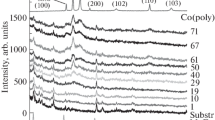
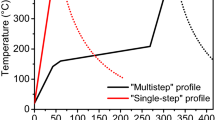
Abstract
The effect of oxygen and water vapor in a sputtering chamber during the deposition of thin-film (Co40Fe40B20)x(LiNbO3)100 – x nanocomposites on the electrical properties of the heterogenous system is investigated. It is found that the resistivity of (Co40Fe40B20)x(LiNbO3)100 – x nanocomposites increases significantly with the partial pressure of reactive gases (oxygen and water vapor). A noticeable shift of the percolation threshold towards higher values of the metal phase volume concentration, which is observed in the plane of the film and in the perpendicular direction during the synthesis of composites with the addition of reactive gases, is attributed to the increase in the volume concentration of the dielectric phase. It is found that the percolation threshold for the measurements in the geometry perpendicular to the plane of the film is characterized by a much lower concentration of the Co40Fe40B20 alloy atoms than that for the measurements in the plane of the film, which is associated with an elongated shape of granules in the film growth direction and the effects of Coulomb blockade suppression by a high transverse electric field.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
V. V. Rylkov, A. V. Emelyanov, S. N. Nikolaev, K. E. Nikiruy, A. V. Sitnikov, E. A. Fadeev, V. A. Demin, and A. B. Granovsky, J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 131 (1), 160 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063776120070109
S. V. Komogortsev, L. A. Chekanova, I. V. Nemtsev, G. Y. Yurkin, R. S. Iskhakov, G. S. Krainova, N. V. Il’in, V. S. Plotnikov, and D. A. Yatmanov, Inorg. Mater.: Appl. Res. 11 (1), 177 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113320010219
A. N. Yurasov, M. M. Yashin, D. V. Semenova, K. B. Mirzokulov, and E. A. Ganshina, Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci.: Phys. 83 (7), 884 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1062873819070438
Yu. E. Kalinin, A. V. Sitnikov, and O. V. Stognei, Al’ternat. Energ. Ekol. 54, 9 (2007).
I. V. Bykov, E. A. Gan’shina, A. B. Granovskii, and V. S. Gushchin, Phys. Solid State 42 (3), 498 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1134/1.1131238
S. A. Gridnev, Yu. E. Kalinin, A. V. Sitnikov, and O. V. Stognei, Nonlinear Phenomena in Nano- and Microheterogeneous Systems (BINOM–Lab. Znanii, Moscow, 2012) [in Russian].
A. N. Matsukatova, A. V. Emelyanov, A. A. Minnekhanov, D. A. Sakharutov, A. Yu. Vdovichenko, R. A. Kamyshinskii, V. A. Demin, V. V. Rylkov, P. A. Forsh, S. N. Chvalun, and P. K. Kashkarov, Tech. Phys. Lett. 46 (1), 73 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063785020010277
A. V. Arkhipov, G. V. Nenashev, and A. N. Aleshin, Fiz. Tverd. Tela 63 (4), 559 (2021). https://doi.org/10.21883/FTT.2021.04.50725.263
W. Li, X. Liu, Y. Wang, Z. Dai, W. Wu, L. Cheng, Y. Zhang, Q. Liu, X. Xiao, and C. Jiang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 153501 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4945982
E. V. Okulich, V. I. Okulich, and D. I. Tetel’baum, Tech. Phys. Lett. 46 (1), 19 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063785020010083
A. Mehonic, A. L. Shluger, D. Gao, I. Valov, E. Miranda, D. Ielmini, A. Bricalli, E. Ambrosi, C. Li, J. J. Yang, Q. Xia, and A. J. Kenyon, Adv. Mater. 30 (43), 1801187 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201801187
Yu. E. Kalinin, A. V. Sitnikov, and O. V. Stognei, Vestn. Voronezh. Gos. Tekh. Univ. 3 (11), 6 (2007).
V. V. Rylkov, S. N. Nikolaev, V. A. Demin, A. V. Emelyanov, A. V. Sitnikov, K. E. Nikiruy, V. A. Levanov, M. Yu. Presnyakov, A. N. Taldenkov, A. L. Vasiliev, K. Yu. Chernoglazov, A. S. Vedeneev, Yu. E. Kalinin, A. B. Granovsky, V. V. Tugushev, et al., J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 126 (3), 353 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063776118020152
Yu. Yu. Tarasevich, Percolation: Theory, Applications, Algorithms (URSS, Moscow, 2002) [in Russian].
A. D. Pomogailo, A. S. Rozenberg, and I. E. Uflyand, Nanoparticles of Metals in Polymers (Nauka, Moscow, 2000) [in Russian].
N. N. Trofimov, M. Z. Kanovich, E. M. Kartashov, V. I. Natrusov, A. T. Ponomarenko, V. G. Shevchenko, V. I. Sokolov, and I. D. Simonov-Emel’yanov, Physics of Composite Materials (Mir, Moscow, 2005), Vol. 2, p. 344 [in Russian].
I. A. Chmutin, S. V. Letyagin, V. G. Shevchenko, and A. T. Ponomarenko, Vysokomol. Soedin. 36, 699 (1994).
B. I. Shklovskii and A. L. Efros, Electronic Properties of Doped Semiconductors (Springer, Berlin, 1984).
A. V. Sitnikov, I. V. Babkina, Yu. E. Kalinin, A. E. Nikonov, M. N. Kopytin, K. E. Nikirui, A. I. Il’yasov, K. Yu. Chernoglazov, S. N. Nikolaev, A. L. Vasil’ev, A. V. Emel’yanov, V. A. Demin, and V. V. Ryl’kov, Nanoindustriya 13 (S4), 570 (2020). https://doi.org/10.22184/1993-8578.2020.13.4s.570.571
O. G. Udalov, N. M. Chtchelkatchev, A. Glatz, and I. S. Beloborodov, Phys. Rev. B 89, 054203 (2014). https://doi.org/.1103/PhysRevB.89.054203
L. V. Gurvich, G. V. Karachevtsev, V. N. Kondrat’ev, Yu. A. Lebedev, V. A. Medvedev, V. K. Potapov, and Yu. S. Khodeev, Chemical Bond-Dissociation Energies. Ionization Potential and Electron Affinity (Nauka, Moscow, 1974) [in Russian].
J. V. Kasiuk, J. A. Fedotova, J. Przewoznik, J. Zukrowski, M. Sikora, Cz. Kapusta, A. Grce, and M. Milosavljevic, J. Appl. Phys. 116, 044301 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4891016
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The structure of the nanocomposite was investigated using the equipment of the Resource Center of Electrophysical Methods (National Research Center “Kurchatov Institute”).
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 19-29-03022 mk.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by N. Wadhwa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sitnikov, A.V., Babkina, I.V., Kalinin, Y.E. et al. The Effect of Oxygen and Water Vapor on the Electric Properties of (Co40Fe40B20)x(LiNbO3)100 – x Nanogranular Composites. Tech. Phys. 66, 1284–1293 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784221090176
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784221090176