Abstract
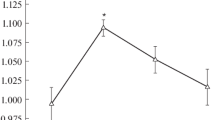
The combined effect of the zinc magnetic isotope 67Zn and weak magnetic field 25–35 mT causes a 2–4-fold increase in the colony-forming ability of bacteria E. coli in comparison with the nonmagnetic isotopes 64, 66Zn. The effects of magnetic field in the range of 2.2–8 mT were detected for all bacteria regardless of the zinc-isotope enrichment of the media. This indicates the sensitivity of intracellular processes to weak magnetic fields. An increase in the ATP concentration in E. coli cells was only detected for the bacteria grown on the medium with the magnetic zinc isotope in the range of 2.2–4.2 mT. The obtained data confirm the existence of stages of intracellular enzymatic processes that are sensitive to magnetic fields and magnetic moments of atomic nuclei.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binhi, V.N., Magnetobiology Underlying Physical Problems, Tokyo: Academic Press, 2009.
Albuquerque, W.W., Costa, R.M., Fernandes, Tde S., and Porto, A.L., Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol., 2016, no. 121, pp. 16–28.
Buchachenko, A., Bioelectromagnetics, 2016, no. 37, pp. 1–13.
Buchachenko, A., Magneto-Biology and Medicine, New York: Nova Science Publishers, 2014.
Letuta, U.G., Berdinskiy, V.L., Udagawa, Ch., and Tanimoto, Y., Bioelectromagnetics, 2017, pp. 1–11.
Letuta, U.G. and Berdinskiy, V.L., Bioelectromagnetics, 2017, Version of Record online: Aug. 7, 2017, pp. 1–11.
Baltaci, A.K., Yuce, K., and Mogulkoc, R., Biol. Trace Elem. Res., Version of Record online: Aug. 15, 2017. doi 10.1007/s12011-017-1119-7
Buchachenko, A.L., Chekhonin, V.P., Orlov, A.P., and Kuznetsov, D.A., Int. J. Mol. Med. Adv. Sci., 2010, no. 6, pp. 34–37.
Buchachenko, A.L., Orlov, A.P., and Kuznetsov, D.A., and Breslavskaya. N.N., Nucleic Acids Res., 2013, no. 41, pp. 8300–8307.
Letuta, U.G. and Avdeeva, E.I., Dokl. Biochem. Biophys., 2017, vol. 474, no. 1, pp. 196–199.
Buchachenko, A.L. and Vasserman, A.M., Stabil’nye radikaly. Elektronnoe stroenie, reaktsionnaya sposobnost' i primenenie (Stable Radicals: Electronic Structure, Reactivity, and Application), Moscow: Khimiya, 1973.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © U.G. Letuta, D.M. Shailina, 2018, published in Doklady Akademii Nauk, 2018, Vol. 479, No. 5, pp. 585–588.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Letuta, U.G., Shailina, D.M. Magnetosensitivity of E. coli Bacteria in the Presence of Zinc Isotopes. Dokl Biochem Biophys 479, 111–113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672918020175
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1607672918020175