Abstract
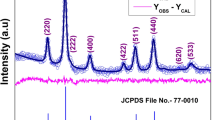
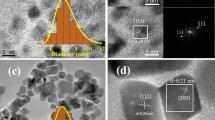
This paper presents the results of investigations of the structural state and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline cupric oxide samples with average particle sizes of approximately 40 and 13 nm, which were synthesized by the electric explosion and gas phase methods, respectively. The samples have been studied using X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction, magnetic measurements, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, and copper nuclear magnetic resonance. It has been shown that, in the initial state, regardless of the synthesis method, CuO nanoparticles are characterized by a heterogeneous magnetic state, i.e., by the existence of long-range antiferromagnetic order, spontaneous magnetization, especially at low temperatures, and paramagnetic centers in the material. The ferromagnetic contribution is probably caused by the formation of magnetic polaron states due to the phase separation induced in the system by excess charge carriers as a result of the existence of point defects (vacancies in the anion sublattice) in the nanocrystalline state. In this state, there is an inhomogeneously broadened nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum, which is a superposition of the spectrum of the initial antiferromagnetic matrix and the spectrum of ferromagnetically ordered regions. At high concentrations of ferromagnetically ordered regions, the antiferromagnetic matrix exhibits a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of CuO nanoparticles, predominantly from regions with the ferromagnetic phase. The appearance of magnetization can also be partly due to the frustration of spins in CuO, and this state is presumably localized near the most imperfect surface of the nanoparticles. The magnetic susceptibility of nanoparticles in the initial state in strong magnetic fields is significantly higher than that for the annealed samples, which, most likely, is associated with the influence of the high concentration of magnetic polarons. No correlation between the ferromagnetic contribution and the size of particles is found. In the CuO samples annealed at 400°C in air, when the average size of CuO nanoparticles remains unchanged, the ferromagnetic contribution completely disappears, and the magnetic behavior of the nanoparticles becomes qualitatively similar to the magnetic behavior of bulk CuO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. L. Nagaev, Phys.—Usp. 38(5), 497 (1995).
M. Yu. Kagan and K. I. Kugel’, Phys.—Usp. 44(6), 553 (2001).
E. Dagotto, J. Burgy, and A. Moreo, Solid State Commun. 126, 9 (2003).
S. A. Makhlouf, H. Al-Attara, and R. H. Kodama, Solid State Commun. 145, 1 (2008).
R. H. Kodama, S. A. Makhlouf, and A. E. Berkowitz, Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 1393 (1997).
S. A. Makhlouf, F. T. Parker, F. E. Spada, and A. E. Berkowitz, J. Appl. Phys. 81, 5561 (1997).
E. Winkler, R. D. Zysler, M. V. Mansilla, D. Fiorani, D. Rinaldi, M. Vasilakaki, and K. N. Trohidou, Nanotechnology 19, 185702 (2008).
S. Mandal, K. S. R. Menon, S. K. Mahatha, and S. Banerjee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 232507 (2011).
M. Jagodic, Z. Jaglicic, A. Jelen, J. B. Lee, Y. M. Kim, H. J. Kim, and J. Dolinsek, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 21, 215302 (2009).
A. Ye. Yermakov, M. A. Uimin, A. A. Mysik, V. B. Vykhodets, T. E. Kurennykh, V. I. Sokolov, V. S. Gaviko, N. N. Schegoleva, and N. B. Gruzdev, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 310, 2102 (2007).
T. I. Arbuzova, S. V. Naumov, V. L. Arbuzov, K. V. Shal’nov, A. E. Ermakov, and A. A. Mysik, Phys. Solid State 45(2), 304 (2003).
J. B. Forsyth, P. J. Brown, and B. M. Wanklyn, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 21, 2917 (1988).
P. J. Brown, T. Chattopadhyay, J. B. Forssyth, V. Nunez, and F. Tasset, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 3, 4281 (1991).
M. Ain, A. Menelle, B. M. Wanklyn, and E. F. Bertaut, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 4, 5327 (1992).
A. Junod, D. Eckert, G. Triscone, J. Müller, and W. Reichardt, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 1, 8021 (1989).
B. X. Yang, T. R. Thurston, J. M. Tranquada, and G. Shirane, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 39, 4343 (1989).
B. X. Yang, J. M. Tranquada, and G. Shirane, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 38, 174 (1998).
X. G. Zheng, H. Yamada, D. J. Scanderbeg, M. B. Maple, and C. N. Xu, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 67, 214516 (2003).
X. G. Zheng, C. N. Xu, Y. Tomokiyo, E. Tanaka, H. Yamada, and Y. Soejima, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 5170 (2000).
T. Tsuda, T. Shimizu, H. Yasuoka, K. Kishio, and K. Kitazawa, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 57, 2908 (1988).
A. Punnoosea and M. S. Seehra, J. Appl. Phys. 91, 7766 (2002).
A. Punnoose, H. Magnone, M. S. Seehra, and J. Bonevich, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 64, 174420 (2001).
G. Zheng, C. N. Xu, K. Nishikubo, K. Nishiyama, W. Higemoto, W. J. Moon, E. Tanaka, and E. S. Otabe, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 72, 014464 (2005).
T. I. Arbuzova, S. V. Naumov, V. L. Arbuzov, and A. P. Druzhkov, Phys. Solid State 51(5), 953 (2009).
A. Ye. Yermakov, M. A. Uimin, V. R. Galakhov, A. A. Mysik, O. V. Koryakova, V. G. Kharchuk, V. A. Vykhodetz, V. S. Gaviko, K. Kuepper, S. Robin, and M. Neumann, J. Metastable Nanocryst. Mater. 24–25, 43 (2005).
A. A. Samokhvalov, T. I. Arbuzova, N. A. Viglin, S. V. Naumov, V. R. Galakhov, D. A. Zatsepin, Yu. A. Kotov, O. M. Samatov, and D. G. Kleshchev, Phys. Solid State 40(2), 268 (1998).
A. Ye. Yermakov, T. A. Feduschak, M. A. Uimin, A. A. Mysik, V. S. Gaviko, O. N. Chupakhin, A. B. Shishmakov, V. G. Kharchuk, L. A. Petrov, Yu. A. Kotov, A. V. Vosmerikov, and A. V. Korolyov, Solid State Ionics 172(1–4), 317 (2004).
W. Wernsdorfer, D. Mailly, and A. Benoit, J. Appl. Phys. 87(5), J094 (2000).
D. D. Awschalom and N. Samarth, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 200, 130 (1999).
J. C. Rodriguez, Physica B (Amsterdam) 192, 55 (1993).
G. Gattow and J. Zemann, Acta Crystallogr. 11, 866 (1958).
Yu. G. Raidugin, V. E. Naish, and E. A. Turov, JETP Lett. 54(11), 650 (1991).
U. Kobler and T. Chattopadhyay, Z. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 82, 383 (1991).
W. Neubecka, C. Vettier, F. de Bergevin, F. Yakhou, D. Mannix, L. Rannod, and T. Chatterji, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 62, 2173 (2001).
T. I. Arbuzova, A. A. Samokhvalov, L. B. Smolyak, B. V. Karpenko, N. M. Chebotaev, and S. V. Naumov, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 95, 168 (1991).
S. Mandal, S. Banerjee, and K. S. R. Menon, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 80, 214420 (2009).
A. P. Druzhkov, B. A. Gizhevskii, V. L. Arbuzov, E. A. Kozlov, K. V. Shalnov, S. V. Naumov, and D. A. Perminov, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 14, 7981 (2002).
V. B. Vykhodets, T. E. Kurennykh, A. E. Ermakov, I. V. Beketov, A. V. Bagazeev, V. S. Gaviko, M. V. Kuznetsov, A. I. Medvedev, M. A. Uimin, K. I. Shabanova, and N. N. Shchegoleva, Nanotechnol. Russ. 8(7–8), 482 (2013).
A. Abragam, Principles of Nuclear Magnetism (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1961; Inostrannaya Literatura, Moscow, 1963).
S. Verkhovskii, K. Mikhalev, A. Gerashenko, Y. Piskunov, V. Kazantsev, V. Bobrovskii, E. Mitberg, A. Podlesnyak, and A. Mirmelstein, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 16, 543 (2003).
M. Abe, K. Kumagai, S. Awaji, and T. Fujita, Physica C (Amsterdam) 160, 8 (1989).
A. Ananyev, A. Gerashenko, K. Okulova, S. Verkhovskii, A. Davletshin, V. Arbuzov, and B. Goshchitskii, Appl. Magn. Reson. 18, 235 (2000).
E. L. Nagaev, JETP Lett. 6(1), 18 (1967).
T. Kimura, Y. Sekio, H. Nakamura, T. Siegrist, and A. P. Ramirez, Nat. Mater. 7, 291 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.Ye. Yermakov, M.A. Uimin, A.V. Korolyov, K.N. Mikhalev, A.N. Pirogov, A.E. Teplykh, N.N. Shchegoleva, V.S. Gaviko, I.V. Byzov, V.V. Maikov, 2015, published in Fizika Tverdogo Tela, 2015, Vol. 57, No. 2, pp. 283–294.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yermakov, A.Y., Uimin, M.A., Korolyov, A.V. et al. Heterogeneous magnetic state in nanocrystalline cupric oxide CuO. Phys. Solid State 57, 296–308 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783415020092
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783415020092