Abstract
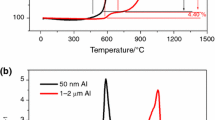
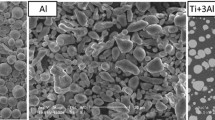
The thermal reaction characterization of micron-sized aluminium powder in carbon dioxide were investigated by simultaneous thermal analysis technology (TG/DSC), using a series of heating rates (5, 10, 15, 20°C/min). The results showed that the reaction process of micron-sized aluminium powder in carbon dioxide was divided into three stages: the initial slow oxidation stage, the sharp oxidation stage and the last oxidation stage. The thermal performance was increased with the increase in the heating rates. Evolution of the samples was determined by collecting the products at the initial, sharp, and last oxidation stages of the process. The reaction products morphology was examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The corresponding chemical changes were analysed by X-ray diffraction spectrometry (XRD). The effects of heating rate on the thermal reaction characteristics were discussed. A new reaction mechanism of micron-sized Al particle in CO2 with gradually increased temperature was proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Yuasa and H. Isoda, Symp. Combust. Proc. 22, 1635 (1989).
E. I. Shafirovich, A. Shiriaev, and U. Goldshleger, J. Propuls. Power 9, 197 (1993).
E. Y. Shafirovich and U. I. Goldshleger, J. Propuls. Power 13, 395 (1997).
E. Y. Shafirovich and U. I. Goldshleger, J. Brit. Interplanet. Soc. 48, 315 (1995).
E. Shafirovich, A. Mukasyan, L. Thiers, A. Varma, B. Legrand, C. Chauveau, and I. Gokalp, Combust. Sci. Technol. 174, 125 (2002).
Y. Yavor, V. Rosenband, and A. Gany, Int. J. Energ. Mater. Chem. Propuls. 9, 477 (2010).
R. A. Yetter, G. A. Risha, and S. F. Son, Combust. Inst. 32, 1819 (2009).
E. L. Dreizin, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 35, 141 (2009).
V. Rosenband and A. Gany, Int. J. Energ. Mater. Chem. Propuls. 10, 19 (2011).
Y. Yavor, V. Rosenband, and A. Gany, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. G: J. Aerospace Eng. (2013). doi 10.1177/ 0954410013495638
X. Zhu, M. Schoenitz, and E. L. Dreizin, J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 6768 (2009).
S. Rossi, E. L. Dreizin, and C. K. Law, Combust. Sci. Technol. 164, 209 (2001).
B. Legrand, M. Marion, C. Chauveau, I. Gokalp, and E. Shafirovich, Combust. Sci. Technol. 165, 151 (2001).
L. Jeurgens, W. Sloof, F. Tichelaar, and E. Mittemeijer, Phys. Rev. B 62, 4707 (2000).
M. A. Trunov, M. Schoenitz, X. Zhu, and E. L. Dreizin, Combust. Flame 140, 310 (2005).
K. Brandstadt, D. L. Frost, and J. A. Kozinski, Proc. Combust. Inst. 32, 1913 (2009).
I. Levin and D. Brandon, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81, 1995 (1998).
M. A. Trunov, M. Schoenitz, and E. L. Dreizin, Propellants, Explos., Pyrotech. 30, 36 (2005).
M. Fanfei and Z. Mingxu, J. Chin. Coal. Soc. 30, 104 (2005).
Q. Nie, S. Sun, Z. Li, X. Zhang, S. Wu, and Y. Qin, J. Combust. Sci. Technol. 7, 72 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, B., Wang, Q., Sun, Y. et al. Thermal reaction characterization of micron-sized aluminum powders in CO2 . Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 10, 644–650 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990793116040163
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990793116040163