Abstract
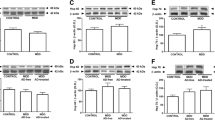
Although borderline personality disorders (BPD) are most common psychiatric diseases, their pathogenesis still remains poorly understood. According to the literature and results of own previous studies, pathological changes associated with BPD may affect not only brain cells, but also cells of the immune system. One of the functionally important examples of communication between the immune and nervous systems in BPD is death of lymphocytes, particularly recognized in the most common mental disorder, depression. We have shown previously that activity of caspases, the key enzymes of programmed cell death increases in some types of BPD. In this study, we have investigated caspase activity in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of BPD patients of different severity. It has been found that in severe depression activity of initiator and executive caspases decreases as compared with control, and patients with a mild form of depression. In contrast, patients with severe form of anxiety were characterized by increased activity of the same enzymes as compared with control and patients with less severe forms of anxiety. Thus, the study of PBMC caspase can not only discriminate mild and severe forms of BPD, but can also help to identify specific molecular mechanisms responsible for the development of depression and anxiety.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleksandrovskii, Yu.A., in Pogranichnyie psikhicheskie rasstroistva: klinicheskie i sotsial’nyie aspekty (Borderline Psychiatric Disorders: Fundamental, Clinical, and Social Aspects), Gusev, E.I., Guekht, A.B., Avedisova, A.S., and Gulyaeva, N.V., Eds., Moscow: FCHO, 2014, pp. 23–43.
Wray, N.R., Pergadia, M.L., Blackwood, D.H.R., Penninx, B.W.J.H., Gordon, S.D., Nyholt, D.R., et al., Mol. Psychiatry, 2012, vol. 17, pp. 36–48.
Raison, C.L., Capuron, L., and Miller, A.H., Trends Immunology, 2006, vol. 27, pp. 24–31.
Yakovlev, A.A., Neurochem. J., 2015, vol. 32, pp. 1–4.
Gladkevich, A., Kauffman, H.F., and Korf, J., Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 2004, vol. 28, pp. 559–576.
Bei, E., Salpeas, V., Pappa, D., Anagnostara, C., Alevizos, V., and Moutsatsou, P., Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2009, vol. 34, pp. 1162–1175.
Szuster-Ciesielska, A., Slotwinska, M., Stachura, A., Marmurowska-Michalowska, H., Dubas-Slemp, H., Bojarska-Junak, A., et al., Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 2008, vol. 32, pp. 686–694.
Gerasimovich, E.S., Yakovlev, A.A., Druzhkova, T.A., Grishkina, M.N., Guekht, A.B., and Gulyaeva, N.V., Biomed. Khim., 2016, vol. 62, pp. 89–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.A. Yakovlev, T.A. Druzhkova, M.N. Grishkina, A.B. Guekht, N.V. Gulyaeva, 2017, published in Biomeditsinskaya Khimiya.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yakovlev, A.A., Druzhkova, T.A., Grishkina, M.N. et al. Caspase activity in lymphocytes of patients with depression and anxiety of different severity. Biochem. Moscow Suppl. Ser. B 11, 76–80 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990750817010103
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990750817010103