Abstract
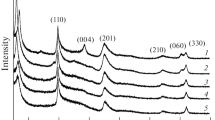
The process of the hydrothermal crystallization of montmorillonite Na2x(Al2(1 – x),Mg2x)-Si4O10(OH)2 · nH2O (0 < x ≤ 1) is studied in a weakly acidic medium with pH 4–4.5 at 220°С using HF as a mineralizer. The results of the study showed that montmorillonite samples in the acidic medium can be obtained both with the use of the HF mineralizer and without it. Under any conditions of carrying out the synthesis, there is an insignificant amount of corundum in the final product. It is established that a weakly acidic medium favors the formation of a dioctahedral structure of smectites with insignificant isomorphic substitutions (0.5 ≤ x ≤ 1). At a higher aluminum content, the acidic medium does not contribute to the formation of two-dimensional silicon-oxygen layers.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Dong, Y. and Feng, S.-S., Poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide)/montmorillonite nanoparticles for oral delivery of anticancer drugs, Biomaterials, 2005, vol. 26, no. 30, pp. 6068–6076.
Joshi, G.V., Patel, H.A., Kevadiya, B.D., and Bajaj, H.C., Montmorillonite intercalated with vitamin B1 as drug carrier, Appl. Clay Sci., 2009, vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 248–253.
Kollar, T., Palinko, I., Konya, Z., and Kiricsi, I., Intercalating amino acid guests into montmorillonite host, J. Mol. Struct., 2003, vols. 651–653, pp. 335–340.
Lee, Y.-H., Kuo, T.-F., Chen, B.-Y., Feng, Y.-K., Wen, Y.-R., Lin, W.-C., and Lin, F.H., Toxicity assessment of montmorillonite as a drug carrier for pharmaceutical applications: Yeast and rats model, Biomed. Eng.: Appl., Basis Commun., 2005, vol. 17, pp. 72–78.
Bukhanov, V.D., Vezentsev, A.I., Ponomareva, N.F., Kozubova, L.A., Korol’kova, S.V., Volovicheva, N.A., and Peristyi, V.A., Antibacterial properties of montmorillonite containing sorbents, Nauch. Vedom., Ser.: Estestv. Nauki, 2011, vol. 111, no. 17, pp. 57–63.
Alexandre, M. and Dubois, Ph., Polymer layered silicate nanocomposites: properties and uses of a new class of materials, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2000, vol. 28, pp. 1–63.
Golubeva, O.Yu., Effect of synthesis conditions on hydrothermal crystallization, textural characteristics and morphology of aluminum-magnesium montmorillonite, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2016, vol. 224, pp. 271–276.
Golubeva, O.Yu., Ul’yanova, N.Yu., Kostyreva, T.G., Drozdova, I.A., and Mokeev, M.V., Synthetic nanoclays with the structure of montmorillonite: preparation, structure, and physico-chemical properties, Glass Phys. Chem., 2013, vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 535–539.
Reinholdt, M., Miehe-Brendle, J., Delmotte, L., Tuolier, M.-H., Dred, R.-E., Cortes, R., and Flank, A.-M., Fluorine route synthesis of montmorillonite containing Mg or Zn and characterization by XRD, thermal analysis, MAS NMR, and EXAFS spectroscopy, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2001, pp. 2831–2841.
Reinholdt, M., Miehe-Brendle, J., Delmotte, L., Le Dred, R., and Tuilier, M.H., Synthesis and characterization of montmorillonite-type phyllosilicates in a fluoride medium, Clay Miner., 2005, vol. 40, pp. 177–190.
Jaber, M. and Miehe-Brendle, J., Synthesis, characterization and applications of 2 : 1 phyllosilicates: contribution of fluoride to study the octahedral sheet, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2008, vol. 107, pp. 121–127.
Iler, R.K., Colloid Chemistry of Silica and Silicates, Ithaca: Cornell Univ. Press, 1955.
Iler, R.K., Chemistry of Silica. Solubility, Polymerization, Colloid and Surface Properties and Biochemistry of Silica, Chichester: Wiley, 1979.
Kukovskii, E.G., Osobennosti stroeniya i fiziko-khimicheskie svoistva glinistykh mineralov (Features of Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Clay Minerals), Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1996.
Komarov, V.S., Adsorbtsionno-strukturnye, fiziko-khimicheskie i kataliticheskie svoistva glin Belorussii (Adsorption-Structural, Physicochemical and Catalytic Properties of Clays of Belarus), Minsk: Nauka Tekhnika, 1970.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
I am grateful to the employees of the analytical group of the Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Glass, Grebenshchikov Institute of Silicate Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, T.G. Kostyreva, L.N. Kurilenko, and L.A. Doronina, for the chemical analysis of the samples.
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 18-03-00156).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by L. Mosina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golubeva, O.Y. Features of the Hydrothermal Synthesis of Montmorillonite in an Acidic Medium. Glass Phys Chem 44, 616–619 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659618060081
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1087659618060081