Abstract
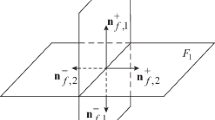
A physicomathematical model of a two-phase liquid flow in a discrete fracture network—taking into account a nonuniform fracture aperture, flow exchange between fractures, capillary and gravitational forces—is presented. Capillary forces are described by the Young-Laplace model that takes into account the rock wetting angle and surface tension. The influence of the structure of the conducting channels in a fracture, capillary and gravitational forces, and the pressure gradient, as well as the water-and-oil viscosity ratio on the flow dynamics and the oil recovery factor, is explored. It is shown that capillary forces and the structure of channels in a fracture can play a decisive role in the process of oil displacement by water.

















Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
F. M. Verga et al., “Calibration of fractured reservoirs with dynamic data,” in Proceedings of the SPE Reservoir Simulation Symposium (Soc. Pet. Eng., 2001).
A. V. Blonskii, D. A. Mitrushkin, and E. B. Savenkov, “Discrete fracture network modelling: physical and mathematical model,” KIAM Preprint No. 65 (Keldysh Inst. Appl. Math., Moscow, 2017). https://doi.org/10.20948/prepr-2017-65
N. Koudina et al., “Permeability of three-dimensional fracture networks,” Phys. Rev. E 57, 4466 (1998).
A. V. Blonskii, D. A. Mitrushkin, and E. B. Savenkov, “Discrete fracture network modelling: a computational algorithms,” KIAM Preprint No. 66 (Keldysh Inst. Appl. Math., Moscow, 2017). https://doi.org/10.20948/prepr-2017-66
Kh. Aziz and A. Settari, Petroleum Reservoir Simulation (Applied Science, London, 1979).
F. Qasem et al., “Role of capillary imbibition in partially fractured reservoirs,” in Proceedings of the Canadian International Petroleum Conference (Pet. Soc. Canada, 2006).
M. R. Carlson, Practical Reservoir Simulation: Using, Assessing, and Developing Results (Penn Well, Tulsa, Okla, 2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by L. Mukhortova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blonsky, A.V., Mitrushkin, D.A. Research on the Influence of Capillary Forces on a Liquid Flow in Fractures with Nonuniform Apertures. Math Models Comput Simul 11, 374–385 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070048219030086
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070048219030086