Abstract
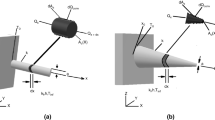
Since energy management is one of the most critical concerns, it is essential to determine the engineering construct irreversibility. Determination of entropy generation as a basis for evaluation of the irreversibility of heat transfer processes has become a significant method to reflect the heat transfer quality. The current study is dedicated to geometric optimization of T-shaped fins and inverted fins (cavities) using the constructal method to reach the minimum entropy generation as the optimization objective. The temperature distribution is determined according to a 1D analytical model and a 2D numerical model for a T-shaped fin and a T-shaped cavity, respectively. Furthermore, a comparison is made between the present optimal designs relying on entropy generation minimization (EGM) and the optimal designs presented in the literature and based on thermal conductance maximization (TCM) for the fin and hotspot temperature minimization (HTM) for the cavity. While the two optimization approaches have the same constraints, the results reveal that the optimal designs mainly have significant dependence on the type of optimization objective. However, it is shown that the T-shaped fin optimized via EGM produces 24% less entropy than the design optimized by TCM, with the thermal conductance lower only by 4%. On the other hand, the EGM-based optimal cavity generates entropy by about 8% less than that of the HTM-based optimal cavity, with an approximately 19% rise in the hotspot temperature. Considering both objectives for a more comprehensive comparison, the current article introduces a multi-objective optimization for fin and cavity.

















Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Nagarani, N., Mayilsamy, K., Murugesan, A., and Kumar, G.S., Review of Utilization of Extended Surfaces in Heat Transfer Problems, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 2014, vol. 29, pp. 604–613; DOI: 10.1016/J.RSER.2013.08.068
Hajmohammadi, M.R., Optimal Design of Tree-Shaped Inverted Fins, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2018, vol. 116, pp. 1352–1360; DOI: 10.1016/J.IJHEATMASSTRANSFER.2017.09.042
Reis, A.H., Constructal Theory: From Engineering to Physics, and How Flow Systems Develop Shape and Structure, Appl. Mech. Rev., 2006, vol. 59, no. 5, pp. 269–282; DOI: 10.1115/1.2204075
Bejan, A., Constructal Tree Network for Fluid Flow between a Finite-Size Volume and One Source or Sink, Rev. Génér. Therm., 1997, vol. 36, no. 8, pp. 592–604; https://doi.org/10.1016/S0035-3159(97)89986-2.
Lucia, U., Grisolia, G., Dolcino, G., Astori, M.R., Massa, E., and Ponzetto, A., Constructal Approach to Bio-Engineering: The Ocular Anterior Chamber Temperature, Sci. Rep., 2016, vol. 6, no. 1, p. 31099; DOI: 10.1038/srep31099
Lucia, U., Grisolia, G., and Astori, M.R., Constructal Law Analysis of Cl- Transport in Eyes Aqueous Humor, Sci. Rep., 2017, vol. 7, no. 1, p. 6856; DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-07357-8
Dutra, R.F., Zinani, F.S.F., Rocha, L.A.O., and Biserni, C., Effect of Non-Newtonian Fluid Rheology on an Arterial Bypass Graft: A Numerical Investigation Guided by Constructal Design, Comput. Methods Programs Biomed., 2021, vol. 201, p. 105944; DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.105944
Hajmohammadi, M.R., Mohammadifar, M., and Ahmadian-Elmi, M., Optimal Placement and Sizing of Heat Sink Attachments on a Heat-Generating Piece for Minimization of Peak Temperature, Thermochim. Acta, 2020, vol. 689, p. 178645; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2020.178645.
Hajmohammadi, M.R., Poozesh, S., and Nourazar, S.S., Constructal Design of Multiple Heat Sources in a Square-Shaped Fin, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part E, J. Process Mech. Eng., 2012, vol. 226, no. 4, pp. 324–336; DOI: 10.1177/0954408912447720
Ahmadian-Elmi, M., Mohammadifar, M, Rasouli, E., and Hajmohammadi, M.R., Optimal Design and Placement of Heat Sink Elements Attached on a Cylindrical Heat-Generating Body for Maximum Cooling Performance, Thermochim. Acta, 2021, vol. 700, p. 178941; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2021.178941
Chen, L., Yang, A., Feng, H., Ge, Y., and Xia, S., Constructal Design Progress for Eight Types of Heat Sinks, Sci. China Technol. Sci., 2020, vol. 63, no. 6, pp. 879–911; DOI: 10.1007/s11431-019-1469-1
Ahmadian-Elmi, M., Mashayekhi, A., Nourazar, S.S., and Vafai, K., A Comprehensive Study on Parametric Optimization of the Pin-Fin Heat Sink to Improve Its Thermal and Hydraulic Characteristics, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2021, vol. 180, p. 121797; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2021.121797.
Bejan, A. and Almogbel, M., Constructal T-Shaped Fins, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2000, vol. 43, no. 12, pp. 2101–2115; https://doi.org/10.1016/S0017-9310(99)00283-5.
Almogbel, M.A., Constructal Tree-Shaped Fins, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2005, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 342–348; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2004.11.002.
Lorenzini, G. and Oliveira Rocha, L.A., Constructal Design of Y-Shaped Assembly of Fins, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2006, vol. 49, no. 23, pp. 4552–4557; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2006.05.019.
Lorenzini, G. and Rocha, L.A.O., Constructal Design of T–Y Assembly of Fins for an Optimized Heat Removal, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2009, vol. 52, no. 5, pp. 1458–1463; https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.ijheatmasstransfer.2008.09.007.
Xie, Z., Chen, L., and Sun, F., Constructal Optimization of Twice Y-Shaped Assemblies of Fins by Taking Maximum Thermal Resistance Minimization as Objective, Sci. China Technol. Sci., 2010, vol. 53, no. 10, pp. 2756–2764; DOI: 10.1007/s11431-010-4037-x
Biserni, C., Rocha, L.A.O., and Bejan, A., Inverted Fins: Geometric Optimization of the Intrusion into a Conducting Wall, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2004, vol. 47, no. 12, pp. 2577–2586; https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2003.12.018.
Rocha, L.A.O., Montanari, G.C., dos Santos, E.D., and Rocha, A.daS., Constructal Design Applied to the Study of Cavities into a Solid Conducting Wall, Rev. Eng. Térmica, vol. 6, no. 1, 2007; https:// revistas.ufpr.br/reterm/article/view/61816.
Lorenzini, G. and Rocha, L.A.O., Geometric Optimization of T–Y-Shaped Cavity According to Constructal Design, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2009, vol. 52, no. 21, pp. 4683–4688; https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2009.06.020.
Lorenzini, G., Biserni, C., Isoldi, L.A., dos Santos, E.D., and Rocha, L.A.O., Constructal Design Applied to the Geometric Optimization of Y-Shaped Cavities Embedded in a Conducting Medium, J. Electron. Packag., 2011, vol. 133, no. 4; DOI: 10.1115/1.4005296
Biserni, C., Rocha, L.A.O., Stanescu, G., and Lorenzini, E., Constructal H-Shaped Cavities According to Bejan’s Theory, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2007, vol. 50, no. 11, pp. 2132–2138; https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.ijheatmasstransfer.2006.11.006.
Lorenzini, G., Biserni, C., Link, F.B., dos Santos, E.D., Isoldi, L.A., and Rocha, L.A.O., Constructal Design of Isothermal X-Shaped Cavities, Therm. Sci., 2014, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 349–356; DOI: 10.2298/TSCI120804005L
Hajmohammadi, M.R., Introducing a Ψ-Shaped Cavity for Cooling a Heat Generating Medium, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2017, vol. 121, pp. 204–212; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2017.07.010.
Estrada, E.S.D., Barreto, E.X., Isoldi, L.A., dos Santos, E.D., Lorente, S., and Rocha, L.A.O., Constructal Design of Tree Shaped Cavities Inserted into a Cylindrical Body with Heat Generation, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2020, vol. 152, p. 106342; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2020.106342.
Bejan, A., Second-Law Analysis in Heat Transfer and Thermal Design, Advances in Heat Transfer, 1982, vol. 15, pp. 1–58; https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2717(08)70172-2.
Bejan, A., Fundamentals of Exergy Analysis, Entropy Generation Minimization, and the Generation of Flow Architecture, Int. J. Energy Res., 2002, vol. 26, no. 7, pp. 1–43; https://doi.org/10.1002/er.804.
Kolenda, Z., Donizak, J., and Hubert, J., On the Minimum Entropy Production in Steady State Heat Conduction Processes, Energy, 2004, vol. 29, no. 12, pp. 2441–2460; https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.energy.2004.03.049.
Ribeiro, P. and Queiros-Condé, D., On the Entropy Production of the Elemental Construct of the Constructal Designed Plate Generating Heat, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2019, vol. 145, p. 106043; https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2019.106043.
Li, W., Xie, Z., Xi, K., Xia, S., and Ge, Y., Constructal Optimization of Rectangular Microchannel Heat Sink with Porous Medium for Entropy Generation Minimization, Entropy, 2021, vol. 23, no. 11; DOI: 10.3390/e23111528
Samal, S.K. and Moharana, M.K., Second Law Analysis of Recharging Microchannel Using Entropy Generation Minimization Method, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2021, vol. 193, p. 106174; https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.ijmecsci.2020.106174.
Jahanbakhshi, A., Ahmadi Nadooshan, A., and Bayareh, M., Investigation of Thermal Performance and Entropy Generation in a Microchannel Heatsink with a Wavy Channel Using Bio Nanofluid, Energy Equip. Syst., 2022, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 27–40; DOI: 10.22059/ees.2022.251133
Bejan, A., A Study of Entropy Generation in Fundamental Convective Heat Transfer, J. Heat Transfer, 1979, vol. 101, no. 4, pp. 718–725; DOI: 10.1115/1.3451063
Incropera, F.P., Lavine, A.S., Bergman, T.L., and DeWitt, D.P., Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 8th ed., New York, Wiley, 2017.
Cheng, C.H., Ma, W.P., and Huang, W.H., Numerical Predictions of Entropy Generations for Mixed Convective Flows in a Vertical Channel with Transverse Fin Array, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer, 1994, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 519–530; DOI: 10.1016/0735-1933(94)90051-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zehisaadat, S., Khalajzadeh, R.K., Hajmohammadi, M.R. et al. Geometric Optimization of T-shaped Fin and Inverted Fin Based on Minimum Entropy Generation Objective. J. Engin. Thermophys. 31, 668–687 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1810232822040129
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1810232822040129