Abstract
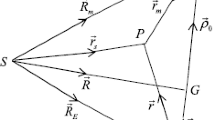
We report the results of an analysis of the variation of the proper rotation of several destabilized satellites over many-year long time intervals. The cause of the cyclic variations of the proper rotation period of “Midas-7” satellite, which has been orbiting the Earth since 1963 at an altitude of 3700 km, have long been unclear. These variations could not be explained either by the influence of the terrestrial atmosphere and terrestrial magnetic field, or by solar activity. Based on the results of 40-year long observations of “Midas-4,” “Midas-6,”, and “Midas-7” satellites it was established that their proper rotation exhibits not only dissipative braking variations, but also long-period variations with the periods of 477 days (“Midas-4”), 466 days (“Midas-6”), and 346 days (“Midas-7”) with different amplitudes. These variations in the case of the above satellites have well-defined resonance nature. An explanation of the processes found is proposed based on the results of this study and simulations of the observed orbital dynamics of the satellites. Long-period variations of the proper spacecraft rotation arise as a result of the combined effect of the gravitational fields of the Earth, Moon, and Sun depending on the orientation of their orbital planes in space. The amplitudes of such variations is determined by the inclination of satellite orbits to the equator: the closer it is to the pole (i.e., to 90◦), the stronger the effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. P. Epishev, I. I. Isak, V. I. Kudak, et al., Space Sci. Technology 18, 60 (2012).
V. V. Beletskii, Motion of the satellite relative to the mass center in gravitational field (Moscow State University,Moscow, 1975).
W. B. Patterson and K. E. Kissell, J. SpacecraftRockets 12, 539 (1975).
A. T. Mecherikunnel, R. B. Lee, III, H. L. Kyle, and E. R. Major, J. Geophys. Research: Atmospheres 93, 9503 (1988).
V. P. Epishev, I. I. Isak, I. I. Motrunich, et al., Space Sci. Technology 10, 152 (2004).
V. P. Epishev, I. I. Isak, I. I. Motrunich, et al., in Transactions of the Near-Earth Conference-2009, Kazan, Russia, 2009 (GEOS, Moscow, 2010), pp. 35–41.
M. M. Lychak, Space Sci. Technology 14, 39 (2008).
Mini-MegaTORTORA (MMT-9), (2014) http://astroguard.ru/satellites.
G. M. Beskin, S. V. Karpov, A. V. Biryukov, et al., Astrophysical Bulletin 72, 81 (2017).
V. I. Kudak, V. P. Epishev, V. M. Perig, and I. F. Neybauer, Astrophysical Bulletin 72, 340 (2017).
M. V. Bratijchuk, Y. M. Motrunich, T. J. Laslo, and S. I. Ignatovich, Astrometriia Astrofizika 21, 109 (1974).
M. V. Bratijchuk, V. P. Epishev, T. I. Laslo, et al., Astrometriia Astrofizika 46, 84 (1982).
S. I. Ihnatovich, Y. M. Motrunich, V. S. Melnik, et al., Uzhhorod Univ. Sci. Herald. Ser. Physics (2006).
I. I. Isak, Nauch. Inform. INASAN 72, 14 (2004).
J. D. Scargle, Astrophys. J. 263, 835 (1982).
V. N. Ishkov, Cosmic Research 55, 381 (2017).
V. I. Levantovskii, Mekhanika kosmicheskogo poleta v elementarnom izlozhenii (Elementary introduction into spaceflight mechanics) (Nauka, Moscow,Москва, 1980).
V. I. Kudak, V. U. Klimik, and V. P. Epishev, Astrophysical Bulletin 65, 300 (2010).
V. P. Epishev, I. I. Isak, I. I. Motrunich, et al., in Abstract Book of 13th Ukrainian Conf. on Space Researches (Eupatoria, 2013), p. 69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.P. Epishev, V.I. Kudak, V.M. Perig, I.I. Motrunich, I.F. Naybauer, E.J. Novak, O.Yu. But, 2018, published in Astrofizicheskii Byulleten’, 2018, Vol. 73, No. 3, pp. 386–396.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Epishev, V.P., Kudak, V.I., Perig, V.M. et al. Influence of the Gravitational Fields of the Moon and the Sun on Long-Period Variations in the Proper Rotation of “Midas” Satellites. Astrophys. Bull. 73, 363–372 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990341318030100
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990341318030100