Abstract
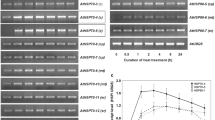
The influence of geldanamycin (GA), a specific inhibitor of heat-shock protein Hsp90, on the synthesis of Hsp70 and Hsp90 and thermotolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings has been studied. Incubation of seedlings with GA under normal conditions induced synthesis of these stress proteins. Treatment of seeds with the Hsp90 inhibitor resulted in elevated constitutive levels of Hsp70 and Hsp90 in seedlings, as well as increased induction of their synthesis under heat shock. The GA effect increased with its concentration. Hsp up-regulation promoted thermotolerance of seedlings. The findings suggest autoregulation of heatshock protein synthesis and regulation of plant tolerance by Hsp90.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GA:
-
geldanamycin
- DMSO:
-
dimethylsulfoxide
- HSE:
-
heat-shock element
- Hsp:
-
heat-shock protein
- Hsf:
-
heat-shock factor
References
Klyueva, N.Yu. and Samokhvalov, I.M., Synthesis of heat shock proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 1990, vol. 37, no. 4, pp. 739–747.
Kozeko, L.Ye., Heat shock proteins 90 kDa: diversity, structure, functions, Tsitologiia, 2010, vol. 52, no. 11, pp. 3–20.
Kozeko, L.Ye., Phenotypic variability of Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings as a result of inhibition of Hsp90 chaperones, Cytol. Genet., 2013, vol. 47, no. 2, pp. 75–87.
Novoselova, T.V., Cherenkov, D.A., Khrenov, M.O., Glushkova, O.V., Lunin, S.M., Novoselova, E.G., and Fesenko, E.E., Effect of geldanamycin on expression of signal proteins and heat-shock proteins in normal mouse lymphocytes, Cell Tis. Biol., 2008, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 366–372.
Sharova, E.I., Protein transport in plant cells, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2002, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 255–268.
Agarwal, M. Katiyar-Agarwal, S., and Grover, A., Plant Hsp100 proteins: structure, function and regulation, Plant Sci., 2002, vol. 163, pp. 397–405.
Ali, A., Bharadwaj, S., O’Carroll, R., and Ovsenek, N., Hsp90 interacts with and regulates the activity of heat shock factor 1 in Xenopus oocytes, Mol. Cell. Biol., 1998, vol. 18, pp. 4949–4960.
Bowen, J., Lay-Yee, M., Plummer, K., and Ferguson, I., The heat shock response is involved in thermotolerance in suspension-cultured apple fruit cells, J. Plant Physiol., 2002, vol. 159, pp. 599–606.
Bradford, M.M., A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding, Anal. Biochem., 1976, vol. 72, pp. 248–254.
Conde, A.G., Lau, S.S., Dillmann, W.H., and Mestril, R., Induction of heat shock proteins by tyrosine kinase inhibitors in rat cardiomyocytes and myogenic cells confers protection against simulated ischemia, Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 1997, vol. 29, pp. 1927–1938.
Duncan, R.F., Inhibition of Hsp90 function delays and impairs recovery from heat shock, FEBS J., 2005, vol. 272, pp. 5244–5256.
Kozeko, L. and Kordyum, E., The Stress protein level under clinorotation in context of the seedling developmental program and the stress response, Microgravity Sci. Technol., 2006, vol. XVIII, nos. 3/4, pp. 254–256.
Krishna, P. and Gloor, G., The Hsp90 family of proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana, Cell Stress Chaperones, 2001, vol. 6, pp. 238–246.
Laemmli, U.K., Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4, Nature, 1970, vol. 227, pp. 680–685.
Lin, B.-L., Wang, J.-Sh., Liu, H.-Ch., Chen, R.-W., Meyer, Y., Barakat, A., and Delseny, M., Genomic analysis of the Hsp70 superfamily in Arabidopsis thaliana, Cell Stress Chaperones, 2001, vol. 6, pp. 201–208.
Mathew, A. and Morimoto, R.I., Role of the heat-shock response in the life and death of proteins, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 1998, vol. 851, pp. 99–111.
Morimoto, R.I., Regulation of the heat shock transcriptional response: cross talk between a family of heat shock factors, molecular chaperones, and negative regulators, Genes Dev., 1998, vol. 12, pp. 3788–3796.
Pelham, H.R.B., A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila Hsp70 heat-shock gene, Cell, 1982, vol. 30, pp. 517–528.
Picard, D., Heat-shock protein 90, a chaperone for folding and regulation, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2002, vol. 59, pp. 1640–1648.
Prodromou, C., Roe, S.M., O’Brien, R., Ladbury, J.E., Piper, P.W., and Pearl, L.H., Identification and structural characterization of the ATP/ADP-binding site in the Hsp90 molecular chaperone, Cell, 1997, vol. 90, pp. 65–75.
Queitsch, C., Hong, S.-W., Vierling, E., and Lidquist, S., Heat shock protein 101 plays a crucial role in thermotolerance in Arabidopsis, Plant Cell, 2000, vol. 12, pp. 479–492.
Queitsch, C., Sangster, T.A., and Lindquist, S., Hsp90 as a capacitor of phenotypic variation, Nature, 2002, vol. 417, pp. 618–624.
Schöffl, F., Prändl, R., and Reindl, A., Regulation of the heat-shock response, Plant Physiol, 1998, vol. 117, pp. 1135–1141.
Sørensen, J.G., Kristensen, T.N., and Loeschcke, V., The evolutionary and ecological role of heat shock proteins, Ecol. Letts., 2003, vol. 6, pp. 1025–1037.
Sung, D.Y., Vierling, E., and Guy, C.L., Comprehensive expression profile analysis of the Arabidopsis Hsp70 gene family, Plant Physiol., 2001, vol. 126, pp. 789–800.
Yamada, K., Fukao, Y., Hayashi, M., Fukazawa, M., Suzuki, I., and Nishimura, M., Cytosolic HSP90 regulates the heat shock response that is responsible for heat acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana, J. Biol. Chem., 2007, vol. 282, no. 52, pp. 37794–37804.
Waters, E.R., The evolution, function, structure, and expression of the plant sHSPs, J. Exp. Bot., 2013, vol. 64, pp. 391–403.
Wu, C., Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin, Nature, 1984, vol. 311, pp. 81–84.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.Ye. Kozeko, 2014, published in Tsitologiya, 2014, Vol. 56, No. 6, pp. 419–426.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozeko, L.Y. Changes in heat-shock protein synthesis and thermotolerance of Arabodopsis thaliana seedlings resulting from Hsp90 inhibition by geldanamycin. Cell Tiss. Biol. 8, 416–422 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X14050046
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X14050046