Abstract
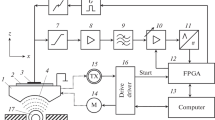
This paper presents a method for measuring the thickness and velocities of body waves and the density of an isotropic layer by a pulse scanning acoustic microscope. The method is based on recording the microscope signal as a function of the displacement magnitude of the focused ultrasonic transducer along its axis perpendicular to the sample surface and on the decomposition of the recorded 2D spatiotemporal signal into the spectrum of plane pulse waves. The velocities of the longitudinal and transverse waves and the layer’s thickness are calculated from the relative delays of the components of the spectrum of plane waves reflected from the surfaces of the layer and the density is computed by the amplitudes of these components. An experimental investigation of a test sample in the form of a glass plate carried out in the 50-MHz range shows that the error in measuring the thickness and velocities of body waves does not exceed 1% and the density measurement error does not exceed 10%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. A. D. Brigg and O. V. Kolosov, Acoustic Microscopy, Sec. Ed., (Oxford Univ., New York, 2010).
V. M. Levin, A. A. Goryunov, Yu. S. Petronyuk, and K. V. Zakutailov, in Proc. 2011 Int. Cong. on Ultrasonics ICU-2011, (Gdansk, Poland, 2011), p.124.
Yu. S. Petronyuk, V. M. Levin, and S. A. Titov, Physics Procedia 70 626–630 (2015).
V. Hänel and B. Kleffner, in Proc. Int. Symp. Acoustical Imaging, (Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 1998).
V. Hänel, J. Appl. Phys. 84 (2), 668–670 (1998).
J. Chen, X. Bai, K. Yang, and B.-F. Ju, Ultrasonics 56, 505–511 (2015).
S. A. Titov, R. G. Maev, and A. N. Bogatchenkov, IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelec. Freq. Contr. 50 (8), 1046–1056 (2003).
L. M. Brekhovskikh and O. A. Godin, Acoustics of Layered Media (Nauka, Moscow, 1989) [in Russian].
J. F. Claerbout, Imaging the Earth’s Interior (Blackwell Sci. Publ., Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985; Nedra, Moscow, 1989).
S. A. Titov and R. G. Maev, Acoust. Phys. 59 (5), 600–607 (2013).
J. Zhang, P. Guy, J. C. Baboux, and Y. Jayet, J. Appl. Phys. 86 (5), 2825–2835 (1999).
A. S. Birks, R. E. Green, and P. McIntire, Ultrasonic Testing (Nondestructive Testing) Handbook 2 nd ed., Vol. 7. (Amer. Soc. NondestructiveTesting, Columbus, OH, 1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.A. Titov, V.M. Levin, Yu.S. Petronyuk, 2017, published in Akusticheskii Zhurnal, 2017, Vol. 63, No. 6, pp. 692–699.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Titov, S.A., Levin, V.M. & Petronyuk, Y.S. Processing an acoustic microscope’s spatiotemporal signal to determine the parameters of an isotropic layer. Acoust. Phys. 63, 744–750 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106377101706015X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S106377101706015X