Abstract
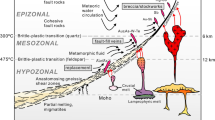
The microprobe and thermomagnetic data for native iron in terrestrial rocks (xenoliths from mantle hyperbasites, Siberian traps, and oceanic basalts) are generalized and compared to the data for native iron from sediments and meteorites. It is found that the native iron particles contained in the continental and oceanic hyperbasites and basites are similar in composition, shape, and grain size. These particles are predominantly nickel-free and similar to the extraterrestrial iron from sediments and meteorites. This similarity suggests the similar sources of origin of these particles. This means that the terrestrial conditions were close to the conditions that existed at the source planets of the meteorites, e.g., the bodies from the asteroid belt which have been subsequently disintegrated, and crushed into cosmic interplanetary dust, which has entered the terrestrial sediments. This similarity originates from the homogeneity of the gasdust cloud at the early stage of the Solar System. The predominance of extraterrestrial native iron in sediments is accounted for by the fact that the interplanetary dust is mainly contributed by the material from the upper mantle of the source planets of cosmic dust.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Florenskii, K.P., On the initial stage of differentiation of the Earth’s matter, Geokhimiya, 1965, no. 8, pp. 1–18.
Grachev, A.F., Kollmann, H.A., Korchagin, O.A., et al., The K/T boundary of Gams (Eastern Alps, Austria) and the nature of terminal Cretaceous mass extinction, Abhandlungen der geologischen bundesanstalt, Grachev, A.F., Ed., 2009, vol. 69, pp. 89–134.
Hubbard, W., Planetary Interiors, New York: Van Nostrand, 1984.
Korchagin, O.A., Tsel’movich, V.A., Pospelov, I.I., and Bian Qiantao, Cosmic magnetite microspherules and metallic particles near the Permian–Triassic boundary in a global stratotype section and point (stratum 27, Meishan, China), Dokl. Earth Sci., 2010, vol. 432, no. 1, pp. 631–637.
Korchagin, O.A., Fossil micrometeorites, microtectites, and microcrystites: methods for studying, classification, and impact–stratigraphic scale, in Stratigrafiya v nachale XXI veka—tendentsii i novye idei. Ocherki po regional’noi geologii Rossii (Stratigraphy at the Beginning of XXI Century: Trends and New Ideas. Essays on Regional Geology of Russia), Moscow: Geolkart-GEOS, 2013, vol. 6, pp. 112–142.
Marakushev, A.A., Granovskii, L.B., and Zinov’eva, N.G., Kosmicheskaya petrologiya (Cosmic Petrology), Moscow: MGU, 1992.
Markov, G.P., Pechersky, D.M., and Tsel’movich, V.A., Magnetic minerals of the Chelyabinsk meteorite, Sol. Sys. Res., 2015, in press.
McFadden, L., Weissman, P.R., and Johnson, T.V., Encyclopedia of the Solar System, 2nd ed., San Diego: Academic, 2007.
Pechersky, D.M., Bagin, V.I., Brodskaya, S.Yu., and Sharonova, Z.V., Magnetizm i usloviya obrazovaniya izverzhennykh porod (Magnetism and Formation Conditions of Igneous Rocks), Moscow: Nauka, 1975.
Pechersky, D.M., Grachev, A.F., Nourgaliev, D.C., Tselmovich, V.A., and Sharonova, Z.V., Magnetolithologic and magnetomineralogical characteristics of deposits at the Mesozoic/Cenozoic boundary: Gams section (Austria), Russ. J. Earth Sci, 2006, vol. 8, no. 3, ES3001. doi 10.2205/2006ES000204
Pecherskii, D.M., Nurgaliev, D.K., and Sharonova, Z.V., Magnetolithologic and magnetomineralogical characteristics of sediments at the Mesozoic/Cenozoic boundary: the Koshak section (Mangyshlak peninsula), Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2006, vol. 42, no. 11, pp. 957–970.
Pecherskii, D.M., Asanidze, B.Z., Nurgaliev, D.K., and Sharonova, Z.V., Petromagnetic and paleomagnetic characterization of Mesozoic/Cenozoic deposits: the Tetritskaro section (Georgia), Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2009, vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 134–149.
Pechersky, D.M., Metallic iron and nickel in Cretaceous and Cenozoic sediments: the results of thermomagnetic analysis, J. Environ. Prot., 2010, vol. 1, pp. 143–154.
Pecherskii, D.M., Nurgaliev, D.K., Fomin, V.A., Sharonova, Z.V., and Gil’manova, D.M., Extraterrestrial iron in the Cretaceous–Danian sediments, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2011, vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 379–401.
Pechersky, D.M., Samorodnoe zhelezo i drugie magnitnye mineraly v osadkakh: termomagnitnye priznaki kosmicheskogo proiskhozhdeniya (Native Iron and Other Magnetic Minerals in Sediments: Thermomagnetic Signs of Extraterrestrial Origin), Saarbrücken: Palmarium Academic Publishing, 2012.
Pechersky, D.M., Markov, G.P., Tsel’movich, V.A., and Sharonova, Z.V., Extraterrestrial magnetic minerals, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2012, vol. 48, nos. 7–8, pp. 653–670.
Pechersky, D.M. and Sharonova, Z.V., Thermomagnetic evidence of native iron in sediments, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2012, vol. 48, no. 4, pp. 320–325.
Pechersky, D.M. and Sharonova, Z.V., A relationship between the concentration of native iron particles in sediments and the rate of their accumulation: a synthesis of thermomagnetic data, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2013, vol. 49, no. 5, pp. 718–724.
Pecherskii, D.M., Gil’manova, D.M., Markov, G.P., Murdmaa, I.O., Nurgaliev, D.K., Tsel’movich, V.A., and Sharonova, Z.V., Native iron and other magnetic minerals in the sediments of the Northwestern Atlantic: thermomagnetic and microprobe evidence, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2013a, vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 426–448.
Pecherskii, D.M., Gil’manova, D.M., Ivanov, E.V., Kuz’min, M.I., Markov, G.P., Nurgaliev, D.K., and Tsel’movich, V.A., Native iron in the sediments of Lake Baikal (borehole BDP-98): results of thermomagnetic analysis, Rus. Geol. Geophys., 2013b, no. 9.
Pechersky, D.M., Gil’manova, D.M., Kazansky, A.Yu., Krivonogov, S.K., Nurgaliev, D.K., and Tsel’movich, V.A., Native iron in Quaternary deposits of the Darkhad Basin (northern Mongolia), Rus. Geol. Geophys., 2013c, no. 12.
Pechersky, D.M. and Kuzina, D.M., Nickel-Free Iron Particles in Sediments, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2015, in press.
Petromagnitnaya model’ litosfery (Petromagnetic Model of the Lithosphere), Pashkevich, I.K. and Pechersky, D.M, Ed., Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1994.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.M. Pechersky, D.M. Kuzina, D.K. Nurgaliev, V.A. Tsel’movich, 2015, published in Fizika Zemli, 2015, No. 5, pp. 140–155.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pechersky, D.M., Kuzina, D.M., Nurgaliev, D.K. et al. The common nature of native iron in terrestrial rocks and meteorites: Microprobe and thermomagnetic data. Izv., Phys. Solid Earth 51, 748–763 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1069351315050109
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1069351315050109