Abstract
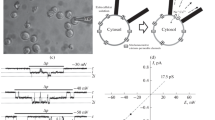
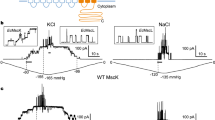
Using the patch–clamp method, mechanosensitive regulation of ion channels was studied in cultivated 3T3 and 3T3-SV40 fibroblasts. The activity of mechanosensitive cation channels with a conductivity 25 pS in response to plasma-membrane stretching was observed in both cell lines. Despite obvious differences in the actin network in normal and transformed cells, the threshold values of the stimulus required for the channel activation were close and were approximately 55 mm Hg. The frequency of channels was significantly higher in transformed 3T3-SV40 fibroblasts than in their untransformed 3T3 analogs. Coupled activation of mechanosensitive calcium-permeable channels and potassium calcium-controlled channels was found in both cell lines. The analysis of flows through single channels allows to detect functional interaction of different channels: stretch-induced local calcium entry activates potassium channels that do not have their own mechanosensitivity. The results of a comparative study show that there is a fundamental similarity between the ion mechanisms of cellular mechanotransduction in normal and transformed fibroblasts. The quantitative differences, first of all, concern the level of functional activity of mechanosensitive channels that provide the development of the local calcium signal in the near-membrane cell region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnadottir, J. and Chalfie, M., Eukaryotic mechanosensitive channels, Annu. Rev. Biophys., 2010, vol. 39, pp. 111–137.
Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin, V.I., Functional coupling of ion channels as universal mechanism of cellular mechanotransduction, Acta Naturae, special issue, 2016, vol. 1, pp. 71–72.
Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin, V.I., Negulyaev, Y.A., and Morachevskaya, E.A., Cholesterol depletion-induced inhibition of stretch-activated channels is mediated via actin rearrangement, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2011, vol. 412, pp. 80–85.
Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin, V.I., Nyapshaev, I.A., Morachevskaya, E.A., and Ankudinov, A.V., Evaluation of the changes of plasma membrane stiffness after partial extraction of membrane cholesterol, Tsitologiia, 2012, vol. 54, no. 9, pp. 714–715.
Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin, V.I., Negulyaev, Y.A., and Morachevskaya, E.A., Functional coupling of ion channels in cellular mechanotransduction, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2014, vol. 451, pp. 421–424.
Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin V.I., Vasileva, V.Y., Pugovkina, N.A., Vassilieva, I.O., Morachevskaya, E.A., Nikolsky, N.N., and Negulyaev, Y.A., Local calcium signalling is mediated by mechanosensitive ion channels in mesenchymal stem cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2017, vol. 482, pp. 563–568.
Coste, B., Mathur, J., Schmidt, M., Earley, T.J., Ranade, S., Petrus, M.J., Dubin, A.E., and Patapoutian, A., Piezo1 and Piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation channels, Science, 2010, vol. 330, pp. 55–60.
Franco, S.J. and Huttenlocher, A., Regulating cell migration: calpains make the cut, J. Cell Sci., 2005, vol. 118, pp. 3829–3838.
Gilbert G., Ducret, T., Marthan, R., Savineau, J.P., and Quignard, J.F., Stretch-induced Ca2+ signalling in vascular smooth muscle cells depends on Ca2+ store segregation, Cardiovasc. Res., 2014, vol. 103, pp. 313–323.
Gueguinou, M., Chantome, A., Fromont, G., Bougnoux, P., Vandier, C., and Potier-Cartereau, M., KCa and Ca2+ channels: the complex thought, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2014, vol. 1843, pp. 2322–2333.
Lee, J., Ishihara, A., Oxford, G., Johnson, B., and Jacobson, K., Regulation of cell movement is mediated by stretch-activated calcium channels, Nature, 1999, vol. 400, pp. 382–386.
Li, C., Rezania, S., Kammerer, S., Sokolowski, A., Devaney, T., Gorischek, A., Jahn, S., Hackl, H., Groschner, K., Windpassinger, C., Malle, E., Bauernhofer, T., and Schreibmayer, W., Piezo1 forms mechanosensitive ion channels in the humanMCF-7 breast cancer cell line, Sci. Rep., 2015, vol. 5, p. 8364. doi doi 10.1038/srep08364
Mamoune, A., Luo, J.H., Lauffenberger, D.A., and Wells, A., Calpain-2 as a target for limiting prostate cancer invasion, Cancer Res., 2003, vol. 63, pp. 4632–4640.
Maroto, R. and Hamill, O.P., MscCa regulation of tumor cell migration and metastasis, in Mechanosensitive Channels. B: Current Topics in Membranes, New York: Academic Press, 2007, pp. 485–509.
McHugh, B.J., Murdoch, A., Haslett, C., and Sethi, T., Loss of integrin-activating transmembrane protein FAM38A (Piezo1) promotes a switch to integrin-independent mode of cell migration, PloS One, 2012, vol. 7, p. e40346.
Morachevskaya, E.A., Sudarikova, A.V., and Negulyaev, Y.A., Mechanosensitive channel activity and Factin organization in cholesterol-depleted human leukaemia cells, Cell Biol. Int., 2007, vol. 31, pp. 374–381.
Rovenskii, Yu.A. and Vasil’ev, Yu.M., Morphogenetic reactions of cells and their disturbances in malignant transformation, in Kantserogenez (Carcinogenesis), Moscow: Meditsina, 2004, pp. 376–414.
Staruschenko A.V. and Vedernikova E.A., Mechanosensitive cation channels in human leukaemia cells: calcium permeation and blocking effect, J. Physiol., 2002, vol. 541, pp. 81–90.
Staruschenko A.V., Negulyaev, Y.A., and Morachevskaya, E.A., Actin cytoskeleton disassembly affects conductive properties of stretch-activated cation channels in leukaemia cells, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2005, vol. 1669, pp. 53–60.
Staruschenko, A.V., Sudarikova, A.V., Negulyaev, Y.A., and Morachevskaya, E.A., Magnesium permeation through mechanosensitive channels: single-current measurements, Cell Res., 2006, vol. 16, pp. 723–730.
Suresh, S., Biomechanics and biophysics of cancer cells, Acta Biomater., 2007, vol. 3, pp. 413–438.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.I. Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin, T.N. Efremova, Yu.A. Negulyaev, E.A. Morachevskaya, 2018, published in Tsitologiya, 2018, Vol. 60, No. 1, pp. 14–20.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin, V.I., Efremova, T.N., Negulyaev, Y.A. et al. Coupled Activation of Mechanosensitive and Calcium-Dependent Potassium Channels in 3T3 and 3T3-SV40 Cells. Cell Tiss. Biol. 12, 231–237 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X18030021
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X18030021