Abstract
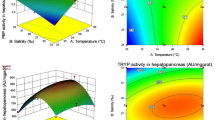
The in vitro effect of Roundup herbicide at a concentration of 25 μg/L on the activity and temperature characteristics (temperature dependence, activation energy Eact, and Q10 temperature coefficient) of maltase in the intestinal mucosa of the juvenile sander, perch, roach, and common carp has been studied. The magnitude and direction of the effect depends on the fish species and the incubation temperature. Roundup does not affect the temperature optimum for maltase (60°C for perch and sander; 50°C for roach and carp). The lower relative activity of the enzyme in the temperature range of 0–30°C indicates a decrease in the efficiency of maltose hydrolysis, while lower Eact values indicate adaptive changes in this parameter in the presence of Roundup.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Brezhnev, V.I., Mechanical method of weed control on open drainage canals with the herbicide Roundup, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Eng.) Dissertation, Novocherkassk, 2004.
Golovanova, I.L. and Aminov, A.I., Influence of the herbicide Roundup on the activity of glycosidases in juvenile fishes and their food items at various temperatures and pH, Vestn. Astrakhan. Gos. Tekh. Univ., Ser. Rybn. Khoz., 2013, no. 1, pp. 129–134.
Golovanova, I.L. and Golovanov, V.K., Digestive glucosidases of fishes under conditions of increased ambient temperature (review), Tr. Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2015, no. 72 (75), pp. 52–59.
Golovanova, I.L. and Filippov, A.A., Characteristics of intestinal glycosidases of bream Abramis brama (L.) from Rybinsk Reservoir regions with different anthropogenic pressure, Tr. Karel. Nauchn. Tsentra Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2012, no. 2, pp. 63–69.
Zhidenko, A.A., Mishchenko, T.V., and Krivopisha, V.V., Response of cyprinid fishes to glyphosate, Nauk. Zap. Ternop. Nats. Pedagog. Univ., Ser. Biol., 2015, vol. 64, no. 3–4, pp. 227–230.
Kuz’mina, V.V., Fiziologo-biokhimicheskie osnovy ekzotrofii ryb (Physiological and Biochemical Basics of Fish Exotrophy), Moscow: Nauka, 2005.
Ponomarev, V.I., Characteristics of digestive processes in fishes of the European North, Extended Abstract of Cand. Sci. (Biol.) Dissertation, Syktyvkar, 1993.
Ugolev, A.M. and Kuz’mina, V.V., Pishchevaritel’nye protsessy i adaptatsii u ryb (Digestive Processes and Adaptations in Fishes), St. Petersburg: Gidrometeoizdat, 1993.
Aparicio, V.C., De Geronimo, E., Marino, D., et al., Environmental fate of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters and soil of agricultural basins, Chemosphere, 2013, vol. 93, no. 9, pp. 1866–1873.
Benbrook, C.M., Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally, Environ. Sci. Eur., 2016, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 1–15.
Cattaneo, R., Clasen, B., Loro, V.L., et al., Toxicological responses of Cyprinus carpio exposed to a commercial formulation containing glyphosate, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2011, vol. 87, no. 6, pp. 597–602.
Fan, J.Y., Geng, J.J., Ren, H.Q., et al., Herbicide roundup and its constituents cause oxidative stress and inhibit acetylcholinesterase in liver of Carassius auratus, J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B, 2013, vol. 48, pp. 844–850.
Filho, J.D.S., Sousa, C.C.N., Da, SilvaC.C., et al., Mutagenicity and genotoxicity in gill erythrocyte cells of Poecilia reticulata exposed to a glyphosate formulation, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2013, vol. 91, pp. 583–587.
Gasiner, C., Dumont, C., Benachour, N., et al., Glyphosate-based herbicides are toxic and endocrine disruptors in human cell lines, Toxicology, 2009, vol. 262, pp. 184–191.
Gelman, A.G., Kuz’mina, V.V., Drabkin, V., and Gladman, M., Temperature adaptations of fish digestive enzymes, in Feeding and Digestive Functions in Fishes, Enfield (NF), Jersey: Sci. Publ., 2008, pp. 155–226.
Giesy, J.P., Dobson, S., and Solomon, K.R., Ecotoxicological risk assessment for roundup herbicide, Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2000, vol. 167, pp. 35–120.
Kier, L.D. and Kirkland, D.J., Review of genotoxicity studies of glyphosate and glyphosate-based formulations, Crit. Rev. Toxicol., 2013, vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 283–315.
Kuz’mina, V.V., Digestion in fish. A new view. Balty: LAP Lambert Acad. Publ., 2017, p. 310.
Le Mer, C., Roy, R.L., Pellerin, J., et al., Effects of chronic exposures to the herbicides atrazine and glyphosate to larvae of the three-spine stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus), Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2013, vol. 89, pp. 174–181.
Lushchak, O.V., Kubrak, O.I., Storey, J.M., et al., Low toxic herbicide roundup induces mild oxidative stress in gold fish tissues, Chemosphere, 2009, vol. 52, no. 7, pp. 932–937.
Struger, J., Thompson, D., Staznik, B., et al., Occurrence of glyphosate in surface waters of southern Ontario, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2008, vol. 80, pp. 378–384.
Tsui, M.T.K. and Chu, L.M., Environmental fate and non-target impact of glyphosate-based herbicide (roundup) in a subtropical wetland, Chemosphere, 2008, vol. 71, pp. 439–446.
Vera, M.S., Fiori, E.D., Lagomarsino, L., et al., Direct and indirect effects of the glyphosate formulation glifosato atanor on freshwater microbial communities, Ecotoxicology, 2012, vol. 21, no. 7, pp. 1805–1816.
Webster, T.M.U. and Santos, E.M., Global transcriptomic profiling demonstrates induction of oxidative stress and of compensatory cellular stress responses in brown trout exposed to glyphosate and roundup, BMC Genomics, 2015, vol. 16, no. 32, pp. 1–14.
Williams, G.M., Kroes, R., and Munro, I.C., Safety evaluation and risk assessment of herbicide roundup and its active ingredient, glyphosate, for humans, Reg. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2000, vol. 31, pp. 117–165.
World Health Organization (WHO), Environmental health criteria 159—Glyphosate, International Programme on Chemical Safety, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by D. Pavlov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Filippov, A.A., Golovanova, I.L. & Smirnov, M.S. Effect of Roundup Herbicide on the Temperature Characteristics of Maltase of the Intestinal Mucosa in Juvenile Fish. Inland Water Biol 12, 248–253 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082919020056
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082919020056