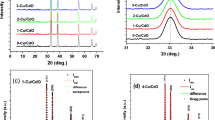
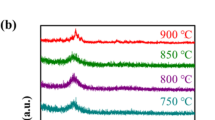
Abstract—Scanning electron and atomic force microscopy, X-ray diffraction, X-ray spectral microanalysis, and diffraction of reflected electrons were used to study changes in the structure, elemental, and phase composition of fullerite–copper films with an atomic metal fraction of 0.5, 1, 2 and 4%, deposited on oxidized single-crystal silicon substrates and subjected to thermal exposure in vacuum at different temperatures (470, 520, 570 and 620 K). It was found that thermal annealing at T = 520 K (t = 1 h) leads to the formation of a nanocrystalline structure with an average structural elements size of 33, 42, 50, and 65 nm for fullerite–copper films with an atomic fraction of metal of 0.5, 1, 2, and 4% respectively. An increase in temperature and annealing time leads to an increase in the size of structural elements and the formation of a new of CuxC60 phase, which belongs to the monoclinic space group P2/m. Electric force microscopy and the four-probe method were used to study changes in the local electrical properties and electrical resistivity of copper-containing fullerite films during vacuum annealing.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
P. M. Allem, K. C. Khemani, A. Koch, et al., Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 253, 301 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.253.5017.301
H. E. Okur and K. Prassides, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 131, 44 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jPcs.2019.03.017
R. A. Lunin, Y. A. Velikodny, B. M. Bulychev, and V. A. Kulbachinskii, Polyhedron 102, 664 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.Poly.2015.10.044
C. L. Liu, Q. H. Gong, Y. X. Chen, et al., Chin. Phys. Lett. 18, 1078 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/18/8/326
M. M. Mestechkin and G. E. Whyman, J. Struct. Chem. 38, 941 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02763814
E. A. Katz, D. Faiman, S. Shtutina, et al., Phys. B (Amsterdam, Neth.) 304, 348 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-4526(01)00544-0
Xiang Li, Y. J. Tang, H. W. Zhao, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 984 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1287910
B. M. Bulychev, R. A. Lunin, A. V. Krechetov, et al., J. Phys. Chem. Solids 65, 337 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jPcs.2003.10.064
B. P. Popov, Semiconductors 39, 455 (2005).
A. Tamai, W. Auwärter, C. Cepek, et al., Surf. Sci. 566, 633 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2004.06.127
R. PoPescu, D. Macovei, A. Devenyi, et al., Eur. Phys. J. B, No. 13, 737 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050093
P. Janda, K. Kojucharow, and L. Dunsch, Surf. Sci. 597, 26 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2004.06.217
A. K. Gatin, M. V. Grishin, N. V. Dokhlikova, S. A. Ozerin, S. Yu. Sarvadii, and B. R. Shub, Nanotechnol. Russ. 13, 453 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078018050063
T. I. Shabatina, O. I. Vernaya, A. V. Nuzhdina, N. D. Zvukova, V. P. Shabatin, A. M. Semenov, V. I. Lozinskii, and M. Ya. Mel’nikov, Nanotechnol. Russ. 13, 182 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078018020106
V. K. Leont’ev, I. P. Pogorel’skii, G. A. Frolov, Ya. N. Karasenkov, A. A. Gusev, N. V. Latuta, L. L. Borozdkin, and D. S. Stefantsova, Nanotechnol. Russ. 13, 195 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078018020040
V. F. Masterov, A. V. Prikhod’ko, O. I. Kon’kov, M. V. Shakhrai, A. A. Shaklanov, Tech. Phys. Lett. 25, 326 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1134/1.1262468
O. I. Kon’kov, Semiconductors 36, 1204 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1134/1.1521216
E. M. Shpilevskii, L. V. Baran, and G. P. Okatova, Perspekt. Mater., No. 3, 56 (2003).
L. V. Baran, E. M. Shpilevskii, and V. A. Ukhov, Vakuum. Tekh. Tekhnol. 14 (1), 47 (2004).
E. M. Shpilevskii and L. V. Baran, “Structural and phase changes in copper - fullerene films during ion implantation and thermal annealing,” Preprint No. 5 (Lykov Inst. Thermal Mass Exchange Natl. Acad. Sci. Belarus’, Minsk, 2004).
L. V. Baran and S. V. Gusakova, Poverkhnost’, No. 12, 49 (2006).
L. V. Baran, Nanostrukt. Materialoved., No. 1, 50 (2011).
V. N. Ivanova, J. Struct. Chem. 41, 135 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02684739
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The author is grateful to S.V. Zlotsky for the XRD patterns of the studied films.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baran, L.V. MODIFICATION OF THE STRUCTURAL-PHASE STATE AND ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF COPPER-CONTAINING FULLERITE FILMS DURING THERMAL ANNEALING IN VACUUM. Nanotechnol Russia 14, 325–333 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078019040037
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078019040037