Abstract
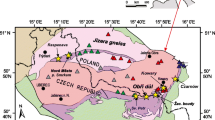
For the first time, from the standpoint of magmatism and subsequent hydrothermal–metasomatic alteration, sulfide and platinum-metal mineral assemblages of rocks of ore-bearing intrusions of the Khudolaz Complex have been characterized. Four types of assemblages have been identified: (1) pentlandite–chalcopyrite–pyrrhotite in the form of drop-shaped and interstitial disseminations with inclusions of sperrylite, moncheite, michenerite, merenskyite, froodite; (2) complex amoebalike inclusions with the composition pyrite ± pyrrhotite–chalcopyrite–violarite ± pentlandite with inclusions of Sb–michenerite, sudburyite, and borovskite; (3) newly formed pyrite–chalcopyrite veins and patches in intensely metasomatized rocks; (4) additionally-formed euhedral pyrite disseminations in metasomatites along zones intersected by dolerite dikes. The formation of these sulfide–platinum-metal assemblages occurred in three stages: (1) magmatic and late magmatic (type 1), 2) hydrothermal–early medium temperature and late low-temperature (types 2, 3), (3) repeated hydrothermal–low–medium temperature (type 4). It is shown that the crystallization of sulfide minerals occurred in a wide temperature range (about 1000–200°C). PGE minerals separated at the late magmatic stage during cooling of a highly fractionated sulfide or immiscible chalcogenide melt and during decomposition of sulfide solid solutions (T ~ 650–300°C). At the early hydrothermal stage (T ~ 300–250°C), pyrrhotite was replaced by pyrite; pentlandite, by violarite; a significant amount of Ni and Co from primary sulfides was inherited by secondary sulfides. Primary chalcopyrite was mainly replaced by silicates (chlorite, amphibole, etc.). It is suggested that the antimony minerals of Pd (including high-antimony michenerite with Sb up to 0.46 apfu) could have crystallized from an Sb-enriched hydrothermal fluid. Host rocks could have been an additional source of antimony in the fluid. At the late hydrothermal stage (T < 200°C), significant dissolution of primary sulfide and platinum-metal phases occurred with redeposition in the upper parts of massifs and in host rocks. The recurring hydrothermal process (T ≤ 200°C) was associated with emplacement of dikes of the Ulugurtau complex and new redeposition of sulfides along zones of fluid action.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Buchkovsky, E.S., Perminov, G.M., Krestinin, B.A., Karavaev, I.N., and Petrov, Yu.N., Assessment of the nickel content of the main intrusions of the Khudolazovsky Complex, Report on the Khudolaz syncline. Scale 1 : 50000 of sulfide copper–nickel ores, Ufa: GosGeolFond, 1974f, vol 1.
Zakharova, A.A., Petrology and metallogeny of the Early Carboniferous gabbro-plagiogranite formation on the eastern slope of the Southern Urals (Khudolaz Complex), Scientific report on the topic “Formation conditions and metamorphism of magmatogenic complexes of the Southern Urals, Ufa: IG BF AN SSSR, 1982f, vol 1.
REFERENCES
Arpalahti, A. and Lundstrom, M., The leaching behavior of minerals from a pyrrhotite–rich pentlandite ore during heap leaching, Minerals Eng., 2018, vol. 119, pp. 116–125.
Ballhaus, C. and Ulmer, P., Platinum-group elements in the Merensky Reef: II. Experimental solubilities of platinum and palladium in Fe1 – xS from 950 to 450°C under controlled fS2 and fH2, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1995, vol. 59, no. 23, pp. 4881–4888.
Barnes, S.J. and Liu, W., Pt and Pd mobility in hydrothermal fluids: evidence from komatiites and from thermodynamic modelling, Ore Geol. Rev, 2012, vol. 44, pp. 49–58.
Cabri, L.J. and Harris, D.C., Michenerite (PdBiTe) redefined and froodite (PdBi2) confirmed from the Sudbury area, Can. Mineral., 1973, vol. 11, pp. 903–912.
Cabri, L.J. and LaFlamme, G.J.H., The mineralogy of the platinum–group elements from some copper–nickel deposits of the Sudbury area, Ontario, Econ. Geol., 1976, vol. 71, pp. 1159–1195.
Cafagna, F. and Jugo, P.J., An experimental study on the geochemical behavior of highly siderophile elements (HSE) and metalloids (As, Se, Sb, Te, Bi) in a mss–iss–pyrite system at 650°C: a possible magmatic origin for Co–HSE-bearing pyrite and the role of metalloid-rich phases in the fractionation of HSE, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2016, vol. 178, no. 1, pp. 233–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2015.12.035
Campos–Alvarez, N.O., Samson, I.M., and Fryer, B.J., The roles of magmatic and hydrothermal processes in PGE mineralization, Ferguson Lake deposit, Nunavut, Canada, Miner. Deposita, 2012, vol. 47, no. 4, pp. 441–465.
Chelle–Michou, C. and Chiaradia, M., Amphibole and apatite insights into the evolution and mass balance of Cl and S in magmas associated with porphyry copper deposits, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2017, vol. 172, no. 11, p. 105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-017-1417-2
Childs, J.D. and Hall, S.R., The crystal of michenerite, PdBiTe, Can. Mineral., 1973, vol. 12, pp. 61–65.
Crerar, D.A., Susak, N.J., Borcsik, M., and Schwartz, S., Solubility of the buffer assemblage pyrite + pyrrhotite + magnetite in NaCl solutions from 200 to 350°C, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1978, vol. 42, no. 9, pp. 1427–1437.
Dare, S.A.S., Barnes, S.–J., and Prichard, H.M., The distribution of platinum group elements (PGE) and other chalcophile elements among sulfides from the Creighton Ni–Cu–PGE sulfide deposit, Sudbury, Canada, and the origin of palladium in pentlandite, Miner. Deposita, 2010, vol. 45, pp. 765–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-010-0295-6
Duran, C.J., Barnes, S.–J., and Corkery, J.T., Geology, petrography, geochemistry, and genesis of sulfide-rich pods in the Lac Des Iles palladium deposits, Western Ontario, Canada, Miner. Deposita, 2016, vol. 51, pp. 509–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-015-0622-z
Durazzo, A. and Taylor, L.A., Exsolution in the mss–pentlandite system: textural and genetic implications for Ni–sulfide ores, Miner. Deposita, 1982, vol. 17, pp. 313–332.
Etschmann, B., Pring, A., Putnis, A., Grguric, B.A., and Studer, A., A kinetic study of the exsolution of pentlandite (Ni,Fe)9S8 from the monosulfide solid solution (Fe, Ni)S, Am. Mineral., 2004, vol. 89, no. 1, pp. 39–50. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2004-0106
Garuti, G., Fiandri, P., and Rossi, A., Sulfide composition and phase relations in the Fe–Ni–Cu ore deposits of the Ivrea–Verbano basic complex (Western Alps, Italy), Miner. Deposita, 1986, vol. 21, pp. 22–34.
Haluzová, E., Ackerman, L., Pašava, J., Jonašova, Š., Svojtka, M., Hrstka, T., and Veselovský, F., Geochronology and characteristics of Ni–Cu–(PGE) mineralization at Rozany, Lusatian granitoid complex, Czech Republic, J. Geosci., 2015, vol. 60, pp. 219–236. https://doi.org/10.3190/jgeosci.204
Helmy, H.M., Ballhaus, C., Berndt, J., Bockrath, C., and Wohlgemuth–Ueberwasser, C., Formation of Pt, Pd and Ni tellurides: experiments in sulfide–telluride systems, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2007, vol. 153, pp. 577–591.
Helmy, H.M., Ballhaus, C., Wohlgemuth–Ueberwasser, C., Fonseca, R.O.C., and Laurenz, V., Partitioning of Se, As, Sb, Te and Bi between monosulfide solid solution and sulfide melt –application to magmatic sulfide deposits, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2010, vol. 74, pp. 6174–6179.
Helmy, H.M. and Fonseca, R.O.C., The behavior of Pt, Pd, Cu and Ni in the Se-sulfide system between 1050 and 700°C and the role of se in platinum-group elements fractionation in sulfide melts, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2017, vol. 216, no. 1, pp. 141–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2017.05.010
Holwell, D.A., Zeinab, A., Warda, L.A., Smith, D.J., Graham, S.D., McDonald, I., and Smith, J.W., Low temperature alteration of magmatic Ni–Cu–PGE sulfides as a source for hydrothermal Ni and PGE ores: a quantitative approach using automated mineralogy, Ore Geol. Rev., 2017, vol. 91, pp. 718–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.08.025
Ivanyuk, G.Yu., Pakhomovsky, Ya.A., Panikorovskii, T.L., Mikhailova, J.A., Kalashnikov, A.O., Bazai, A.V., Yakovenchuk, V.N., Konopleva, N.G., and Goryainov, P.M., Three–D mineralogical mapping of the Kovdor phoscorite–carbonatite complex, NW Russia: II. Sulfides, Minerals, 2018, vol. 8, no. 7, p. 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8070292
Junge, M., Wirth, R., Oberthür, T., Melcher, F., and Schreiber, A., Mineralogical siting of platinum-group elements in pentlandite from the bushveld complex, South Africa, Miner. Deposita, 2015, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 41–54.
Kholodnov, V.V., and Bushlyakov, I.N., Galogeny v endogennom rudoobrazovanii (Halogens in Endogenous Ore Formation), Yekaterinburg: UrO RAN, 2002.
Kullerud, G., Monoclinic pyrrhotite, Bull. Geol. Soc. Finland, 1986, vol. 58, pp. 293–305.
Liu, W., Migdisov, A., and Williams–Jones, A., The stability of aqueous nickel (II) chloride complexes in hydrothermal solutions: results of UV–visible spectroscopic experiments, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2012, no. 94, pp. 276–290.
Liu, Y. and Brenan, J., Partitioning of platinum-group elements (PGE) and chalcogens (Se, Te, As, Sb, Bi) between monosulfide–solid solution (mss), intermediate solid solution (iss) and sulfide liquid at controlled fO2–fS2 conditions, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2015, vol. 159, pp. 139–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2015.03.021
Lu, Z.Y., Jeffrey, M.I., Zhu, Y., and Lawson, F., Studies of pentlandite leaching in mixed oxygenatedacidic chloride–sulfate solutions, Hydrometallurgy, 2000, vol. 56, pp. 63–74.
Marakushev, A.A., Thermodynamic principles of the formation of chemical element paragenesis in processes of deep mineral formation, Ocherki Fiz.–Khim. Petrol. 1975, vol. 5, pp. 121–125.
Maslov, V.A. and Artyushkova, O.V., Stratigrafiya i korrelyatsiya devonskikh otlozhenii Magnitogorskoi megazony Yuzhnogo Urala (Stratigraphy and Correlation of Devonian Sediments of the Magnitogorsk Megazone, South Urals), Ufa: DizainPoligrafServis, 2010.
Misra, K.C. and Fleet, M.E., Chemical composition and stability of violarite, Econ. Geol., 1974, vol. 69, pp. 391–403.
Morimoto, N., Gyobu, A., Mukaiyama, H., and Izawa, E., Crystallography and stability of pyrrhotites, Econ. Geol., 1975, vol. 70, no. 4, pp. 824–833.
Mountain, B.W. and Wood, S.A., Chemical controls on the solubility, transport, and deposition of platinum and palladium in hydrothermal solutions: a thermodynamic approach, Econ. Geol., 1988, vol. 83, pp. 492–510.
Naldrett, A.J., From the mantle to the bank: the life of a Ni–Cu–(PGE) sulfide deposit, S. Afr. J. Geol, 2010, vol. 113, no. 1, pp. 1–32.
Nickel, E.H., Ross, J.R., and Thornber, M.R., The supergene alteration of pyrrhotite–pentlandite ore at Kambalda, Western Australia, Econ. Geol., 1974, vol. 69, pp. 93–107.
Nozaki, H., Onoda M., and Kosuda K. Crystal structures and galvanomagnetic properties of epitaxial films in a Ni–S system, Progress in Solid State Chemistry Research, Buckley. R.W., Ed., Nova Science Publishers, 2007, pp. 239–284.
Ohmoto, H. and Rye, R.O., Isotopes of sulfur and carbon, Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits, Barnes, H.L., Ed., 2nd ed. New York: Wiley, 1979, pp. 509–567.
Pan, L.-C., Hu, R.-Z., Wang, X.-S., Bi, X.-W., Zhu, J.-J., and Li, C., Apatite trace element and halogen compositions as petrogenetic–metallogenic indicators: examples from four granite plutons in the Sanjiang Region, SW China, Lithos, 2016, vol. 254–255, pp. 118–130.
Pašava, J., Vavřín, I., Frýda, J., Janoušek, V., and Jelínek, E., Geochemistry and mineralogy of platinum-group elements in the Ransko gabbro–peridotite massif, Bohemian massif (Czech Republic), Miner. Deposita, 2003, vol. 38, pp. 298–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-002-0343-y
Peng, G., Luhr, J.F., and McGee, J.J., Factors controlling sulfur concentrations in volcanic apatite, Am. Mineral., 1997, vol. 82, pp. 1210–1224.
Qian, G., Xia, F., Brugger, J., Skinner, W.S., Bei, J., Chen, G., and Pring, A., Replacement of pyrrhotite by pyrite and marcasite under hydrothermal conditions up to 220°C: an experimental study of reaction textures and mechanisms, Am. Mineral., 2011, vol. 96, pp. 1878–1893.
Rakhimov, I.R., Geology, Petrology, and Ore Potential of the Late Devonian—Carboniferous intrusive magmatism of the Western–Magnitogors zone of the South Urals, Extended Abstract of Candidate’s (Geol.-Min.) Dissertation, Ufa, 2017.
Rakhimov, I.R., Mineralogy and main petrological aspects of the Malyutka massif, of the Khudolaz Complex, South Urals, Vestn. Geonauk, 2020, no. 1, pp. 8–18.
Rakhimov, I.R., Ankusheva, N.N., and Kholodnov, V.V., Co–Pd–Ag and Th–REE mineralization of host rocks of the exocontact zone of the Tashly–Tau massif of the Khudolaz Complex (South Urals): conditions of formation and sources, Izv. Tomsk. Politekhn. Univ., 2020, vol. 331, no. 8, pp. 77–91.
Rakhimov, I.R. and Kholodnov, V.V., Accessory apatite from metasomatized rocks of the ore-bearing and barren massifs of the Khudolazh Complex: morphological features and chemical composition, Geol. Izv. Otd. Nauk Zemle Prir. Res AN RB, 2019, vol. 26. pp. 29–36.
Rakhimov, I.R., Vishnevskiy, A.V., Vladimirov, A.G., Savel’ev, D.E., Puchkov, V.N., and Salikhov, D.N., First finds of platinum and palladium minerals in sulfide ores of the Khudolaz Intrusive Complex (Southern Urals), Dokl. Earth Sci., 2018, vol. 479, no. 2, pp. 439–442.
Sadove, G., Konecke, B.A., Fiege, A., and Simon, A.C., Structurally bound S2−, S1−, S4+, S6+ in terrestrial apatite: the redox evolution of hydrothermal fluids at the Phillips mine, New York, USA, Ore Geol. Rev., 2019, vol. 107, pp. 1084–1096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.03.033
Salikhov, D.N. and Pshenichnyi, G.N., Magmatizm i orudenenie zony rannei konsolidatsii Magnitogorskoi evgeosinklinali (Magmatism and Mineralization of the early consolidation zone of the Magnitogorsk Eugeosyncline), Ufa: BFAN SSSR, 1984. 112 s.
Smith, J.W., Holwell, D.A., McDonald, I., and Boyce, A.J., The application of s isotopes and S/Se ratios in determining ore–forming processes of magmatic Ni–Cu–PGE sulfide deposits: a cautionary case study from the Northern Bushveld Complex, Ore Geol. Rev., 2016, no. 73, pp. 148–174.
Spiridonov, E.M., Kulagov, E.A., Serova, A.A., Kulikova, I.M., Korotaeva, N.N., Sereda, E.V., Tushentsova, I.N., Belyakov, S.N., and Zhukov, N.N., Genetic Pd, Pt, Au, Ag, and Rh mineralogy in Noril’sk sulfide ores, Geol Ore Deposits, 2015,vol. 57, no. 5, pp. 402–432.
Suárez, S., Prichard, H.M., Velasco, F., Fisher, P.C., and McDonald, I., Alteration of platinum-group minerals and dispersion of platinum-group elements during progressive weathering of the Aguablanca Ni–Cu deposit, SW Spain, Miner. Deposita, 2010, vol. 45, pp. 331–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-009-0275-x
Sugaki, A. and Kitakaze, A., High form of pentlandite and its thermal stability, Am. Mineral., 1998, vol. 83, no. 1, pp. 133–140.
Tenailleau, C., Pring, A., Etschmann, B., Brugger, J., Grguric, B., and Putnis, A., Transformation of pentlandite to violarite under mild hydrothermal conditions, Am. Mineral., 2006, vol. 91, pp. 706–709. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2006.2131
Tolstykh, N.D., Orsoev, D.A., Krivenko, A.P., and Izokh, A.E., Blagorodnometall’naya mineralizatsiya v rassloennykh ul’trabazit–bazitovykh massivakh yuga Sibirskoi platformy (Noble-Metal Mineralization in Layered Ultramafic–Mafic Massifs, Southern Siberian Platform), Novosibirsk: Parallel’, 2008.
Tuba, G., Molnar, F., Ames, D.E., Péntek, A., Watkinson, D.H., and Jones, P.C., Multi–stage hydrothermal processes involved in “low–sulfide” Cu(–Ni)–PGE mineralization in the footwall of the Sudbury Igneous Complex (Canada): Amy Lake PGE zone, East Range, Mineral. Deposita, 2014, vol. 49, pp. 7–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-013-0468-1
Valsami–Jones, E., Ragnarsdottir, K.V., Putnis, A., Bosbach, D., Kemp, A.J., and Cressey, G., The dissolution of apatite in the presence of aqueous metal cations at pH 2–7, Chem. Geol., 1998, vol. 151, pp. 215–233.
Wood, S.A. and Mountain, B.W., Thermodynamic constraints on the solubility of platinum and palladium in hydrothermal solutions: reassessment of hydroxide, bisulfide, and ammonia complexing, Econ. Geol., 1989, vol. 84, pp. 2020–2028.
Wu, C.–Z., Xie, S.–W., Gu, L.–X., Samson, I.M., Yang, T., Lei, R.–X., Zhu, Z.–Y., and Dang, B., Shear zone-controlled post-magmatic ore formation in the Huangshandong Ni–Cu sulfide deposit, NW China, Ore Geol. Rev., 2018, vol. 100, pp. 545–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.015
Xia, F., Brugger, J., Chen, G., Ngothai, Y., O’Neill, B., Putnis, A., and Pring, A., Mechanism and kinetics of pseudomorphic mineral replacement reactions: a case study of the replacement of pentlandite by violarite, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2009, vol. 73, pp. 1945–1969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2009.01.007
Zhu, W.–G., Zhong, H., Hu, R.–Z., Liu, B.–G., He, D.–F., Song, X.–Y., and Deng, H.–L., Platinum–group minerals and tellurides from the PGE-bearing Xinjie layered intrusion in the Emeishan large igneous province, SW China, Mineral. Petrol., 2010, vol. 98, pp. 167–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-009-0077-y
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to the reviewers (M.A. Yudovskaya and E.V. Belogub) for critical remarks that improved the quality of the article.
Funding
The research was carried out with the financial support of the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 18-35-00391) and the state task of IG UFRC RAS (topic no. 0246-2019-0080).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakhimov, I.R., Vishnevskiy, A.V., Saveliev, D.E. et al. Multi-Stage Magmatic-Hydrothermal Sulfide-PGE Mineralization of the Khudolaz Complex (South Urals). Geol. Ore Deposits 63, 341–367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1075701521040061
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1075701521040061