V.V., Golubtzova, N.N., et al., Age-related changes in angiogenesis in human dermis, Exp. Gerontol., 2014, vol. 55, pp. 143–151.
Hirano, Y., Hizume, K., Kimura, H., et al., Lamin B receptor recognizes specific modifications of histone H4 in heterochromatin formation, J. Biol. Chem., 2012, vol. 287, no. 51, pp. 42654–42663.
Lukasova, E., Kovarík, A., Bacíková, A., et al., Loss of lamin B receptor is necessary to induce cellular senescence, Biochem. J., 2017, vol. 474, no. 2, pp. 281–300.
Olins, A.L., Rhodes, G., Welch, D.B., et al., Lamin B receptor: multi-tasking at the nuclear envelope, Nucleus, 2010, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 53–70.
Sola Carvajal, A., McKenna, T., Wallen Arzt, E., et al., Overexpression of lamin B receptor results in impaired skin differentiation, PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10, no. 6, p. e0128917.
Solovei, I., Wang, A.S., Thanisch, K., et al., LBR and lamin A/C sequentially tether peripheral heterochromatin and inversely regulate differentiation, Cell, 2013, vol. 152, no. 3, pp. 584–598.
Tseng, L.C. and Chen, R.H., Temporal control of nuclear envelope assembly by phosphorylation of lamin B receptor, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2011, vol. 22, no. 18, pp. 3306–3317.
Tu, J.B., Ma, R.Z., Dong, Q., et al., Induction of apoptosis in infantile hemangioma endothelial cells by propranolol, Exp. Ther. Med., 2013, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 574–578.
Xie, W. and Burke, B., Lamins, Curr. Biol., 2016, vol. 26, no. 9, pp. R348–R350.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golubtsova, N.N., Filippov, F.N. & Gunin, A.G. Age-Related Changes in the Expression of Lamin B Receptors in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Adv Gerontol 7, 296–301 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079057017040051
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079057017040051