Abstract
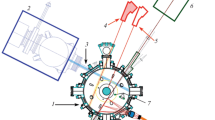
Research data for drag currents in the Globus-M spherical tokamak are presented. The currents are generated by injecting atomic beams of hydrogen and deuterium. Experiments were carried out in the hydrogen and deuterium plasma of the tokamak. It has a divertor configuration with a lower X-point, a displacement along the larger radius from–1.0 to–2.5 cm, and a toroidal field of 0.4 T at a plasma current of 0.17–0.23 MA. The beam is injected into the tokamak in the equatorial plane tangentially to the magnetic axis of the plasma filament with an impact diameter of 32 cm. To provide a 28-keV 0.5-MW atomic beam with geometrical sizes of 4 × 20 cm (at a power level of 1/e), an IPM-2 ion source is used. The generation of noninductive currents is detected from a rise in the loop current and a simultaneous dip of the loop voltage. The injection of the hydrogen and deuterium atomic beams into the deuterium plasma results in a noticeable and reproducible dip of the loop voltage (up to 0.5 V). Using the ASTRA transport code, a model is constructed that allows rapid calculation of noninductive currents. Calculations performed for a specific discharge confirm that the model adequately describes the effect of drag current generation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Ohkawa, Nucl. Fusion 10, 185 (1970).
W. H. M. Clark, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 45, 1101 (1980).
M. Zarnstorff, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 1306 (1988).
C. Challis, et al., in Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics, Madrid, Spain, 1987, Ed. by S. Methfessel (European Physical Society, Petit-Lancy, Switzerland, 1987).
T. Suzuki, R. J. Akers, D. A. Gates, et al., Nucl. Fusion 51, 083020 (2011).
V. K. Gusev, V. E. Golant, E. Z. Gusakov, et al., Tech. Phys. 44, 1054 (1999).
L. Spitzer, Physics of Fully Ionized Gases (Wiley, New York, 1962).
V. I. Pistunovich, Sov. J. Plasma Phys. 2, 1 (1976).
B. A. Trubnikov, in Reviews of Plasma Physics, Ed. by M. A. Leontovich (Consultants Bureau, New York, 1963), Vol. 1, pp. 98–182.
D. V. Sivukhin, in Reviews of Plasma Physics, Ed. by M. A. Leontovich (Consultants Bureau, New York, 1963), Vol. 4, pp. 81–187.
J. G. Cordey and M. J. Houghton, Nucl. Fusion 13, 215 (1973).
J. W. Connor and J. G. Cordey, Nucl. Fusion 14, 185 (1974).
V. V. Fomenko, Nucl. Fusion 15, 1091 (1975).
J. G. Cordey and W. G. F. Core, Phys. Fluids 17, 1626 (1974).
W. W. Heidbrink and G. J. Sadler, Nucl. Fusion 34, 535 (1994).
V. K. Gusev, in Proceedings of the 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference, St. Petersburg, 2014, Poster No. OV/P-03.
N. N. Bakharev, in Proceedings of the 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference, St. Peterburg, 2014, Poster No. EX/P1-33.
Kenro Miyamoto, Fundamentals of Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion (Iwanami Book Service Center, 1997).
D. F. H. Start, J. G. Cordey, and E. M. Jones, Plasma Phys. 22, 303 (1980).
V. K. Gusev, A. V. Dech, L. A. Esipov, et al., Tech. Phys. 52, 1127 (2007).
G. V. Pereverzev and P. N. Yushmanov, “ASTRA automated system for transport analysis,” Preprint No. IPP-5/98 (IPP, Garching, 2002).
V. K. Gusev, S. E. Bender, A. V. Dech, et al., Tech. Phys. 51, 987 (2006).
V. K. Gusev, E. A. Azizov, A. B. Alekseev, et al., Nucl. Fusion 53, 093013 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © P.B. Shchegolev, N.N. Bakharev, V.K. Gusev, G.S. Kurskiev, V.B. Minaev, M.I. Patrov, Yu.V. Petrov, N.V. Sakharov, 2015, published in Zhurnal Tekhnicheskoi Fiziki, 2015, Vol. 85, No. 9, pp. 62–66.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shchegolev, P.B., Bakharev, N.N., Gusev, V.K. et al. Pioneering experiments on atomic-beam-assisted generation of drag currents in the Globus-M spherical tokamak. Tech. Phys. 60, 1321–1325 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784215090194
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784215090194