Abstract
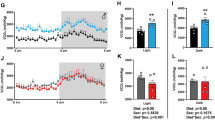
One approach to correction of diabetes mellitus 2 type (DM2) and its complications is the use of bromocriptine mesylate (BCM), a selective agonist of the dopamine receptor type 2 (DA2R). However, the effectiveness and mechanisms of the action of BCM in the treatment of severe forms of DM2 forms currently not understood. The purpose of this study was to investigate the influence of 4-week treatment of male rats with neonatal DM2 model using BCM (300 mg/kg daily) on their metabolic parameters and on the activity of the adenylyl cyclase signaling system (ACSS) in the hypothalamus. Exposure to BCM restored glucose tolerance and glucose utilization by exogenous insulin, normalized lipid metabolism, and lowered triglycerides and atherogenic cholesterol levels, which are elevated in DM2. In the hypothalamus of diabetic rats treated with BCM, the regulation of ACSS by agonists of melanocortin receptors type 4 (MC4R), DA2R, and serotonin 1B-subtype receptors and expression of the Mc4r gene encoding MC4R were restored. Furthermore, BCM treatment did not influence the insulin levels in the blood and its production by pancreatic β-cells. The data indicate that the use of BCM to correct severe forms of experimental DM2 holds promise and show that the therapeutic potential of this drug is based on its ability to restore signaling systems of the hypothalamus that are sensitive to monoamines and peptides of the melanocortin family, which are responsible for the control of energy metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
adenylyl cyclase
- ACSS:
-
adenylyl cyclase signaling system
- BCM:
-
bromocriptine mesylate
- GTT:
-
glucose-tolerance test
- DA1R and DA2R:
-
dopamine receptors 1 and 2 types, respectively
- IGTT:
-
insulin glucose-tolerance test
- MC4R:
-
melanocortin receptor 4-type
- α-MSH:
-
α-melanocyte stimulating hormone
- 5-NOT:
-
5-nonyloxytryptamine
- DM2:
-
diabetes mellitus type 2
- HT1ВR:
-
serotonin receptor 1B-subtype
- TG:
-
triglycerides
- HDL-C and LDL-C:
-
a complex of cholesterol with lipoproteins of high and low density, respectively
References
Beaulieu, J.M., Gainetdinov, R.R., and Caron, M.G., The Akt-GSK-3 signaling cascade in the actions of dopamine, Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 2007, vol. 28, pp. 166–172.
Chamarthi, B., Gaziano, J.M., Blonde, L., Vinik, A., Scranton, R.E., Ezrokhi, M., Rutty, D., and Cincotta, A.H., Timed bromocriptine-QR therapy reduces progression of cardiovascular disease and dysglycemia in subjects with well-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus, J. Diabet. Res., 2015, vol. 2015, p. 157698.
Derkach, K.V., Bondareva, V.M., Moiseyuk, I.V., and Shpakov, A.O., The effect of 2-month bromocriptine treatment on the activity of the adenylate cyclase signaling system in the myocardium and testes of rats with type 2 diabetes, Cell Tissue Biol., 2014, vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 395–405.
Derkach, K.V., Bondareva, V.M., Chistyakova, O.V., Berstein, L.M., and Shpakov, A.O., The effect of long-term intranasal serotonin treatment on metabolic parameters and hormonal signaling in rats with high-fat diet/low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes, Int. J. Endocrinol., 2015, vol. 2015, pp. 245459.
Deuschle, M., Effects of antidepressants on glucose metabolism and diabetes mellitus type 2 in adults, Curr. Opin. Psychiatry, 2013, vol. 26, pp. 60–65.
Fan, W., Dinulescu, D.M., Butler, A.A., Zhou, J., Marks, D.L., and Cone, R.D., The central melanocortin system can directly regulate serum insulin levels, Endocrinology, 2000, vol. 141, pp. 3072–3079.
Farooqi, I.S., Keogh, J.M., Yeo, G.S., Lank, E.J., Cheetham, T., and O’Rahilly, S., Clinical spectrum of obesity and mutations in the melanocortin 4 receptor gene, New Engl. J. Med., 2003, vol. 348, pp. 1085–1095.
Gaziano, J.M., Cincotta, A.H., Vinik, A., Blonde, L., Bohannon, N., and Scranton, R., Effect of bromocriptine-QR (a quick-release formulation of bromocriptine mesylate) on major adverse cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes subjects, J. Amer. Heart Assoc., 2012, vol. 1, p. E002279.
Grunberger, G., Novel therapies for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: part 1, pramlintide and bromocriptine-QR, J. Diabetes, 2013, vol. 5, pp. 110–117.
Kerr, J.L., Timpe, E.M., and Petkewicz, K.A., Bromocriptine mesylate for glycemic management in type 2 diabetes mellitus, Ann. Pharmacother., 2010, vol. 44, pp. 1777–1785.
Luo, S., Luo, J., and Cincotta, A.H., Association of the antidiabetic effects of bromocriptine with a shift in the daily rhythm of monoamine metabolism within the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the Syrian hmster, Chronobiol. Int., 2000, vol. 17, pp. 155–172.
Lustman, P.J. and Clouse, R.E., Depression in diabetic patients: the relationship between mood and glycemic control, J. Diabetes Complicat., 2005, vol. 19, pp. 113–122.
Mebel, D.M., Wong, J.C., Dong, Y.J., and Borgland, S.L., Insulin in the ventral tegmental area reduces hedonic feeding and suppresses dopamine concentration via increased reuptake, Eur. J. Neurosci., 2012, vol. 36, pp. 2336–2346.
Mikhail, N., Quick-release bromocriptine for treatment of type 2 diabetes, Curr. Drug Deliv., 2011, vol. 8, pp. 511–516.
Morgan, D.A., McDaniel, L.N., Yin, T., Khan, M., Jiang, J., Acevedo, M.R., Walsh, S.A., Ponto, L.L., Norris, A.W., Lutter, M., Rahmouni, K., and Cui, H., Regulation of glucose tolerance and sympathetic activity by MC4R signaling in the lateral hypothalamus, Diabetes, 2015, vol. 64, pp. 1976–1987.
Nade, V.S., Kawale, L.A., Todmal, U.B., and Tajanpure, A.B., Effect of bromocriptine on cardiovascular complications associated with metabolic syndrome in fructose fed rats, Indian J. Pharmacol., 2012, vol. 44, pp. 688–693.
Nogueiras, R., Wiedmer, P., Perez-Tilve, D., Veyrat-Durebex, C., Keogh, J.M., Sutton, G.M., Pfluger, P.T., Castaneda, T.R., Neschen, S., Hofmann, S.M., Howles, P.N., Morgan, D.A., Benoit, S.C., Szanto, I., Schrott, B., Schürmann, A., Joost, H.G., Hammond, C., Hui, D.Y., Woods, S.C., Rahmouni, K., Butler, A.A., Farooqi, I.S., O’Rahilly, S., Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F., and Tschöp, M.H., The central melanocortin system directly controls peripheral lipid metabolism, J. Clin. Invest., 2007, vol. 117, pp. 3475–3488.
Pandit, R., de, Jong, J.W., Vanderschuren, L.J., and Adan, R.A., Neurobiology of overeating and obesity: the role of melanocortins and beyond, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2011, vol. 660, pp. 28–42.
Pijl, H., Ohashi, S., Matsuda, M., Miyazaki, Y., Mahankali, A., Kumar, V., Pipek, R., Iozzo, P., Lancaster, J.L., Cincotta, A.H., and DeFronzo, R.A., Bromocriptine: a novel approach to the treatment of type 2 diabetes, Diabetes Care, 2000, vol. 23, pp. 1154–1161.
Ryan, G., Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease or risk factors, Postgrad. Med., 2015, vol. 127, pp. 842–854.
Scranton, R. and Cincotta, A., Bromocriptine—unique formulation of a dopamine agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, Expert. Opin. Pharmacother., 2010, vol. 11, pp. 269–279.
Shpakov, A.O. and Derkach, K.V., The functional state of hormone-sensitive adenylyl cyclase signaling system in diabetes mellitus, J. Signal Transduct., 2013, vol. 2013, p. 594213.
Shpakov, A.O. and Derkach, K.V., Gormonal’nye sistemy mozga i sakharny diabet 2-go tipa (The Brain Hormonal Signaling Systems and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus), St. Petersburg: Izd. Politekh. Univ., 2015. ISBN 978-5-7422-4955-9.
Shpakov, A.O., Chistyakova, O.V., Derkach, K.V., Moiseyuk, I.V., and Bondareva, V.M., Intranasal insulin affects adenylyl cyclase system in rat tissues in neonatal diabetes, Central Eur. J. Biol., 2012, vol. 7, pp. 33–47.
Shpakov, A.O., Derkach, K.V., Chistyakova, O.V., and Bondareva, V.M., The influence of bromocryptine treatment on activity of the adenylyl cyclase system in the brain of rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus induced by high-fat diet, Dokl. Biochem. Biophys., 2014, vol. 459, no. 1, pp. 186–189.
Sukhov, I.B., Derkach, K.V., Chistyakova, O.V., Bondareva, V.M., and Shpakov, A.O., The effect of prolonged intranasal administration of serotonin on the activity of hypothalamic signaling systems in male rats with neonatal diabetes, Cell Tissue Biol., 2016, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 314–323.
Tao, Y.X., Mutations in melanocortin-4 receptor and human obesity, Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci., 2009, vol. 88, pp. 173–204.
Vinik, A.I., Cincotta, A.H., Scranton, R.E., Bohannon, N., Ezrokhi, M., and Gaziano, J.M., Effect of bromocriptine-qr on glycemic control in subjects with uncontrolled hyperglycemia on one or two oral anti-diabetes agents, Endocr. Pract., 2012, vol. 18, pp. 931–943.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © K.V. Derkach, A.O. Ivantsov, I.B. Sukhov, A.O. Shpakov, 2017, published in Tsitologiya, 2017, Vol. 59, No. 2, pp. 140–147.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Derkach, K.V., Ivantsov, A.O., Sukhov, I.B. et al. Restoration of hypothalamic signaling systems as a cause of improved metabolic parameters in rats with neonatal diabetes model during treatment with bromocriptine mesylate. Cell Tiss. Biol. 11, 234–241 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X17030038
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X17030038