Abstract
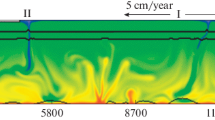
In the kinematic theory of lithospheric plate tectonics, the position and parameters of the plates are predetermined in the initial and boundary conditions. However, in the self-consistent dynamical theory, the properties of the oceanic plates (just as the structure of the mantle convection) should automatically result from the solution of differential equations for energy, mass, and momentum transfer in viscous fluid. Here, the viscosity of the mantle material as a function of temperature, pressure, shear stress, and chemical composition should be taken from the data of laboratory experiments. The aim of this study is to reproduce the generation of the ensemble of the lithospheric plates and to trace their behavior inside the mantle by numerically solving the convection equations with minimum a priori data. The models demonstrate how the rigid lithosphere can break up into the separate plates that dive into the mantle, how the sizes and the number of the plates change during the evolution of the convection, and how the ridges and subduction zones may migrate in this case. The models also demonstrate how the plates may bend and break up when passing the depth boundary of 660 km and how the plates and plumes may affect the structure of the convection. In contrast to the models of convection without lithospheric plates or regional models, the structure of the mantle flows is for the first time calculated in the entire mantle with quite a few plates. This model shows that the mantle material is transported to the mid-oceanic ridges by asthenospheric flows induced by the subducting plates rather than by the main vertical ascending flows rising from the lower mantle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albarede, F. and van der Hilst, R.D., Zoned mantle convection, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, 2002, vol. A360, pp. 2569–2592.
Andrews, E. and Billen, M., Rheologic controls on the dynamics of slab detachment, Tectonophysics, 2009, vol. 464, pp. 60–69.
Becker, T., A numerical study on the effects of surface boundary condition and rheology on slab dynamics, Bollettino di Geofisica, 2008, vol. 49, pp. 177–182.
Bercovici, D., Plate generation in a simple-model of lithosphere-mantle flow with dynamic self-lubrication, Tectonophysics, 1996, vol. 144, pp. 41–51.
Bonnardot, M.-A., Hassani, R., and Tric, E., Numerical modelling of lithosphere-asthenosphere interaction in a subduction zone, Tectonophysics, 2008, vol. 272, pp. 698–708.
Crameri, F., Tackley, P.J., Meilick, I., Gerya, T.V., and Kaus, B.J.P., A free plate surface and weak oceanic crust produce single-sided subduction on Earth, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2012, vol. 39, L03306. doi: 10.1029/2011GL050046
Evans, R.L., Hirth, G., Baba, K., Forsyth, D., Chave, A., and Mackie, R., Geophysical evidence from the melt area for compositional controls on oceanic plates, Nature, 2005, vol. 437, pp. 249–252.
Foley, B.J. and Becker, T.W., Generation of plate-like behavior and mantle heterogeneity from a spherical, viscoplastic convection model, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 2009, vol. 10, Q08001. doi: 10.1029/2009GC002378
Gerya, T. and Stockhert, B., Two-dimensional numerical modeling of tectonic and metamorphic histories at active continental margins, Int. J. Earth Sci. (Geologische Rundschau), 2006, vol. 95, pp. 250–274.
Gerya, T.V., Connolly, J.A.D., and Yuen, D.A., Why is terrestrial subduction one-sided?, Geology, 2008, vol. 36, pp. 43–46.
Grigne, C., Labrosse, S., and Tackley, P.J., Convection under a lid of finite conductivity: heat flux scaling and application to continents, J. Geophys. Res., 2007, vol. 112, p. B08402. doi: 10.1029/2005JB004192
Hirth, G. and Kohlstedt, D.L., Water in the oceanic mantle: implications for rheology, melt extraction, and the evolution of the lithosphere, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1996, vol. 144, pp. 93–108.
Hirth, G., Laboratory constraints on the rheology of the upper mantle, in: Plastic Deformation of Minerals and Rocks, Karato, S.I. and Wenk, H.R., Eds., Washington: Mineralogical Society of America, 2003, vol. 51, pp. 97–116.
Karason, H. and van der Hilst, R.D., Constraints on mantle convection from seismic tomography, in The History and Dynamics of Global Plate Motion, Richards, M.R., Gordon, R., and van der Hilst, R.D., Eds., Washington: American Geophysical Union, 2000, vol. 121, pp. 277–288.
Karato, S., Deformation of Earth Materials, Cambridge: Cambridge Univ., 2008.
Kaus, B.J.P. and Becker, T.W., A numerical study on the effects of surface boundary condition and rheology on slab dynamics, Bollettino di Geofisica, 2008, vol. 49, pp. 177–182.
Kneller, E., Keken, P., Karato, Sh., and Park, J., B-type olivine fabric in the mantle wedge: insights from high resolution non-newtonian subduction zone models, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2005, vol. 237, pp. 781–797.
Korenaga, J., Thermal cracking and the deep hydration of oceanic lithosphere: a key to the generation of plate tectonics?, J. Geophys. Res., 2007, vol. 112, p. B05408. doi: 10.1029/2006JB004502
Korenaga, J. and Karato, S., A new analysis of experimental data on olivine rheology, J. Geophys. Res., 2008, vol. 113, B02403. doi: 10.1029/2007JB005100
Korenaga, J., Scaling of plate tectonic convection with pseudoplastic rheology, J. Geophys. Res., 2010, vol. 115, B11405. doi: 10.1029/2010JB007670
Lay, Th., Hernlund, J., and Buffett, B., Core-mantle boundary heat flow, Nat. Geosci., 2008, vol. 1, pp. 25–32.
McNamara, A., Karato, Sh., and Keken, P., Localization of dislocation creep in the lower mantle: implication for the origin of seismic anisotropy, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2001, vol. 191, pp. 85–99.
Moresi, L.N., Zhong, Sh., and Gurnis, M., The accuracy of finite elements of stokes’ flow with strong varying viscosity, Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., 1996, vol. 97, pp. 83–94.
Moresi, L.N. and Solomatov, V., Mantle convection with a brittle lithosphere: thoughts on the global tectonic styles of the Earth and Venus, Geophys. J. Int., 1998, vol. 133, pp. 669–682.
O’Neill, C., Lenardic, A., Moresi, L., Torsvik, T.H., and Lee, C., Episodic Precambrian subduction, Earth Planet Sci. Lett., 2007, vol. 262, pp. 552–562.
O’Neill, C., Lenardic, A., and Jellinek, A., Plate tectonics or not: lithospheric stress on terrestrial planets and super Earths, in Lunar Planet. Sci., 2008, vol. 38.
Parsons, B. and McKenzie, D., Mantle convection and the thermal structure of the plates, J. Geophys. Res., 1978, vol. 83, no. B9, pp. 4485–4496.
Paulson, A., Zhong, Sh., and Wahr, J., Modelling post-glacial rebound with lateral viscosity variations, Geophys. J. Int., 2005, vol. 163, pp. 357–371.
Petitjean, S., Rabinowicz, M., Gregoire, M., and Chevrot, S., Differences between Archean and Proterozoic lithospheres: assessment of the possible major role of thermal conductivity, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 2006, vol. 7, pp. 1–26.
Richards, M.A., Yang, W.S., Baumgardner, J.R., and Bunge, H.P., Role of a low viscosity zone in stabilizing plate tectonics: implications for comparative terrestrial planetology, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 2001, vol. 2, no. 8, GC000115.
Schubert, G., Turcotte, D.L., and Olson, P., Mantle Convection in the Earth and Planets, Cambridge: Cambridge Univ., 2001.
Stocker, R.L. and Ashby, M.F., On the rheology of the upper mantle, Rev. Geophys., 1977, vol. 11, pp. 391–426.
Tackley, P.J., Self-consistent generation of tectonic plates in three-dimensional mantle convection, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1998, vol. 157, pp. 9–22.
Tackley, P.J., Self-consistent generation of tectonic plates in time-dependent, three-dimensional mantle convection simulations. 1. Pseudoplastic yielding, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 2000a, vol. 1, p. 1021. doi: 10.1029/2000GC000036
Tackley, P.J., Self-consistent generation of tectonic plates in time-dependent, three-dimensional mantle convection simulations. 2. Strain weakening and asthenosphere, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 2000b, vol. 1, p. 1026. doi: 10.1029/2000GC000043
Tagawa, M., Nakakuki, T., and Fumiko, T., Dynamical modeling of trench retreat driven by the slab interaction with the mantle transition zone, Earth Planets Space, 2007, vol. 59, pp. 65–74.
Tan, E., Choi, E., Thoutireddy, P., Gurnis, M., and Aivazis, M., Geoframework: coupling multiple models of mantle convection within a computational framework, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 2006, vol. 7, Q06001. doi: 10.1029/2005GC001155
Tosi, N. and Yuen, D., Bent-shaped plumes and horizontal channel flow beneath the 660 km discontinuity, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2011, vol. 312, pp. 348–359.
Trompert, R. and Hansen, U., Mantle convection simulations with rheologies that generate platelike behavior, Nature, 1998, vol. 395, pp. 686–689.
Trubitsyn, V.P., Principles of the tectonics of floating continents, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2000, vol. 36, no. 9, pp. 708–741.
Trubitsyn, V.P. and Rykov, V.V., A numerical evolutionary model of interacting continents floating on a spherical Earth, Russ. J. Earth Sci., 2001, vol. 3, no. 2. doi: 20.2205/2001ES000057
Trubitsyn, V.P., Mooney, W.D., and Abbott, D.A., Cool cratons and thermal blankets: how continents affect mantle convection, Int. Geol. Review, 2003, vol. 45, pp. 479–496.
Trubitsyn, V.P., Evolutionary models of floating continents, Russ. J. Earth Sci., 2004, vol. 6, no. 5. doi: 10.2205/2004ES000147
Trubitsyn, V.P., The tectonics of floating continents, Herald Russ. Acad. Sci., 2005, no. 1, pp. 7–18.
Trubitsyn, V.P., Geodynamic model of the evolution of the Pacific Ocean, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2006, vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 93–114.
Trubitsyn, V., Kaban, M., Mooney, W., Reigber, Ch., and Schwintzer, P., Simulation of active tectonic processes for a convecting mantle with moving continents, Geophys. J. Int., 2006, vol. 164, pp. 611–623.
Trubitsyn, V.P., Seismic tomography and continental drift, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2008, vol. 44, no. 11, pp. 857–872.
Trubitsyn, V.P., Evseev, A.N, Baranov, A.A., and Trubitsyn, A.P., Influence of an endothermic phase transition on mass transfer between the upper and the lower mantle, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2008a, vol. 44, no. 6, pp. 443–456.
Trubitsyn, V.P., Evseev, A.N., Baranov, A.A., and Trubitsyn, A.P., Phase transition zone width implications for convection structure, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2008b, vol. 44, no. 8, pp. 603–614.
Trubitsyn, V., Kaban, M., and Rothacher, M., Mechanical and thermal effects of floating continents on the global mantle convection, Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., 2008c, vol. 171, pp. 313–322.
Trubitsyn, V.P., Control gear for oceanic tectonic plates, Dokl. Earth Sci., 2010, vol. 434,part 1, pp. 1205–1207.
Trubitsyn, V.P., Rheology of the mantle and tectonics of the oceanic lithospheric plates, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2012, vol. 48, no. 6, pp. 467–485.
Trubitsyn, V.P., Evseev, A.N, Evseev, M.N., and Evseeva, A.V., The structure of convection in the spherical mantle with internal heating, Izv., Phys. Solid Earth, 2013, vol. 49, no. 5, pp. 660–667.
Yoshida, M., Preliminary three-dimensional model of mantle convection with deformable, mobile continental lithosphere, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2010, vol. 295, pp. 205–218.
Yoshida, M. and Santosh, M., Supercontinents, mantle dynamics and plate tectonics: a perspective based on conceptual vs. numerical models, Earth Sci. Rev., 2011a, vol. 105, pp. 1–24.
Yoshida, M. and Santosh, M., Future supercontinent assembled in the northern hemisphere, Terra Nova, 2011b, vol. 23, pp. 333–338.
Yoshida, M., Dynamic role of the rheological contrast between cratonic and oceanic lithospheres in the longevity of cratonic lithosphere: a three-dimensional numerical study, Tectonophysics, 2012, vols. 532–535, pp. 156–166.
Zhong, S., Zuber, M.T., Moresi, L.N., and Gurnis, M., The role of temperature-dependent viscosity and surface plates in spherical shell models of mantle convection, J. Geophys. Res., 2000, vol. 105, pp. 11063–11082.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.P. Trubitsyn, A.P. Trubitsyn, 2014, published in Fizika Zemli, 2014, No. 6, pp. 138–147.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trubitsyn, V.P., Trubitsyn, A.P. Numerical model for the generation of the ensemble of lithospheric plates and their penetration through the 660-km boundary. Izv., Phys. Solid Earth 50, 853–864 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106935131406010X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S106935131406010X