Abstract
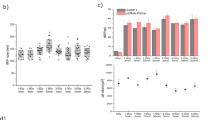
The kinetics of formation and elimination of γH2AX/53ВР1 foci induced by accelerated 11B, 20Ne, and 15N ions with different physical characteristics in human skin fibroblasts have been investigated. The results of the elimination kinetics for radiation-induced γH2AX/53BP1 foci (RIF) reveal that a decrease in the energy and an increase of the linear energy transfer (LET) of the particles reduce the efficiency of doublestrand break (DSB) repair. An investigation into the structure of RIF induced by accelerated 20Ne and 11B ions with various physical parameters shows significant differences in the nature of the RIF that is formed. It is found that 20Ne ions with a high density of δ rays in tracks (Z*2/β2 = 1454) induce larger clustered γH2AX/53BP1 foci with a more complex structure than 11B ions with a lower density of δ rays in tracks (Z*2/β2 = 494), which indicates the formation of more severe complex damage to genetic structures, first and foremost, DNA DSBs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Jezkova, M. Zadneprianetc, E. Kulikova, E. Smirnova, T. Bulanova, D. Depes, I. Falkova, A. Boreyko, E. Krasavin, M. Davidkova, S. Kozubek, O. Valentova, and M. Falk, “Particles with similar LET values generate DNA breaks of different complexity and reparability: a high-resolution microscopy analysis of γH2AX/53BP1 foci,” Nanoscale 10, 1162–1179 (2018).
A. M. Miterev, “Theoretical aspects of the formation and evolution of charged particle tracks,” Phys. Usp. 45, 1019 (2002).
M. G. Zadneprianetc, A. V. Boreyko, T. S. Bulanova, L. Ježkova, E. A. Krasavin, E. A. Kulikova, E. V. Smirnova, M. Falk, and I. Falkova, “Regularities in the Formation and Elimination of γH2AX/53ВР1 Foci after γ-Ray and Accelerated Heavy Ion Irradiation,” Radiats. Biol.: Radioekol., No. 2, 146–156 (2018).
J. Kiefer, “The physical basis for the biological action of heavy ions,” New J. Phys. 10, 1–15 (2008).
A. Chatterjee and H. J. Schaefer, “Microdosimetric structure of heavy ion tracks in tissue,” Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 13, 215–227 (1976).
A. Chatterjee and W. R. Holley, “Computer simulation of initial events in the biochemical mechanisms of DNA damage,” Adv. Rad. Biol. 17, 181–226 (1993).
V. Michalik, “Estimation of double strand break quality based on track structure calculations,” Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 32, 251–258 (1993).
H. Nikjoo, P. O’ Neill, W. E. Wilson, and D. T. Goodhead, “Computational approach for determining the spectrum of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation,” Radiat. Res. 156, 577–583 (2001).
K. A. George, M. Hada, L. Chappell, and F. A. Cucinotta, “Biological effectiveness of accelerated particles for the induction of chromosome damage: track structure effects,” Radiat. Res. 180, 25–33 (2013).
D. M. Sridharan, L. J. Chappell, M. K. Whalen, F. A. Cucinotta, J. M. Pluth, “Defining the biological effectiveness of components of high-LET track structure,” Radiat. Res. 184, 105–119 (2015).
F. Antonelli, A. Campa, G. Esposito, P. Giardullo, M. Belli, V. Dini, S. Meschini, G. Simone, E. Sorrentino, S. Gerardi, G. A. Cirrone, and M. A. Tabocchini, “Induction and repair of DNA DSB as revealed by H2AX phosphorylation foci in human fibroblasts exposed to low-and high-LET radiation: relationship with early and delayed reproductive cell death,” Radiat. Res. 183, 417–431 (2015).
A. Asaithamby, N. Uematsu, A. Chatterjee, M. Story, S. Burma, and D. J. Chen, “Repair of HZE-particleinduced DNA double-strand breaks in normal human fibroblasts,” Radiat. Res. 169, 437–446 (2008).
J. Saha, P. Wilson, P. Thieberger, D. Lowenstein, M. Wang, and F. A. Cucinotta, “Biological characterization of low-energy ions with high-energy deposition on human cells,” Radiat. Res. 182, 282–291 (2014).
A. Chatterjee and W. R. Holley, “Biochemical mechanisms and clusters of damage for high-LET radiation,” Adv. Space Res. 12, 33–43 (1992).
A. Asaithamby and D. J. Chen, “Mechanism of cluster DNA damage repair in response to high-atomic number and energy particles radiation,” Mutat. Res. 711, 87–99 (2011).
G. Du, G. A. Drexler, W. Friedland, C. Greubel, V. Hable, R. Krucken, A. Kugler, L. Tonelli, A. A. Friedl, and G. Dollinger, “Spatial dynamics of DNA damage response protein foci along the ion trajectory of high-LET particles,” Radiat. Res. 176, 706–715 (2011).
B. Jakob, J. Splinter, M. Durante, and G. Taucher-Scholz, “Live cell microscopy analysis of radiationinduced DNA double-strand break motion,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 3172–3177 (2009).
N. I. Nakajima, H. Brunton, R. Watanabe, A. Shrikhande, R. Hirayama, N. Matsufuji, A. Fujimori, T. Murakami, R. Okayasu, P. Jeggo, and A. Shibata, “Visualisation of γH2AX foci caused by heavy ion particle traversal; distinction between core track versus non-track damage,” PLoS One 8, e70107 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.G. Zadneprianetc, A.V. Boreyko, T.S. Bulanova, L. Ježková, E.A. Krasavin, E.A. Kulikova, E.V. Smirnova, 2018, published in Pis’ma v Zhurnal Fizika Elementarnykh Chastits i Atomnogo Yadra, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zadneprianetc, M.G., Boreyko, A.V., Bulanova, T.S. et al. The Influence of Physical Characteristics of Accelerated Heavy Ions on the Formation and Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Phys. Part. Nuclei Lett. 15, 693–699 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1547477118060183
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1547477118060183