Abstract
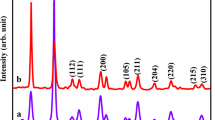
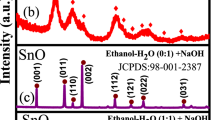
In the present study, SnS and Cr-doped SnS nanoparticles were synthesized by solvothermal method. The structural, functional, elemental, morphological, and electrochemical properties of the as-synthesized non-doped and Cr-doped SnS nanoparticles were examined using XRD, Raman, FTIR, SEM/EDX, and cyclic voltammetry analysis. The XRD results indicated a good crystallinity of the sample and confirmed the formation of the SnS nanoparticles in orthorhombic structure. The FTIR result also confirmed the functional groups present in the Cr-doped SnS nanoparticles. The well-formed SnS nanoparticles are observed as spherical shapes confirmed from the SEM analysis. EDX spectra confirmed the presence of Sn, Cr, and S elements in the Cr-doped SnS nanoparticles. The electrochemical performance of Cr-doped SnS nanoparticles shows higher specific capacitance of 375 F/g compared with 284 F/g of bare SnS nanoparticles, which confirms that Cr-doped SnS nanoparticles are promising candidate for supercapacitor applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. Starvinadis, J. M. Smith, C. A. Cattley, A. G. Cook, P. S. Grant, and A. A. R. Watt, Nanotechnology 21, 185202 (2010).
S. S. Hegde, A. G. Kunjomana, K. Ramesh, K. A. Chandrasekharan, and M. Prashantha, Int. J. Soft Comput. Eng. 1, 38 (2011).
M. M. El-Nahass, H. M. Zeyada, M. S. Aziz, and N. A. El-Ghamaz, Opt. Mater. 20, 159 (2002).
Y. Guo, W. Shi, Y. Zhang, L. Wang, and G. Wei, Proc. SPIE 69841, Q1 (2008).
R. Mariappan, T. Mahalingam, and V. Ponnuswamy, Optik 122, 2216 (2011).
S. M. Ahmed, L. A. Latif, and A. K. Salim, J. Basrah Res. Sci. 37, 1 (2011).
G. G. Ninan, V. G. Rajeshmon, C. S. Kartha, and K. P. Vijayakumar, AIP Conf. Proc. 1591, 1440 (2014).
Y. Yang, S. Cheng, and S. Lai, Adv. Mater. Res. 60, 105 (2009).
K. Saminathan, Eur. J. Appl. Sci. Tech. 1, 68 (2014).
N. Koteeswara Reddy, M. Devika, and E. S. R. Gopal, Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 40, 359 (2015).
H. Ke, W. Luo, G. Cheng, X. Tian, and Z. Pi, Micro Nano Lett. 4, 177 (2009).
W. Cai, J. Hu, Y. Zhao, H. Yang, J. Wang, and W. Xiang, Adv. Powder Technol. 23, 850 (2012).
S. Biswas, S. Kar, and S. Chaudhuri, Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 9259 (2007).
Q. Wu, L. Jiao, J. Du, J. Yang, L. Guo, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, and H. Yuan, J. Power Sources 239, 89 (2013).
H. Hu, B. Yang, J. Zeng, and Y. Qian, Mater. Chem. Phys. 86, 233 (2004).
H. Liu, Y. Su, P. Chen, and Y. Wang, J. Mol. Catal. A 378, 285 (2013).
T. Srinivasa Reddy and M. C. Santhosh Kumar, Ceram. Int. 42, 12262 (2016).
W. H. Hall, Proc. Phys. Soc., Sect. A 62 (359), 741 (1949).
S. Sohila, M. Rajalakshmi, C. Ghosh, A. K. Arora, and C. Muthamizhchelvan, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 5843 (2011).
T. S. Reddy and M. S. Kumar, Ceram. Int. 42, 12262 (2016).
M. Li, Y. Wu, T. Li, Y. Chen, H. Ding, Y. Lin, N. Pan, and X. Wang, RSC Adv. 7, 48759 (2017).
Y. Xu, N. Al-Salim, and R. D. Tilley, Nanomaterials 2, 54 (2012).
G. Hatui, G. C. Nayak, G. Udayabhanu, Y. Kumar Mishra, and D. Deo Pathak, New J. Chem. 41, 2702 (2017).
J. Johny, S. Sepulveda-Guzman, B. Krishnan, D. A. Avellaneda, J. A. Aguilar Martinez, M. R. Anantharamand, and S. Shaji, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 189, 53 (2019).
V. Velmurugan, U. Srinivasarao, R. Ramachandran, M. Saranya, and A. N. Grace, Mater. Res. Bull. 84, 145 (2016).
H. Chu, F. Zhang, L. Pei, Z. Cui, J. Shen, and M. Ye, J. Alloys Compd. 767, 583 (2018).
B. G. S. Raj, J. J. Wu, A. M. Asiri, and S. Anandan, RSC Adv. 6, 33361 (2016).
F. Beguin and E. Frackowiak, Supercapacitors: Materials, Systems and Applications (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dar, M.A., Govindarajan, D. & Dar, G.N. Comparing the Electrochemical Performance of Bare SnS and Cr-Doped SnS Nanoparticles Synthesized through Solvothermal Method. Phys. Solid State 63, 1343–1350 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783421090055
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783421090055