Abstract
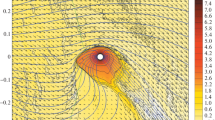
The orientation parameter effect of a hot Jupiter’s intrinsic dipole magnetic field on the flow structure in an extended gaseous (ionospheric) envelope of the planet is studied with a three-dimensional numerical simulation. For example, the hot Jupiter HD 209458b is considered. The magnitude of the planet’s magnetic momentum was set equal to 0.1 of the magnetic momentum of Jupiter. The parameters of the stellar wind’s magnetic field corresponding to the case of a super-Alfvén flow regime around the planet’s atmosphere was taken into account. Under such conditions, calculations have shown that a quasi-closed gaseous (ionospheric) envelope with an induced shock magnetosphere is formed around a hot Jupiter, with a detailed structure determined by the magnetic dipole’s slope angle. In this case, the mass-loss rate depends on the orientation of the planet’s dipole magnetic field and increases with an increasing angle between the direction to the star and the direction closest to the inner Lagrange point’s magnetic pole. This is due to the electromagnetic force increase that impedes the free movement of the matter in the emerging outflow when the magnetic pole approaches the inner Lagrange point.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. A. Murray-Clay, E. I. Chiang, and N. Murray, Astrophys. J. 693, 23 (2009).
M. Mayor and D. Queloz, Nature (London, U.K.) 378, 355 (1995).
D. Lai, C. Helling, and E. P. J. van den Heuvel, Astrophys. J. 721, 923 (2010).
S.-L. Li, N. Miller, D. N. C. Lin, and J. J. Fortney, N-ature (London, U.K.) 463, 1054 (2010).
A. Vidal-Madjar, A. Lecavelier des Etangs, J.-M. Desert, G. E. Ballester, et al., Nature (London, U.K.) 422, 143 (2003).
A. Vidal-Madjar, A. Lecavelier des Etangs, J.-M. Desert, G. E. Ballester, et al., Astrophys. J. 676, L57 (2008).
L. Ben-Jaffel, Astrophys. J. 671, L61 (2007).
A. Vidal-Madjar, J.-M. Desert, A. Lecavelier des Etangs, G. Hebrard, et al., Astrophys. J. 604, L69 (2004).
L. Ben-Jaffel and S. Sona Hosseini, Astrophys. J. 709, 1284 (2010).
J. L. Linsky, H. Yang, K. France, C.S. Froning, et al., Astrophys. J. 717, 1291 (2010).
R. V. Yelle, Icarus 170, 167 (2004).
A. Garcia Munoz, Planet. Space Sci. 55, 1426 (2007).
T. T. Koskinen, M. J. Harris, R. V. Yelle, and P. Lavvas, Icarus 226, 1678 (2013).
D. E. Ionov, V. I. Shematovich, and Ya. N. Pavlyuchenkov, Astron. Rep. 61, 387 (2017).
D. V. Bisikalo, P. V. Kaigorodov, D. E. Ionov, and V. I. Shematovich, Astron. Rep. 57, 715 (2013).
A. A. Cherenkov, D. V. Bisikalo, and P. V. Kaigorodov, Astron. Rep. 58, 679 (2014).
D. V. Bisikalo and A. A. Cherenkov, Astron. Rep. 60, 183 (2016).
A. Cherenkov, D. Bisikalo, L. Fossati, and C. Mostl, Astrophys. J. 846, 31 (2017).
A. A. Cherenkov, D. V. Bisikalo, and A. G. Kosovichev, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 475, 605 (2018).
D. V. Bisikalo, A. A. Cherenkov, V. I. Shematovich, L. Fossati, and C. Mostl, Astron. Rep. 62, 648 (2018).
I. F. Shaikhislamov, M. L. Khodachenko, H. Lammer, A. G. Berezutsky, I. B. Miroshnichenko, and M. S. Rumenskikh, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 481, 5315 (2018).
J.-M. Grießmeier, A. Stadelmann, T. Penz, et al., Astron. Astrophys. 425, 753 (2004).
A. Sanchez-Lavega, Astrophys. J. 609, L87 (2004).
A. A. Vidotto, M. Jardine, and Ch. Helling, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 411, L46 (2011).
K. G. Kislyakova, M. Holmstrom, H. Lammer, et al., Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 346, 981 (2014).
D. J. Stevenson, Rep. Prog. Phys. 46, 555 (1983).
A. P. Showman and T. Guillot, Astron. Astrophys. 385, 166 (2002).
K. Batygin, S. Stanley, and D. J. Stevenson, Astrophys. J. 776, 53 (2013).
T. M. Rogers and A. P. Showman, Astrophys. J. 782, L4 (2014).
T. M. Rogers and T. D. Komacek, Astrophys. J. 794, 132 (2014).
T. M. Rogers, Nat. Astron. 1, 0131 (2017).
K. M. Moore, R. K. Yadav, L. Kulowski, et al., Nature (London, U.K.) 561, 76 (2018).
C. A. Jones, Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 43, 583 (2011).
C. A. Jones, Icarus 241, 148 (2014).
S. I. Braginskii, Sov. Phys. JETP 20, 1462 (1964).
E. N. Parker, Cosmical Magnetic Fields: Their Origin and Their Activity (Clarendon, Oxford, 1979).
T. G. Cowling, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 94, 39 (1933).
A. S. Arakcheev, A. G. Zhilkin, P. V. Kaigorodov, D. V. Bisikalo, and A. G. Kosovichev, Astron. Rep. 61, 932 (2017).
D. V. Bisikalo, A. S. Arakcheev, and P. V. Kaigorodov, Astron. Rep. 61, 925 (2017).
T. T. Koskinen, J. Y.-K. Cho, N. Achilleos, and A. D. Aylward, Astrophys. J. 722, 178 (2010).
G. B. Trammell, P. Arras, and Z.-Y. Li, Astrophys. J. 728, 152 (2011).
I. F. Shaikhislamov, M. L. Khodachenko, Y. L. Sasunov, H. Lammer, et al., Astrophys. J. 795, 132 (2014).
M. L. Khodachenko, I. F. Shaikhislamov, H. Lammer, and P. A. Prokopov, Astrophys. J. 813, 50 (2015).
G. B. Trammell, Z.-Y. Li, and P. Arras, Astrophys. J. 788, 161 (2014).
T. Matsakos, A. Uribe, and A. Konigl, Astron. Astrophys. 578, A6 (2015).
A. G. Zhilkin and D. V. Bisikalo, Astron. Rep. 63, 550 (2019).
W.-H. Ip, A. Kopp, and J. H. Hu, Astrophys. J. 602, L53 (2004).
E. S. Belenkaya, Phys. Usp. 52, 765 (2009).
C. T. Russell, Rep. Prog. Phys. 56, 687 (1993).
P. Zarka, Planet. Space Sci. 55, 598 (2007).
A. Strugarek, A. S. Brun, S. P. Matt, and V. Reville, Astrophys. J. 815, 111 (2015).
P. V. Kaigorodov, E. A. Ilyina, and D. V. Bisikalo, Astron. Rep. 63, 365 (2019).
A. G. Zhilkin, D. V. Bisikalo, and P. V. Kaigorodov, Astron. Rep. 97 (2020, in press).
S. Czesla, P. C. Schneider, M. Salz, et al., Astron. Astrophys. 629, A5 (2019).
D. V. Bisikalo, A. G. Zhilkin, and A. A. Boyarchuk, Gas Dynamics of Close Binary Stars (Fizmatlit, Moscow, 2013) [in Russian].
A. G. Zhilkin, D. V. Bisikalo, and A. A. Boyarchuk, Phys. Usp. 55, 115 (2012).
T. Tanaka, J. Comput. Phys. 111, 381 (1994).
K. G. Powell, P. L. Roe, T. J. Linde, T. I. Gombosi, and D. L. de Zeeuw, J. Comput. Phys. 154, 284 (1999).
F. F. Chen, Introduction to Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion (Springer, Berlin, 1984).
M. J. Owens and R. J. Forsyth, Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 10, 5 (2013).
V. B. Baranov and K. V. Krasnobaev, Hydrodynamic Theory of Cosmic Plasma (Nauka, Moscow, 1977) [in Russian].
E. J. Weber and L. Davis, Jr., Astrophys. J. 148, 217 (1967).
J. C. Brandt, C. Wolff, and J. P. Cassinelli, Astrophys. J. 156, 1117 (1969).
T. Sakurai, Sol. Phys. 76, 301 (1982).
M. L. Goelzer, N. A. Schwadron, and C. W. Smith, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 119, 115 (2014).
D. Fabbian, R. Simoniello, R. Collet, et al., Astron. Nachr. 338, 753 (2017).
H. Lammer, M. Gudel, Y. Kulikov, et al., Earth Planets Space 64, 179 (2012).
D. Charbonneau, T. M. Brown, D. W. Latham, and M. Mayor, Astrophys. J. 529, L45 (2000).
G. L. Withbroe, Astrophys. J. 325, 442 (1988).
P. L. Roe, Lect. Notes Phys. 141, 354 (1980).
P. D. Lax, Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 7, 159 (1954).
R. O. Friedrihs, Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 7, 345 (1954).
V. V. Rusanov, Sov. Phys. JETP 14, 192 (1961).
P. Cargo and G. Gallice, J. Comp. Phys. 136, 446 (1997).
A. G. Kulikovskii, N. V. Pogorelov, and A. Yu. Semenov, Mathematical Aspects of Numerical Solution of Hyperbolic Systems (Fizmatlit, Moscow, 2001; CRC, Boca Raton, FL, 2019).
S. R. Chakravarthy and S. Osher, AIAA Papers No. 85-0363 (AIAA, 1985).
A. G. Zhilkin, A. V. Sobolev, D. V. Bisikalo, and M. M. Gabdeev, Astron. Rep. 63, 751 (2019).
B. Einfeldt, SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 25, 294 (1988).
A. Harten and J. Hyman, J. Comp. Phys. 50, 235 (1983).
A. Dedner, F. Kemm, D. Kroner, C.-D. Munz, T. Schnitzer, and M. Wesenberg, J. Comput. Phys. 175, 645 (2002).
W. M. Farrell, T. J. W. Lazio, M. D. Desch, T. S. Bastian, and P. Zarka, in Bioastronomy 2002: Life among the Stars, Proceedings of the 213th IAU Symposium, Ed. by R. Norris and F. Stootman (Astron. Soc. Pacif., San Francisco, CA, 2004), p. 73.
C. Weber, H. Lammer, I. F. Shaikhislamov, et al., Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 469, 3505 (2017).
J. E. Owen and F. C. Adams, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 444, 3761 (2014).
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (contract no. 18-12-00447). The study was carried out using capacities of the collective usage center “Complex for modeling of the data of mega-class research equipment” of the National Research Center “Kurchatov Institute” (http://ckp.nrcki.ru/) and Interdepartmental Supercomputer Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by L. Yungelson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhilkin, A.G., Bisikalo, D.V. & Kaygorodov, P.V. The Orientation Influence of a Hot Jupiter’s Intrinsic Dipole Magnetic Field on the Flow Structure in Its Extended Envelope. Astron. Rep. 64, 259–271 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063772920030063
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063772920030063