Abstract
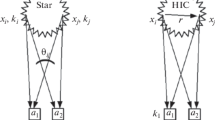
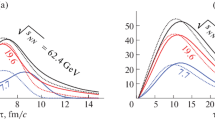
Heavy-ion collisions provide information about the properties of the matter under extreme conditions. Measurement of strangeness production properties provides important information about the collision region evolution. The spatial and temporal characteristics of particle emission can be extracted using femtoscopy technique. The collision energy, centrality, and transverse mass dependence of the three-dimensional charged kaon femtoscopic radii for Au + Au collisions in the Beam Energy Scan program is presented.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. Adams et al. (STAR Collab.), Nucl. Phys. A 757, 102 (2005);
K. Adcox, et al. (PHENIX Collab.), Nucl. Phys. A 757, 184 (2005);
B. B. Back, et al. (PHOBOS Collab.), Nucl. Phys. A 757, 28 (2005);
I. Arsene et al. (BRAHMS Collab.), Nucl. Phys. A 757, 1 (2005).
Y. Aoki, G. Endrodi, Z. Fodor, S. Katz, and K. Szabo, Nature 443, 675 (2006);
S. Borsanyi, et al. (Wuppertal-Budapest Collab.), J. High Energy Phys. 09, 073 (2010).
M. A. Halasz, A. D. Jackson, R. E. Shrock, M. A. Stephanov, and J. J. M. Verbaarschot, Phys. Rev. D 58, 096 007 (1998);
N. G. Antoniou and A. S. Kapoyannis, Phys. Lett. B 563, 165 (2003).
J. Randrup, Phys. Rev. C 82, 034902 (2010).
G. I. Kopylov and M. I. Podgoretsky, Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 15, 219. (1972);
G. I. Kopylov, Phys. Lett. B 50, 472 (1974);
M. I. Podgoretsky, Sov. J. Part. Nucl. 20, 266 (1989).
R. Lednicky and V. L. Lyuboshitz, Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 35, 770 (1982).
R. Lednicky et al., Phys. Lett. B 373, 30 (1996).
D. H. Rischke and M. Gyulassy, Nucl. Phys. A 608, 479 (1996).
M. A. Lisa, S. Pratt, R. Soltz, and U. Wiedemann, Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 55, 357 (2005).
J. Adams et al. (STAR Collab.), Phys. Rev. C 71, 044 906 (2005).
L. Adamczyk et al. (STAR Collab.), Phys. Rev. C 92, 014 904 (2015).
G. Bertsch, M. Gong, and M. Tohyama, Phys. Rev. C 37, 1896 (1988);
S. Pratt, Phys. Rev. D: Part. Fields 33, 1314 (1986).
M. G. Bowler, Phys. Lett. B 270, 69 (1991);
Yu. Sinyukov, R. Lednicky, S. V. Akkelin, J. Pluta, and B. Erazmus, Phys. Lett. B 432, 248 (1998).
K. Aamodt et al. (ALICE Collab.), Phys. Lett. B 696, 328–337 (2011).
L. Malinina (for ALICE Collab.), Nucl. Phys. A 956, 373–376 (2016).
M. A. Lisa et al. (E895 Collab.), Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 2798 (2000).
L. Ahle et al. (E866 Collab.), Phys. Rev. C 66, 054906 (2002).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The part of our work was performed using resources of NRNU MEPhI high-performance computing center.
Funding
The reported study was funded by RFBR according to the research project no. 16-02-01119a, partially supported the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation, grant no. 3.3380.2017/4.6, and by the National Research Nuclear University MEPhI in the framework of the Russian Academic Excellence Project (contract no. 02.a03.21.0005, 27.08.2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nigmatkulov, G., for the STAR Collaboration. Femtoscopic Probes with Strange Particles in STAR. Phys. Part. Nuclei 51, 248–251 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063779620030223
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063779620030223