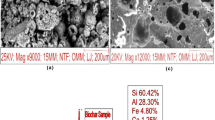
Abstract
A field experiment was conducted to investigate the effect of biochar, organic matter (hundz soil) and mycorrhiza on soil hydrophysical properties, irrigation water applied and water productivity of soybean crop in arid soils. The treatments included eight practices i.e., control (C), 15 t ha–1 biochar (B), 15 t ha–1 hundz soil (H), 2.5 kg ha–1 mycorrhiza (M), 15 t ha–1 B + 2.5 kg ha–1 M (B + M), 15 t ha–1 H + 2.5 kg ha–1 M (H + M), 7.5 t ha–1 B + 7.5 kg ha–1 H (50% B + 50% H) and 7.5 t ha–1 B + 7.5 t ha–1 H + 2.5 kg ha–1 (50% B + 50% H + M). The results observed that there is a significant decrease in soil bulk density at the mixture of B, H and M. Also, a significant increase in soil porosity and hydraulic conductivity were recorded. The reduction of actual evapotranspiration (ETa) and irrigation water applied (IWA) by the treatments could be set in the descending order: 50% B + 50% H + M > 50% B + 50% H > H + M > B + M > H > B > M > C. The highest relative decrease (mean of both seasons) of ETa and IWA were 25.98% and 23.46%, respectively at 50% B + 50% H + M treatment. Also, crop water productivity and irrigation water productivity were significantly (P ≤ 0.05) increased as compared to control. Plant height, seed index, seed yield, portion content and oil content were significantly (P ≤ 0.05) increased as a result applying of B, H and M. The results imply that the mixture of biochar, hundz soil and treated soybean seed with mycorrhiza are considered a valuable approach to improve soil hydrophysical properties, water productivity and soybean yield in arid regions.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
T. Abedi, A. Alemzadeh, and S. A. Kazemeini, “Effect of organic and inorganic fertilizers on grain yield and protein banding pattern of wheat,” Aust. J. Crop Sci. 4 (6), 384–389 (2010). https://search.informit.org/doi/ 10.3316/informit.414808187764069
A. A. Abo-Baker, “Successive application impact of some organic amendments combined with acid producing bacteria on soil properties, NPK availability and uptake by some plants,” Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 6, 2394–2413 (2017). https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.603.274
V. Abrol, M. Ben-Hur, F. G. Verheijen, J. J. Keizer, M. A. Martins, H. Tenaw, L. Tchehansky, and E. R. Graber, “Biochar effects on soil water infiltration and erosion under seal formation conditions: rainfall simulation experiment,” J. Soils Sediments 16 (12), 2709–2719 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1448-8
T. M. Agbede, A. O. Adekiya, and J. S. Ogeh, “Effects of organic fertilizers on yam productivity and some soil properties of a nutrient depleted tropical Alfisol,” Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 59 (4–6), 803–822 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2012.683423
G. H. D. Agbna, S. Dongli, L. Zhipeng, N. A. Elshaikh, S. Guangcheng, and L. C. Timm, “Effects of deficit irrigation and biochar addition on the growth, yield, and quality of tomato,” Sci. Hortic. 222, 90–101 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.05.004
K. Ahmad, K. Wajid, Z. I. Khan, I. Ugulu, H. Memoona, M. Sana, and M. Sher, “Evaluation of potential toxic metals accumulation in wheat irrigated with wastewater,” Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 102 (6), 822–828 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02605-1
A. G. Alghamdi, A. Alkhasha, and H. M. Ibrahim, “Effect of biochar particle size on water retention and availability in a sandy loam soil,” J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 24, 1042–1050 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2020.11.003
S. Ali, A. Jan, A. Sohail, A. Khan, M. I., Khan, J. Zhang, and I. Daur, “Soil amendments strategies to improve water-use efficiency and productivity of maize under different irrigation conditions,” Agric. Water Manage. 210, 88–95 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.08.009
N. Ameloot, E. R. Graber, F. G. Verheijen, and S. De Neve, “Interactions between biochar stability and soil organisms: review and research needs” Eur. J. Soil Sci. 64 (4), 379–390 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12064
R. Anderson, D. Keshwani, A. Guru, H. Yan, S. Irmak, and J. Subbiah, “An integrated modeling framework for crop and biofuel systems using the DSSAT and GREET models,” Environ. Modell. Software 108, 40–50 (2018). https:// doi. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2018.07.004
F. Anwar, G. M. Kamal, F. Nadeem, and G. Shabir, “Variations of quality characteristics among oils of different soybean varieties,” J. King Saud Univ., Sci. 28, 332–338 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2015.10.001
AOCS, Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists Society, 5th Ed. (AOCS Press, Champaign, 2009), p. 39.
M. A. Ashour, S. T. El Attar, Y. M. Rafaat, and M. N. Mohamed, “Water resources management in Egypt,” J. Eng. Sci. Assiut Univ. 37, 269–279 (2009). https://doi.org/10.21608/JESAUN.2009.121215
A. S. Basso E. M. Ferrando, D. A. Laird, R. Horton, and M. Westgate, “Assessing potential of biochar for increasing water-holding capacity of sandy soils,” Bioenergy 5 (2), 132–143 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12026
G. R. Blake and K. H. Hartge, Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1: Physical and Mineralogical Methods, Ed. by A. Klute (Madison, 1986), pp. 363–375 (1986). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.1.2ed.c13
H. Blanco-Canqui and R. Lal, “Crop residue removal impacts on soil productivity and environmental quality,” Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 28, 139–163 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680902776507
M. G. Bos, “Summary of ICID definitions of irrigation efficiency,” ICID Bulletin 34, 28–31 (1985).
M. Choudhary, V. S. Meena, S. C. Panday, T. Mondal, R. P. Yadav, P. K. Mishra, J. K. Bisht, and A. Pattanayak, “Long-term effects of organic manure and inorganic fertilization on biological soil quality indicators of soybean-wheat rotation in the Indian mid-Himalaya,” Appl. Soil Ecol. 157, 103745 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103754
L. Dong, W. Zhang, Y. Xiong, J. Zou, Q. Huang, X. Xu, and G. Huang, “Impact of short-term organic amendments incorporation on soil structure and hydrology in semiarid agricultural lands,” Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 10 (3), 457–469 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2021.10.003
R. Duponnois, L. Ouahmane, A. Kane, J. Thioulouse, M. Hafidi, and A. Boumezzough, “Nurse shrubs increased the early growth of Cupressus seedlings by enhancing belowground mutualism and soil microbial activity,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 43, 2160–2168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.06.020.
A. El Sabagh, S. I. Mohammad, U. Akihiro, S. Hirofumi, and B. Celaleddin “Increasing reproductive stage tolerance to salinity stress in soybean,” Int. J. Agric. Crop Sci. 8 (5), 738–745 (2015).
S. Fahmy, M. Ezzat, A. Shalby, H. Kandil, M. Sharkawy, M. Allam, I. Assiouty, and A. Tczap, Water Policy Review and Integration Study, Report No. 65 (Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation, Cairo, 2002).
M. Falkenmark and G. Lindh, Water for a Starving World (Routledge, Abingdon, 2019).
G. W. Gee and D. Or, “Particle size analysis,” in Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 4: Physical Methods, Ed. by D. L. Sparks (Madison, 2002), pp. 255–293.
P. H. Graham and C. P. Vance, “Legumes: importance and constraints to greater use,” Plant Physiol. 131, 872–877 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.017004
N. Habashy and M. S. A. Ewees, “Improving productivity of zucchini squash grown under moderately saline soil using gypsum, organo-stimulants and AM-fungi,” J. Appl. Sci. Res. 7 (12), 2112–2126 (2011).
V. Hansen, H. H. Nielsen, C. T. Petersen, T. N. Mikkelsen, and D. M. Stöver, “Effects of gasification biochar on plant-available water capacity and plant growth in two contrasting soil types,” Soil Tillage Res. 161, 1–9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2016.03.002
H. M. S. K. Herath, A. M. Camps, and M. Hedley, “Effect of biochar on soil physical properties in two contrasting soils: an Alfisol and an Andisol,” Geoderma 209–210, 188–197 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.06.016
O. W. Israelsen and V. E. Hansen, Irrigation Principles and Practices (John Willey and Sons. Inc., New York, 1962). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1963.03615995002700020010x
IUSS Working Group WRB, World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015, International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Leg- ends for Soil Maps, World Soil Resources Reports No. 106 (UN Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome, 2015).
A. Jamiołkowska, A. Ksiezniak, A. Gałazka, B. Hetman, M. Kopacki, and B. Skwaryło-Bednarz, “Impact of abiotic factors on development of the community of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the soil: a review,” Int. Agrophys. 32 (1), 133–140 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/intag-2016-0090
S. R. Joshi, G. D. Sharma, and R. R. Mishra, “Microbial enzyme activities related to litter decomposition near a highway in a sub-tropical forest of northeast India,” Soil Biol. Biochem. 25, 1763–1770 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(93)90181-A
I. Jośko, P. Oleszczuk, J. Pranagal, J. Lehmann, B. Xing, and G. Cornelissen, “Effect of biochar activated carbon and multiwalled carbon nanotubes on phytotoxicity of sediment contaminated by inorganic and organic pollutants,” Ecol. Eng. 60, 50–59 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.07.064
S. Khaim, M. A. H. Chowdhury, and B. K. Saha, “Organic and inorganic fertilization on the yield and quality of soybean,” J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 11 (1), 23–28 (2013). https://www.banglajol.info/index.php/JBAU/ article/view/18199.
Z. I. Khan, H. Safdar, K. Ahmad, K. Wajid, H. Bashir, I. Ugulu, and Y. Dogan, “Copper bioaccumulation and translocation in forages grown in soil irrigated with sewage water,” Pak. J. Bot. 52 (1), 111–119 (2020). https://doi.org/10.30848/PJB2020-1(12)
A. Klute, Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1: Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd. Ed. (American Society of Agronomy, Madison, 1986).
A. Klute and C. Dirksen, “Hydraulic conductivity and diffusivity: laboratory methods,” in Methods of Soil Analysis, Ed. by A. Klute (Am. Soc. of Agron. Publications, Madison, 1986), Part 1, pp. 687–734.
N. Kranz, R. A. McLaughlin, A. Johnson, G. Miller, and J. L. Heitman, “The effects of compost incorporation on soil physical properties in urban soils–a concise review,” J. Environ. Manage. 261, 110209 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110209
T. J. Lim, K. Spokas, G. Feyereisen, and J. Novak, “Predicting the impact of biochar additions on soil hydraulic properties,” Chemosphere 142, 136–144 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.06.069
S. G. Lu, F. F. Sun, and Y. T. Zong, “Effect of rice husk biochar and coal fly ash on some physical properties of expansive clayey soil (Vertisol),” Catena 114, 37–44 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.10.014
V. Martinsen, V. Alling, N. L. Nurida, J. Mulder, S. E. Hale, C. Ritz, D. W. Rutherford, A. Heikens, G. D. Breedveld, and G. Cornelissen, “pH effects of the addition of three biochars to acidic Indonesian mineral soils,” Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 61 (5), 821–834 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2015.1052985
A. M. Miglierinaa, J. O. Iglesiasa, G. C. Laurenta, R. A. Rodrigueza, M. E. Ayastuya, and J. C. Lobartinia, “Application of compost to different texture soils: effect on soil properties and productivity of lettuce crop,” Acta Hortic. 10, 17660 (2015).
O. I. Nicholas O. B. Olubukola, C. Xavier, and T. Baldwyn, “Effects of rhizobia and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on yield, size distribution and fatty acid of soybean seeds grown under drought stress,” Microbiol. Res. 242, 126640 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2020.126640
A. M. O’Neal, “A key for evaluating soil permeability by means of certain field clues,” Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 16, 312–315 (1952). https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1952.03615995001600030024x
L. Ouyang, W. J. Tang, and R. Zhang, “Effects of biochar amendment on soil aggregates and hydraulic properties,” J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 13, 991–1002 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162013005000078
A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, and D. R. Keeney, Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties (American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, 1982).
M. Parihar, A. Rakshit, V. S. Meena, V. K. Gupta, K. Rana, and M. Choudhary, “The potential of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in C cycling: a review,” Arch. Microbiol. 202, 581–1596 (2020). https://doi. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01915-x
R. Prasad, D. Bhola, K. Akdi, C. Cruz, K. V. S. S. Sairam, N. Tuteja, and A. Varma, “Introduction to mycorrhiza: historical development,” in Mycorrhiza - Function, Diversity, State of the Art (Springer, Cham, 2017), pp. 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-53064-2_1
M. Qaswar, H. Jing, W. Ahmed, L. Dongchu, L. Shujun, Z. Lu, and Z. Huimin, “Yield sustainability, soil organic carbon sequestration and nutrients balance under long-term combined application of manure and inorganic fertilizers in acidic paddy soil,” Soil Tillage Res. 198, 104569 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104569
M. F. Qayyum, G. Haider, M. A. Raza, A. K. S. H. Mohamed, M. Rizwan, M. A. El- Sheikh, M. N. Alyemeni, and S. Ali, “Straw-based biochar mediated potassium availability and increased growth and yield of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.),” J. Saudi Chem. 24, 963–973 (2020). https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2020.10.004
A. Rahimi, S. S. Moghaddam M., Ghiyasi, S. Heydarzadeh, K. Ghazizadeh, and J. Popović-Djordjević, “The influence of chemical, organic and biological fertilizers on agrobiological and antioxidant properties of Syrian Cephalaria (Cephalaria syriaca L.),” Agriculture 9 (6), (2019). 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9060122
E. Y. Rizhiya, N. P., Buchkina, I. M., Mukhina, A. S. Belinets, and E. V. Balashov, “Effect of biochar on the properties of loamy sand Spodosol soil samples with different fertility levels: a laboratory experiment,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 48 (2), 192–200 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229314120084
Y. Shenglan, L. Tiancheng, and Y. Niu, “Effects of organic fertilizer on water use, photosynthetic characteristics, and fruit quality of pear jujube in northern Shaanxi,” Open Chem. 18, 537–545 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2020-0060
V. Simanský, “Effects of biochar and biochar with nitrogen on soil organic matter and soil structure in Haplic Luvisol,” Acta Fytotech. Zootech. 19, 129–138 (2016). https://doi.org/10.15414/afz.2016.19.04.129-138
L. Toková, D. Igaz, J. Horák, and E. Aydin, “Effect of biochar application and re-application on soil bulk density, porosity, saturated hydraulic conductivity, water content and soil water availability in a Silty Loam Haplic Luvisol,” Agronomy 10, 1005 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10071005
M. M. Turky, M. M. El-Sayed, M. Y. Awad, and A. S. A. Abdel-Mawgoud, “Use natural soil amendments in improving hydro-physical properties and wheat crop production of a new reclaimed area, Sohag Governorate, Egypt,” Arch. Agric. Sci. J. 13 (3), 214–230 (2020). https:// doi. https://doi.org/10.21608/AASJ.2020.132456
K. Wajid, K. Ahmad, Z. I. Khan, M. Nadeem, H. Bashir, F. Chen, and I. Ugulu, “Effect of organic manure and mineral fertilizers on bioaccumulation and translocation of trace metals in maize,” Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 104 (5), 649–657 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02841-w
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Authors would like to thank and appreciate Soils and Water Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Al-Azhar University in Assiut and Cairo and Agronomy Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Al-Azhar University, Assiut, Egypt for support this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
EL-Sayed, M.M., Mahdy, A.Y., Gebreel, M. et al. Effectiveness of Biochar, Organic Matter and Mycorrhiza to Improve Soil Hydrophysical Properties and Water Relations of Soybean under Arid Soil Conditions. Eurasian Soil Sc. 56, 1055–1066 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229323600276
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229323600276