Abstract
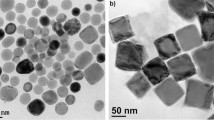
Synthesis of the single-phase γ′-Fe4N on the surface of the micron-sized particles of iron at low-temperature gaseous nitriding of carbonyl iron powder in a stream of ammonia is studied. It is shown that synthesis of particles with such structure is possible with simultaneous control of the number of process parameters: temperature, degree of dissociation of ammonia, and treatment time. It is found that, at temperature T = 400°C and nitriding potential of the atmosphere r N ≈ 1.3 atm−1/2, the shells with a thickness of about 1 μm are formed on the particles within ~15–20 min and the powder consists of the γ-Fe4N phase within ~60 min of treatment. The mechanisms of formation of microparticles with a core–shell structure are considered. A qualitative model for the thermochemical treatment of the micron iron powder with consideration of the diffusion processes of the transport of ammonia molecules in the pore space of the powder and atomic nitrogen diffusion inside the particles is developed. Geometric and dimensional effects at nitriding of iron powders are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
02 August 2016
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113316040389
References
Chaudhuri, R.G. and Paria, S., Core/shell nanoparticles: Classes, properties, synthesis mechanisms, characterization, and applications, Chem. Rev., 2011, vol. 112, pp. 2373–2433.
Bychkova, A.V., Sorokina, O.N., Rosenfeld, M.A., and Kovarski, A.L., Multifunctional biocompatible coatings on magnetic nanoparticles, Russ. Chem. Rev., 2012, vol. 81, no. 11, pp. 1026–1050.
Gervald, A.Yu., Gritskova, I.A., and Prokopov, N.I., Synthesis of magnetic polymeric microspheres, Russ. Chem. Rev., 2010, vol. 79, no. 3, pp. 219–229.
Bhattacharyya, S., Iron nitride family at reduced dimensions: A review of their synthesis protocols and structural and magnetic properties, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, vol. 119, pp. 1601–1622.
Kita, E., Shibata, K., Yanagihara, H., Sasaki, Y., and Kishimoto, M., Magnetic properties of core-shell type Fe16N2 nanoparticles, J. Magnetism Magn. Mater., 2007, vol. 310, pp. 2411–2413.
Yamashita, S., Masubuchi, Y., Nakazawa, Y., Okayama, T., Tsuchiya, M., and Kikkawa, S., Crystal structure and magnetic properties of “α″3-Fe16N2” containing residual α-Fe prepared by low-temperature ammonia nitridation, J. Solid State Chem., 2012, vol. 194, pp. 76–79.
Cao, M., Wang, R., Fang, X., Cui, Z., Chang, T., and Yang, H., Preparing γ′-Fe4N ultrafine powder by twice-nitriding method, Powder Technol., 2001, vol. 115, pp. 96–98.
Huang, W., Wu, J., Guo, W., Li, R., and Cui, L., Preparation and magnetic properties of nanoscale ε-Fe3N particles, J. Alloys Compd., 2007, vol. 443, pp. 48–52.
Yamaguchi, T., Sakita, M., Nakamura, M., and Kobira, T., Synthesis and characteristics of Fe4N powders and thin films, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2000, vol. 215, pp. 529–531.
Luo, X. and Liu, S., Preparation and chemical stability of iron-nitride-coated iron microparticles, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2007, vol. 308, pp. L1–L4.
Kovalev, E.P., Alymov, M.I., Ankudinov, A.B., Gnedovets, A.G., and Zelenskii, V.A., Low-temperature synthesis of micron nitride powders of the Fe–N system, Inorg. Mater.: Appl. Res., 2014, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 168–172.
Wang, T.C. and Kimura, S., Fluidized-bed nitridation of stainless steel powder, Mater. Manufact. Proc., 1997, vol. 12, pp. 275–290.
Belyanchikov, L.N., New high-nitrogen corrosionresistant tool and high-speed steels, Russ. Metall. (Metally), 2008, no. 8, pp. 761–765.
Antsiferov, V.N., Gorbachyov, I.I., Oglezneva, S.A., and Popov, V.V., Structure-phase composition and properties of mechanically alloyed high-nitrogen powder steels, Russ. J. Non-Ferrous Metals, 2012, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 321–329.
Lakhtin, Yu.M. and Kogan, Ya.D., Azotirovanie stali (Nitriding of Steel), Moscow: Mashinostroenie, 1976.
Mittemeijer, E.J. and Somers, M.A., Thermochemical Surface Engineering of Steels: Improving Materials Performance, Elsevier, 2014.
Minagawa, M., Yanagihara, H., Kishimoto, M., and Kita, E., Synthesis of ε-FexN (2 ≤ x ≤ 3) submicron particles and the diffusion mechanism of nitrogen atoms, Mater. Trans., 2010, vol. 51, pp. 2173–2176.
Qiu, Y. and Gao, L., Nitridation reaction of aluminum powder in flowing ammonia, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2003, vol. 23, pp. 2015–2022.
Pelka, R., Kielbasa, K., and Arabczyk, W., Catalytic ammonia decomposition during nanocrystalline iron nitriding at 475°C with NH3/H2 mixtures of different nitriding potentials, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, vol. 118, pp. 6178–6185.
Moszynski, D., Nitriding of nanocrystalline iron in the atmospheres with variable nitriding potential, J. Phys. Chem., 2014, vol. 118, pp. 15440–15447.
Bannykh, O.A., Zinchenko, V.M., Prusakov, B.A., and Syropyatov, V.Y., Development of nitriding in Russia. Fourth period (1980–Present Time): New directions in the development of LTCTT, Metal Sci. Heat Treat., 2001, vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 131–137.
Mittemeijer, E.J. and Somers, M.A., Thermodynamics, kinetics, and process control of nitriding, Surf. Eng., 1997, vol. 13, pp. 483–497.
Hirschfelder, J.O., Curtiss, C.F., and Bird, R.B., Molecular Theory of Gases and Liquids, New York: Wiley, 1954.
Cunningham, R.E. and Williams, R.J.J., Diffusion in Gases and Porous Media, New York: Springer Sci., 1980.
Somers, M.A. and Mittemeijer, E.J., Layer-growth kinetics on gaseous nitriding of pure iron: Evaluation of diffusion coefficients for nitrogen in iron nitrides, Metallur. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26, pp. 57–74.
Belmonte, T., Gouné, M., and Michel, H., Numerical modeling of interstitial diffusion in binary systems. Application to iron nitriding, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, vol. 302, pp. 246–257.
Levenspiel, O., Chemical Reaction Engineering, New York: Wiley, 1999.
Geguzin, Ya.E., Diffuzionnaya zona (The Diffusion Zone), Moscow: Nauka, 1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.G. Gnedovets, A.B. Ankudinov, V.A. Zelenskii, E.P. Kovalev, H. Wisniewska-Weinert, M.I. Alymov, 2015, published in Perspektivnye Materialy, 2015, No. 12, pp. 62–71.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gnedovets, A.G., Ankudinov, A.B., Zelenskii, V.A. et al. Synthesis of micron particles with Fe–Fe4N core–shell structure at low-temperature gaseous nitriding of iron powder in a stream of ammonia. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 7, 303–309 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113316020106
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113316020106