Abstract
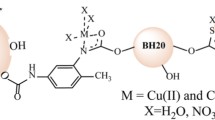
A highly efficient hybrid adsorbent has been synthesized, which is based on an industrially available biodegradable nontoxic flax cellulose modified with hyperbranched polyester polybenzoylthiocarbamate. The synthesis has been carried out using toluene diisocyanate (TDI) as a linker. The second-generation hyperbranched polyester polybenzoylthiocarbamate contains eight terminal benzoylthiocarbamate and eight hydroxyl groups according to 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and IR spectroscopy. In the first stage, the reaction of TDI with flax cellulose has been carried out, which provided 27% content of TDI according to potentiometric titration. The resulting modified flax cellulose has reacted with hyperbranched polyester polybenzoylthiocarbamate. The content of hyperbranched polymer in cellulose (5%) has been evaluated by the weight method. The unreacted isocyanate groups have been neutralized with isobutyl alcohol. The structure of the hybrid material has been proven by IR spectroscopy. The adsorption properties of the polydentate adsorbent have been studied with for the Cu(II) ions. It has been found that the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent is 6.93 mg/g. The methods of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) have been used to evaluate the temperature characteristics, thermal effects, and mass loss of the obtained polydentate compound and its complexes. Desorption of the Cu(II) and Co(II) ions with the regeneration of the hybrid adsorbent has been shown to occur in an acidic medium at pH 3–4.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Nikiforov, T.E., Bogrovskaya, N.A., Kozlov, V.A., and Lilin, S.A., Sorption properties and the nature of interaction of cellulose containing polymers with metal ions, Khim. Rastit. Syr’ya, 2009, no. 1, pp. 5–14.
He, J.-M., Wang, F.-W., Wu, Y.-D., Gu, H.-B., Huang, Y.-D., and Zhang, H.-W., Progress in functional modification of typical biomedical absorbable hemostatic agents, Xiandai Huagong, 2010, vol. 30, no. 12, pp. 11–15.
Tkacheva, N.I., Morozov, S.V., Grigor’ev, I.A., Mognonov, D.M., and Kolchanov, N.A., Modification of cellulose as a promising direction in the design of new materials, Polymer Sci., Ser. B, 2013, vol. 55, no. 8, pp. 409–429. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1560090413070063
Bagheri, M., Rodriguez, M., Swatloski, R., Spear, S., Daly, T., and Rogers, R., Ionic liquid-based preparation of cellulose-dendrimer films as solid supports for enzyme immobilization, Biomacromolecules, 2008, no. 9, pp. 381–387. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm701023w
Montanez, M.I., Hed, Y., Utsel, S., Ropponen, J., Malmstrom, E., Wagberg, L., Hult, A., and Malkoch, M., Bifunctional dendronized cellulose surfaces as biosensors, Biomacromolecules, 2011, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 2114–2125.https://doi.org/10.1021/bm200201y
Hassan, M.L., Moorfield, C.N., and Newkome, G.R., Regioselective dendritic functionalization of cellulose, Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2004, vol. 25, pp. 1999–2002. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.200400423
Hassan, M.L., Moorfield, C.N., Kotta, K., and Newkome, G.R., Regioselective combinatorial-type synthesis, characterization, and physical properties of dendronized cellulose, Polymer, 2005, vol. 46, pp. 8947–8955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2005.06.028
Östmark, E., Lindqvist, J., Nystrom, D., and Malmstrom, E., Dendronized hydroxypropyl cellulose: Synthesis and characterization of biobased nanoobjects, Biomacromolecules, 2007, vol. 8, no. 12, pp. 3815–3822. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm7007394
Henriksson, M., Fogelström, L., Berglund, L.A., Johansson, M., and Hult, A., Novel nanocomposite concept based on cross-linking of hyperbranched polymers in reactive cellulose nanopaper templates, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2011, vol. 71, no. 1, pp. 13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.09.006
Zhang, F., Zhang, D., Chen, Y., and Lin, H., The antimicrobial activity of the cotton fabric grafted with an amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer, Cellulose, 2009, vol. 16, pp. 281–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-008-9253-1
Liu, P.A., Novel degradable adsorbent of the hyperbranched aliphatic polyester grafted cellulose for heavy metal ions, Turk. J. Chem., 2007, vol. 31, pp. 457–462
Kutyrev, G.A., Busygina, A.A., Akhmadulina, E.N., Rakhmatulina, L.R., Kutyreva, M.P., and Gataulina, A.R., Synthesis, structure and fungicidal properties of hyperbranched polyesterpoly(N-phenylthiocarbamates), Vestn. Tekhnol. Univ., 2016, vol. 19, no. 14, pp. 15–18.
Kutyrev, G.A., Maksimov, A.F., Kutyreva, M.P., Gataulina, A.R., and Ernandes, A.M.P., Hyperbranched polyesters containing terminal benzoyl and benzoylthiocarbamate groups, Vestn. Tekhnol. Univ., 2018, vol. 21, no. 9, pp. 69–73.
Kutyreva, M.P., Babkina, S.S., and Atanasyan, T.K., Novye materialy: biologicheski aktivnye giperrazvetvlennye polimery i ikh metallokompleksy (New Materials: Biologically Active Hyperbranched Polymers and their Metal Complexes), Moscow: MPGU, 2014.
Gataulina, A.R., Kutyreva, M.P., Ukhalovich, N.A., Shigapov, M.Ya., Khasanova, E.M., and Kutyrev G.A., Synthesis and spectral characteristics of a hyperbranched polyester poly(phenylcarbamate), Russ. J. Org. Chem., 2015, vol. 51, no. 10, pp. 1499–1501.
Klimenko, N.S., Shevchuk, A.V., Vortman, M.Ya., Privalko, E.G., and Shevchenko, V.V., Synthesis of hyperbranched poly(ester urethane isocyanates) and their derivatives, Polymer Sci., Ser. A, 2008, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 160–165.
Prevec, G., Yagar, E., and Yigon, M., Carboxylated polyurethanes with polyester soft segments, Chem. Ind., 2006, vol. 55, no. 9, pp. 365–372.
Kutyreva, M.P., Maksimov, A.F., Ernandes A.-M.P., Zhukova, A.A., Gataulina, A.R., and Kutyrev, G.A., Interaction of poly(benzoyl thiocarbamate)-modified hyperbranched polyester with Co(II) and Cu(II) nitrates, Russ. J. Gen. Chem., 2020, vol. 90, no. 2, pp. 268–273.
Nugmanov, O.K., Grigor’eva, N.P., Lebedev, N.A., Khlebnikov, V.N., and Yarullin, R.N., The method of obtaining semi-cellulose, RF Patent No. 2343240, 2009.
Kutyrev, G.A., Maksimov, A.F., Ernandes, A.-M.P., Kutyreva, M.P., and Gataulina, A.R., Hyperbranched polyesters containing terminal groups, Vestn. Tekhnol. Univ., 2018, vol. 21, no. 9, pp. 69–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by A. Levina
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernandez, AM.P., Maksimov, A.F., Zhukova, A.A. et al. Polydentate Adsorbent Based on Flax Cellulose Modified by Hyperbranched Polyester Polybenzoylthiocarbamate. Russ J Bioorg Chem 48, 1399–1404 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1068162022070056
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1068162022070056