Abstract
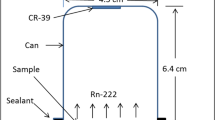
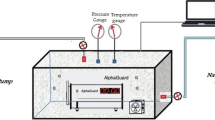
Background: From the health physics perspective, radon gas is one of the most dangerous gases in residential and business environments. According to the WHO (World Health Organization), radon gas is considered the second cause of lung cancer in societies after smoking. Methods: In this study, the environmental radon gas has been measured using a built radon gas detector on a specific preamplifier circuit and then the perceived results were compared with an Alpha-Guard detector. Specific activity and output ratio on radon concentration in air were measured on three different floors of a residential building covered by different materials. Results: The results showed a good correlation between the outputs and data gathered by the Alpha-Guard. In underground covered by plaster and cement, the detector responses showed approximately double amounts in comparison with the ground floor. The different covered places revealed dissimilar responses, so that the screened granite had greater amounts by 347 ± 37 Bq/m3. Besides, the minimum response was revealed on the first floor using Alpha-Guard by 47 ± 6 Bq/m3. Results confirmed that on each floor, which has a good ventilation system, the exposure due to the radon isotopes can be immensely reduced. Conclusions: This system can also be used to measure the radon concentration changes in the environment and groundwater.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
P. Korhonen, H. Kokotti, and P. Kalliokoski, “Behavior of radon, radon progenies and particle levels during room depressurization,” Atmos. Environ. 34, 2373–2378 (2000).
A. Kies, A. Biell, L. Rowlinson, and M. Feider, “Investigation of the dynamics of indoor radon and radon progeny concentration,” Environ. Int. 22, 899–904 (1996).
J. U. Ahmed, P. Stegnar, and F. Steinhäusler, “IAEA-coordinated research programme on radon in the human environment,” Environ. Int. 22, 773–777 (1996).
K. Ghosh, A. Deb, and K. Kumar Patra, “Measurements of alpha radioactivity in arsenic contaminated tubewell drinking water using CR-39 detector,” Radiat. Meas. 38, 19–22 (2004).
Pr. Singh, Pa. Singh, S. Singh, B. K. Sahoo, B. K. Sapra, and B. S. Bajwa, “A study of indoor radon, thoron and their progeny measurement in Tosham region Haryana, India,” J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 8, 226–233 (2015).
World Nuclear Association, WNA. http://world-nuclear.org/.
D. C. Thomas, Statistical Methods in Environmental Epidemiology (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, UK, 2009).
M. M. Ei-Toony and Aly Has, “Trapping of alpha particles and radon using epoxy/poly vinyl acetate blend foam,” J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1, 102 (2012).
WHO, Handbook on Indoor Radon: A Public Health Perspective (World Health Organization, 2009).
WHO, “Radon and health,” Fact Sheet No. 291 (World Health Organization, 2014).
United Nation Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation UNSCEAR, Sources and Effect of Ionization Radiation (UN, 2000).
N. Sharma, J. Singh, C. Esakki, and R. M. Tripathi, “A study of the natural radioactivity and radon exhalation rate in some cements used in india and its radiological significance,” J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 9, 47–56 (2016).
National Research Council, Assessment of the Scientific Information for the Radiation Exposure Screening and Education Program (Natl. Acad. Press, Washington, 2005).
J. Seco, B. Clasie, and M. Partridge, “Review on the characteristics of radiation detectors for dosimetry and imaging,” Phys. Med. Biol. 59, R303–R347 (2014).
G. E. Knoll, Radiation Detection and Measurement, 4th ed. (Wiley, Antioch, CA, 2010).
J. Chen and M. Deborah, “A study on the thoron sensitivity of radon detectors available to canadians,” J. Radiol. Prot. 32, 419–425 (2012).
S. Tokonami, M. Yang, and T. Sanada, “Contribution from thoron on the response of passive radon detectors,” Health Phys. 80, 612–615 (2001).
K. Hadad, M. R. Hakimdavoud, and M. H. Tilehnoee, “Indoor radon survey in shiraz-iran using developed passive measurement method,” Iran. J. Radiat. Res. 9, 175–182 (2011).
K. Hosokawa, A. Murata, Y. Nakano, Y. Onishi, H. Sekiya, Y. Takeuchi, and S. Tasaka, “Development of a high sensitivity radon detector for purified gases,” J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 469, 1–4 (2013).
Y. M. Gavrilyuk, A. M. Gangapshev, A. M. Gezhaev, R. A. Etezov, V. V. Kazalov, V. V. Kuzminov, S. I. Panasenko, S. S. Ratkevich, D. A. Tekueva, and S. P. Yakimenko, “High-resolution ion pulse ionization chamber with air filling for the 222Rn decays detection,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 801, 27–33 (2015).
Y. Nakano, H. Sekiya, S. Tasaka, Y. Takeuchi, R. A. Wendell, M. Matsubara, and M. Nakahata, “Measurement of radon concentration in Super-Kamiokande’s buffer gas,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 867, 108–114 (2017).
Z. Wang, Y. Shen, and J. An, “A new method for measuring the response time of the high pressure ionization chamber,” Appl. Radiat. Isot. 70, 1718–1722 (2012).
A. Hartmann, J. Hutsch, F. Krüger, M. Sobiella, H. Wilsenach, and K. Zuber, “Design and performance of an ionisation chamber for the measurement of low alpha-activities,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 814, 12–18 (2016).
J. S. Nabipour and A. Khorshidi, “Report on correlation between radon outgassing and aftershocks activity along the bam fault in Kerman province of Iran,” Braz. J. Rad. Sci. 5, 1–12 (2017).
A. Khorshidi, M. Ashoor, S. H. Hosseini, and A. Rajaee, “Estimation of fan beam and parallel beam parameters in a wire mesh design,” J. Nucl. Med. Tech. 40, 37–43 (2012).
A. Khorshidi, M. Ashoor, S. H. Hosseini, and A. Rajaee, “Evaluation of collimators' response: round and hexagonal holes in parallel and fan beam,” Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 109, 59–66 (2012).
A. Khorshidi and M. Ashoor, “Modulation transfer function assessment in parallel beam and fan beam collimators with square and cylindrical holes,” Ann. Nucl. Med. 28, 363–370 (2014).
M. Ashoor, A. Asgari, A. Khorshidi, and A. Rezaei, “Evaluation of compton attenuation and photoelectric absorption coefficients by convolution of scattering and primary functions and counts ratio on energy spectra,” Indian J. Nucl. Med. 30, 239–247 (2015).
M. Ashoor and A. Khorshidi, “Evaluation of crystals' morphology on detection efficiency using modern classification criterion and Monte Carlo method in nuclear medicine,” Proc. Natl. Sci. India A (2018, in press). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-018-0482-x
F. Ahmadov, O. Abdinov, G. Ahmadov, N. Anfimov, A. Garibov, E. Guliyev, Z. Krumshtein, R. Madatov, A. Olshevski, V. Shvetsov, A. Sadigov, Z. Sadygov, A. Titov, and V. Zhezher, “Alpha particle detector based on micropixel avalanche photodiodes,” Phys. Part. Nucl. Lett. 10, 1265–1267 (2013).
A. Khorshidi, “Gold nanoparticles production using reactor and cyclotron based methods in assessment of 196,198Au production yields by 197Au neutron absorption for therapeutic purposes,” Mater. Sci. Eng. C 68, 449–454 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.06.018
J. Soltani Nabipour, and A. Khorshidi, “Spectroscopy and optimizing semiconductor detector data under X and γ photons using image processing technique,” J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 49, 194–200 (2018).
A. Khorshidi, “Neutron activator design for 99Mo production yield estimation via lead and water moderators in transmutation’s analysis,” Instrum. Exp. Tech. 61, 198–204 (2018).
A. Khorshidi and A. Pazirandeh, “Molybdenum transmutation via 98Mo samples using bismuth/lead neutron moderators,” Europhys. Lett. 123, 12001 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/123/12001
A. Khorshidi, A. Rajaee, M. Ahmadinejad, M. Ghoranneviss, and M. Ettelaee, “Low energy electron generator design and depth dose prediction for micro-superficies tumor treatment purposes,” Phys. Scr. 89, 095001-6 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/89/9/095001
E. V. Samsonov, B. N. Gikal, O. N. Borisov, and I. A. Ivanenko, “Accumulation of spatial charge in the time projection chamber of a multipurpose detector,” Pis’ma Fiz. Elem. Chastits At. Yadra 10 (1) (2013).
A. Khorshidi, “Molybdenum-99 production via lead and bismuth moderators and milli-structure-98Mo samples by indirect production technique using Monte Carlo method,” Phys. Usp. (2019, in press). https://doi.org/10.3367/UFNe.2018.09.038441
A. Khorshidi, “Accelerator driven neutron source design via beryllium target and 208Pb moderator for boron neutron capture therapy in alternative treatment strategy by Monte Carlo method,” J. Cancer Res. Ther. 13, 456–465 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1482.179180
A. Khorshidi, “Accelerator-based methods in radio-material 99Mo/99mTc production alternatives by Monte Carlo method: the scientific-expedient considerations in nuclear medicine,” J. Multiscale Model. 10, 1930001 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1756973719300016
A. Khorshidi, Ghafoori-A. Fard, and M. Sadeghi, “Epithermal neutron formation for boron neutron capture therapy by adiabatic resonance crossing concept,” Int. J. Mod.Phys. E 23, 1–16 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218301314500323
A. Khorshidi, M. Ahmadinejad, and S. H. Hosseini, “Evaluation of a proposed biodegradable 188Re source for brachytherapy application,” Medicine 94, 1–7 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000001098
A. Asgari, M. Ashoor, L. Sarkhosh, A. Khorshidi, and P. Shokrani, “Determination of gamma camera’s calibration factors for quantitation of diagnostic radionuclides in simultaneous scattering and attenuation correction,” Curr. Radiopharm. 12, 29–39 (2019).
S. D. Chambers, S. B. Hong, A. G. Williams, J. Crawford, A. D. Griffiths, and S. J. Park, “Characterizing terrestrial influences of antarctic air masses using radon-222 measurements at King George island,” Atmos. Chem. Phys. 14, 9903-–9916 (2014).
M. Schubert, A. Paschke, E. Lieberman, and W. C. Burnett, “Air-water partitioning of 222Rn and its dependence on water temperature and salinity,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 3905–3911 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamshid Soltani-Nabipour, Khorshidi, A. & Sadeghi, F. Constructing Environmental Radon Gas Detector and Measuring Concentration in Residential Buildings. Phys. Part. Nuclei Lett. 16, 789–795 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S154747711906030X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S154747711906030X