Abstract
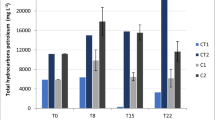
It was shown for the first time that the red alga Palmaria palmata (Linnaeus) F. Weber et D. Mohr, 1805 not only retained its physiological activity under the conditions of moderate pollution of the seawater with diesel fuel, but also exhibited a pronounced ability for sorption and destruction of petroleum products. The content of diesel fuel components in seawater decreased simultaneously with their accumulation in the algae. Apparently, the entire thallus of P. palmata participated in the destruction of diesel fuel: this process began on the algal surface via the activity of epiphytic hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacteria that provide the conversion of petroleum products into a plant-accessible form available for macrophytes. Subsequently, the petroleum products were neutralized by algal cells. The resilience of P. palmata under the influence of diesel fuel was confirmed by the consistently high metabolic activity of P. palmata cells throughout the 21-day experiment. It is assumed that the ability of macroalgae to form symbiotic associations with hydrocarbon-oxidizing microorganisms is the main factor in their bioremediation.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Voznesenskii, V.L., Zalenskii, O.V., and Semikhatova, O.A., Metody issledovaniya fotosinteza i dykhaniya rastenii (Methods to Study Photosynthesis and Respiration of Plants), Leningrad: Nauka, 1965.
Voskoboynikov, G.M., Il’inskii, V.V., Lopushanskaya, E.M., et al., Sanitary algae plantation for the bioremediation of coastal waters from oil: from theory to practice, Vopr. Sovrem. Al’gologii, 2017, no. 3(15). http://algology.ru/1184.
Voskoboinikov, G.M., Matishov, G.G., Metelkova, L.O., et al., Participation of the green algae Ulvaria obscura in bioremediation of sea water from oil products, Dokl. Biol. Sci., 2018, vol. 481, pp. 139–141.
Gusev, M.V., Koronelli, T.V., Lin’kova, M.A., and Il’inskii, V.V., The study of the association of cyanobacteria and oil-oxidizing bacteria in oil pollution, Mikrobiologiya, 1981, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 1092–1097.
Korolyuk, M.A., Ivanova, L.I., Maiorova, I.G., and Tokarev, V.E., Method for determination of catalase activity, Lab. Delo, 1988, no. 1, pp. 16–19.
Li, B.D., Separation, identification and quantification of photosynthetic pigments of macrobenthic algae, in Ekologicheskie aspekty fotosinteza morskikh makrovodoroslei (Ecological Aspects of Marine Macroalgae Photosynthesis), Vladivostok: Dal’nevost. Nauchn. Tsentr, Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1978, pp. 38–54.
Milchakova, N.A. and Shakhmatova, O.A., Catalase activity of the widely-distributed macroalgae of the Black Sea by gradient of the sewage pollution, Morsk. Ekol. Zh., 2007, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 44–57.
Mironov, O.G., Vzaimodeistvie organizmov s neftyanymi uglevodorodami (The Interaction of Organisms with Petroleum Hydrocarbons), Leningrad: Gidrometeoizdat, 1985.
Nemirovskaya, I.A., Neft’ v okeane (Zagryaznenie i prirodnye potoki) (Oil in the Ocean (Pollution and Natural Flows)), Moscow: Nauchnyi Mir, 2013.
Pugovkin, D.V., Liaimer, A., and Jensen, J.B., Epiphytic bacterial communities of the alga Fucus vesiculosus in oil-contaminated water areas of the Barents Sea, Dokl. Biol. Sci., 2016, vol. 471, pp. 269–271.
Semenov, A.M., Fedorenko, V.N., and Semenova, E.V., Microorganisms on the surfaces of marine macrophytes in the northern seas of Russia and prospects for their practical application, Biosfera, 2014, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 60–76.
Semenova, E.V., Semenov, A.M., Ivanov, M.N., et al., The role of epiphytic microorganisms of Fucus algae in the degradation of hydrocarbon pollution in waters of the northern seas, Ekol. Prom-st., 2009, no. 3, pp. 16–18.
Stepaniyan, O.V., Effects of crude oil on major functional characteristics of macroalgae of the Barents Sea, Russ. J. Mar. Biol., 2008, vol. 34, pp. 131–134.
Atlas, R.M., Horowitz, A., and Busdosh, M., Prudhoe crude oil in Arctic marine ice, water and sediment ecosystems: Degradation and interactions with microbial and benthic communities, J. Fish. Res. Board Can., 1978, vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 585–590.
Pilatti, F.K., Ramlov, F., Schmidt, E.C., et al., In vitro exposure of Ulva lactuca Linnaeus (Chlorophyta) to gasoline – Biochemical and morphological alterations, Chemosphere, 2016, no. 156, pp. 428–437.
Ramadass, K., Megharaj, M., Venkateswarlu, K., and Naidu, R., Toxicity of diesel water accommodated fraction toward microalgae, Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata and Chlorella sp. MM3, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2017, vol. 142, pp. 538–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.052
Rosenberg, G., Ecological growth strategies in the seaweeds Gracilaria folifera (Rhodopyceae) and Ulva sp. (Chlorophyceae), Ph. D. Thesis, New Haven, Conn.: Yale Univ., 1981.
Seely, G.R., Duncan, M.J., and Vidaver, W.E., Preparative and analytical extraction of pigments from brown algae with dimethyl sulfoxide, Mar. Biol., 1972, vol. 12, pp. 184–188.
Wrabel, M.L. and Peckol, P., Effects of bioremediation on toxicity and chemical composition of no. 2 fuel oil: Growth responses of the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus,Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2000, vol. 40, no. 2, pp. 135–139.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
FUNDING
This work was financially supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 18-05-80058, the Dangerous Events program.
Additional information
Translated by I. Barsegova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voskoboinikov, G.M., Ryzhik, I.V., Salakhov, D.O. et al. Absorption and Conversion of Diesel Fuel by the Red Alga Palmaria palmata (Linnaeus) F. Weber et D. Mohr, 1805 (Rhodophyta): The Potential Role of Alga in Bioremediation of Sea Water. Russ J Mar Biol 46, 113–118 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063074020020108
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063074020020108