Abstract
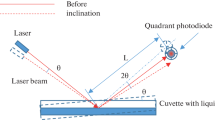
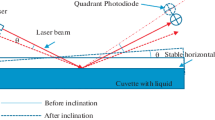
An experimental method for the compensation of the noise originated by the laser ray angular oscillations was proposed and experimentally proved for the Precision Laser Inclinometer (PLI). The PLI noise spectral density was reduced by factor 30× and reached 10–8 rad/Hz1/2 level at the frequency of 5 × 10–5 Hz. The angular noise of a laser ray leaving the one-mode optical fiber in the vacuum and in stabilized temperature conditions has been measured. The amplitude of the oscillations for one-day observation reached 0.46 μrad.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Batusov, J. Budagov, and M. Lyablin, “A laser sensor of a seismic slope of the Earth surface,” Phys. Part. Nucl. Lett. 10, 43–48 (2013).
J. Budagov et al., “The search for and registration of superweak angular ground motions,” JINR Commun. E18-2013-107 (JINR, Dubna, 2013).
N. Azaryan et al., “The precision laser inclinometer long-term sensitivity in thermo-stabilized conditions,” Report Presented at CLIC Workshop 2015, Jan. 26–30, 2015, CERN, JINR Preprint E13-2015-35 (JINR, Dubna, 2015).
N. Azaryan, V. Batusov, J. Budagov, V. Glagolev, M. Lyablin, G. Trubnikov, G. Shirkov, J.-Ch. Gayde, B. di Girolamo, D. Mergelkuhl, and M. Nessi, “The precision laser inclinometer long-term measurement in thermo-stabilized conditions (first experimental data),” Phys. Part. Nucl. Lett. 12, 532–535 (2015).
O. Iwasinska-Kowalska, “A system for precise laser beam angular steering,” Meas. Syst. 21, 27–36 (2014).
I. Buske et al., “A real–time sub–µrad laser beam tracking system,” Proc. SPIE 6738, 67380–1–9 (2007).
Y. Zhu et al., “A piezoelectric unimorph actuator based tip-tilt-piston micromirror with high fill factor and small tilt and lateral shift,” Sens. Actuators A 167, 495–501 (2011).
Y. Yin et al., “Preparation and characterization of unimorph actuators based on piezoelectric Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3 materials,” Sens. Actuators A 171, 332–339 (2011).
L. Germann and J. Braccio, “Fine-steering mirror technology supports 10 nanoradian system,” Opt. Eng. 29, 1351–1359 (1990).
N. Rijnvelda et al., “A tip/tilt mirror with large dynamic range for the ESO VLT four laser guide star facility,” Proc. SPIE 8125, 812503P1 (2011)
Qingkun Zhou et al., “Goldenberg design of fast steering mirror systems for precision laser beams steering,” in Proceedings of the ROSE 2008, IEEE International Workshop on Robotic and Sensors Environments, Ottawa, Canada, Oct. 17–18, 2008.
R. W. Cochran and R. H. Vassar, “Fast steering mirrors in optical control systems,” SPIE Proc. 1303, 245–251 (1990).
https://www.physikinstrumente.com/en/products/z-tiptilt-platforms/piezo-platforms/s-325-piezo-z-tip-tiltplatform-300650/#c16797.
D. Dragan, “Hysteresis in piezoelectric and ferroelectric materials,” in The Science of Hysteresis, Ed. by I. Mayergoyz and G. Bertotti (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2005), Vol. 3, Chap.4.
V. Batusov et al., “Photodetector noise limitations of the laser ray space localization precision,” JINR Preprint E13-2008-90 (JINR, Dubna, 2008).
R. Hedding and R. A. Lewis, “Fast steering mirror design and performance for stabilization and single axis scanning,” Proc. SPIE 1304, 14–24 (2005)
P. Kwee et al., “Laser beam quality and pointing measurement with an optical resonator,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78, 073103 (2007).
G. Stern et al., “Experiments of laser pointing stability in air and in vacuum to validate micrometric positioning sensor,” in Proceedings of 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference IPAC 2014, Dresden, Germany, pp. 1793–1795.
J. Gray, “Laser pointing stability measured by an oblique-incidence optical transmittance difference technique,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 72, 3714–3717 (2001).
N. Azaryan et al., “Comparative analysis of earthquakes data recorded by the innovative precision laser inclinometer instruments and the classic hydrostatic level system,” Phys. Part. Nucl. Lett. 14, 480–492 (2017).
J. Budagov, V. Glagolev, M. Lyablin, G. Shirkov, and H. Mainaud Durand, “Air temperature stabilization in the thermally isolated optical laboratory,” Phys. Part. Nucl. Lett. 11, 294–298 (2014).
N. Azaryan et al., “The innovative method of high accuracy interferometric calibration of the precision laser inclinometer,” Phys. Part. Nucl. Lett. 14, 112–122 (2017).
N. Azaryan et al., “The monitoring of the effects of Earth surface inclination with the precision laser inclinometer for high luminosity colliders,” in Proceedings of the RuPAC 2016, 25th Russian Particle Accelerator Conference, Nov. 21–25, 2016, St. Petersburg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azaryan, N., Budagov, J., Lyablin, M. et al. The compensation of the noise due to angular oscillations of the laser beam in the Precision Laser Inclinometer. Phys. Part. Nuclei Lett. 14, 930–938 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S154747711706022X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S154747711706022X