Abstract
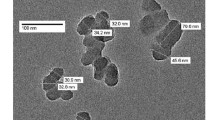
Aqueous solutions of the fullerene C60 (nC60) were prepared by simple mixing of the solution of C60 in N-methylpyrrolidone (MP) with deionized water or an aqueous solution of a low-molecular-weight natural substance (L-amino acids, monosaccharides, peptides, or glycerol) used as stabilizing agents (SAs) followed by exhaustive dialysis against distilled water. During dialysis, all low-molecular-weight compounds are removed through the pores and the fullerene clusters remain in the solution. The efficiency of conversion of C60 from the crystalline state to the solution approaches the quantitative value, and solutions with a C60 concentration of up to 250 mg/L can be obtained; moreover, these solutions are stable for at least 10–12 months. The formation of insoluble aggregates has been observed when basic and acidic organic compounds were used as SA. The UV-VIS spectra of solutions have a profile characteristic of nC60 solutions obtained by other well-known procedures (maxima at 220, 265, 340, and 450 nm). Mass spectra of aqueous solutions and FTIR spectra of dried nC60 samples were indicative of the possible partial hydroxylation of the fullerene. A measurement of the sizes and ξ potential of the C60 particles in solutions by the dynamic light scattering method showed that their average diameter is about 100 nm and the charge is −30 mV, whereas the electron microscopy data demonstrated that the particles have a typical size of approximately 20 nm and contain both crystalline and amorphous phases. The proposed method is promising for the preparation of solutions of endofullerenes and, probably, higher fullerenes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Kratschmer, L. D. Lamb, K. Fostiropoulos, and D. R. Hoffman, “Solid C60: a new form of carbon,” Nature, No. 347, 354–356 (1990).
A. Bianko, T. Da Ros, M. Prato, and C. Toniolo, “Fullerene-based amino acid and peptides,” J. Pep. Sci. 4(7), 208–219 (2001).
S. Bosi, T. Da Ros, G. Spalluto, and M. Prato, “Fullerene derivatives: an attractive tool for biological applications,” Eur. J. Med. Chem., No. 38, 913–923 (2003).
D. Pantarotto, J. P. Briand, M. Prato, and A. Bianco, “Translocation of bioactive peptides across cell membranes by carbon nanotubes,” Chem. Commun., No. 1, 6–17 (2004).
L. B. Piotrovskii and O. I. Kiselev, Fullerens in Biology (Rostok, St. Petersburg, 2006) [in Russian].
J. L. Gilmore, X. Yi, L. Quan, and A. V. Kabanov, “Novel nanomaterials for clinical neuroscience,” J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2(3), 83–94 (2008).
I. Andreev, A. Petrukhina, A. Garmanova, S. Andreev, V. Romanova, P. Troshin, O. Troshina, and L. DuBuske, “Penetration of fullerene C60 derivatives through biological membranes,” Fullerenes, Nanotubes, Carbon Nanostruct., No. 16, 89–102 (2008).
A. Dellinger, Z. Zhou, R. Lenk, D. MacFarland, D. Conrad, and C. L. Kepley, “Fullerene nanomaterials inhibit phorbol myristate acetate-induced inflammation,” Exp. Derm. 18(12), 1079–1081 (2009).
M. Satoh, K. Matsuo, H. Kiriya, et al., “Inhibitory effect of a fullerene derivative, monomalonic acid C60, on nitric oxide-dependent relaxation of aortic smooth muscle,” Gen. Pharmacol. 29(3), 345–351 (1997).
M. Roursgaard, S. S. Poulsen, C. L. Kepley, M. Hammer, G. D. Nielsen, and S. T. Larsen, “Polyhydroxylated C60 fullerene attenuates neutrophilic lung inflammation in mice,” Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol., No. 103(4), 386–388 (2008).
T. Baati, F. Bourasset, N. Gharbi, L. Njim, M. Abderrabba, A. Kerkeni, H. Szwarc, and F. Moussa, “The prolongation of the lifespan of rats by repeated oral administration of 60. fullerene,” Biomaterials, No. 33, 4936–4946 (2012).
N. G. Vengerovich, M. A. Tyunin, E. V. Antonenkova, Yu. O. Kon’shakov, A. V. Bolekhan, O. B. Zaitseva, A. N. Stukov, M. N. Boyarkin, and V. A. Popov, “Biological activity of fullerene 60 nanobiocomposites,” Immunologiya, No. 12, 161–177 (2012).
N. Gharbi, M. Pressac, M. Hadchouel, H. Szwarc, S. R. Wilson, and F. Moussa, “60. Fullerene is a powerful antioxidant in vivo with no acute or subacute toxicity,” Nano Lett., No. 5(12), 2578–2585 (2005).
N. O. Mchedlov-Petrosyan, “S60 fullerene solution: colloid aspect,” Khim., Fiz. Tekhnol. Poverkhn. 1(1), 19–37 (2010).
N. O. Mchedlov-Petrossyan, “Fullerenes in liquid media: an unsettling intrusion into the solution chemistry,” Chem. Rev. 113, 5149–5193 (2013). DOI: 10.1021/cr3005026.
R. S. Ruoff, D. S. Tse, R. Malhotra, and D. C. Lorents, “Solubility of fullerene (C60) in a variety of solvents,” J. Phys. Chem. 97, 3379–3383 (1993).
V. N. Bezmel’nitsyn, A. V. Eletskii, and M. V. Okun’, “Fullerens in solutions,” Usp. Fiz. Nauk, No. 168, 1195–1120 (1998).
Sh. Deguchi and S. A. Mukai, “Top-down preparation of dispersions of C60 nanoparticles in organic solvents,” Chem. Lett. No. 35(4), 396–397 (2006).
G. V. Andrievsky, M. V. Kosevich, O. M. Vovk, V. S. Shelkovsky, L. A. Vashcenko, “On the production of an aqueous colloidal solution of fullerenes,” J. Chem. Soc., No. 12, 1281–1282 (1995).
D. V. Konarev and R. N. Lyubovskaya, “Donor-acceptor complexes and radical ionic salts based on fullerenes,” Russ. Chem. Rev., No. 68(1), 19–38 (1999).
V. M. Torresa, M. Posac, B. Srdjenovicc, and A. L. Simplicioa, “Solubilization of fullerene C60 in micellar solutions of different solubilizers,” Colloids Surf. B: Biointerf., No. 82, 46–53 (2011).
B. S. Murdianti, J. T. Damron, M. E. Hilburn, R. D. Maples, H. R. S. Koralege, S. I. Kuriyavar, and K. D. Ausman, “C60 oxide as key component of aqueous C60 colloidal suspensions,” Environ. Sci. Technol., No. 46, 7446–7453 (2012).
T. Andersson, K. Nilsson, M. Sundahl, G. Westman, and O. Wennerström, “C60 embedded in γ-cyclodextrin: a water-soluble fullerene,” J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., No. 8, 604–605 (1992).
M. V. Avdeev, V. L. Aksenov, and T. V. Tropin, Models of cluster formation in solutions of fullerenes. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A, No. 84, D. 1273–1283 (2010).
D. V. Konarev, A. L. Litvinov, A. Yu. Kovaltvsky, N. V. Drichko, R. N. Coppens, and R. N. Lubovskaya, “Molecular complexes of fullerene C60 with aromatic hydrocarbons: crystal structures of (TPE)2C60 and DPA·C60,” Synth. Met., Nos. 133–134, 675–677 (2003).
M. K. Shukla and J. Leszczynski, “Fullerene (C60) forms stable complex with nucleic acid base guanine,” Chem. Phys. Lett., No. 469, 207–209 (2009).
E. Oberdörster, S. Zhu, T. M. Blickley, P. McClellan-Green, and M. L. Haasch, “Ecotoxicology of carbon-based engineered nanoparticles: effects of fullerene (C60) on aquatic organisms,” Carbon, No. 44, 1112–1120 (2006).
R. V. Bemasson, E. Bienvenue, M. Dellinger, S. Leach, and P. Setat, “C60 in model biological systems. A visible-UV absorption study of solvent-dependent parameters and solute aggregation,” J. Phys. Chem., No. 98, 3492–3500 (1994).
N-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone. Concise International Chemical Assessment Document No. 35 (World Health Organization, 2001).
K. N. Semenov, N. A. Charykov, V. A. Keskinov, A. K. Piartman, A. A. Blokhin, and A. A. Kopyrin, “Solubility of light fullerenes in organic solvents,” J. Chem. Eng. Data, No. 55, 13–36 (2010).
A. De Leon, A. F. Jalbout, and V. A. Basiuk, “Fullerene-amino acid interactions. A theoretical study,” Chem. Phys. Lett., No. 452, 306–314 (2008).
N. O. Mchedlov-Petrossyan, “Fullerenes in molecular liquids. Solutions in “good” solvents: another view,” J. Mol. Liquids, No. 161, 1–12 (2011).
K. L. Chen, B. A. Smith, P. B. William, and D. H. Fairbrother, “Assessing the colloidal properties of engineered nanoparticles in water: case studies from fullerene C60 nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes,” Environ. Chem., No. 7, 10–27 (2010).
G. V. Andrievsky, V. K. Klochkov, E. L. Karyakina, and N. O. Mchedlov-Petrossyan, “Studies of aqueous colloidal solutions of fullerene C60 by electron microscopy,” Chem. Phys. Lett., No. 300, 392–396 (1999).
L. Pospíšl, M. Gál, M. Hromadová, J. Bulíćková, V. Kolivoška, J. Cvaćka, K. Nováková, L. Kavan, M. Zukalová, and L. Dunsch, “Search for the form of fullerene C(60) in aqueous medium,” Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 42(12), 14095–14101 (2010).
K. L. Chen and M. Elimelech, “Relating colloidal stability of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles to nanoparticle charge and electrokinetic properties,” Environ. Sci. Technol., No. 43, 7270–7276 (2009).
J. Labille, A. Masion, F. Ziarelli, J. Rose, J. Brant, F. Villieras, M. Pelletier, D. Borschneck, M. R. Wiesner, and J. Y. Bottero, “Hydration and dispersion of C60 in aqueous systems: the nature of water-fullerene interactions,” Langmuir 19(25), 11232–11235 (2009).
International Centre for Diffraction Data JCPDS card #44-0558.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.M. Andreev, D.D. Purgina, E.N. Bashkatova, A.V. Garshev, A.V. Maerle, M.R. Khaitov, 2014, published in Rossiiskie Nanotekhnologii, 2014, Vol. 9, Nos. 7–8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andreev, S.M., Purgina, D.D., Bashkatova, E.N. et al. Facile preparation of aqueous fullerene C60 nanodispersions. Nanotechnol Russia 9, 369–379 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S199507801404003X
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S199507801404003X