Abstract
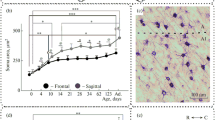
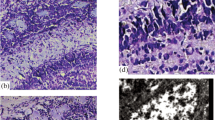
The aim of the research was to study morphological changes that occur in cortical catecholaminergic forebrain structures of Wistar rats during postnatal development. Rat’s forebrain sections at different stages of postnatal development (postnatal day 7, postnatal day 30, 4–6 months, and 23 months) were studied using immunohistochemistry methods. It has been shown that distinct cortical areas perform a unique distribution of catecholaminergic fibers due to their functional features. Age-related changes in density of the distribution of catecholaminergic fibers were analyzed, and it has been stated that the density of catecholaminergic fibers in the sensorimotor cortex increases with aging. It has been demonstrated that confocal laser scanning microscopy offers a wide variety of opportunities for qualitative and quantitative analysis of immunohistochemical results and can be a useful tool for tyrosine hydroxylase distribution studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Areal, L.B. and Blakely, R.D., Neurobehavioral changes arising from early life dopamine signaling perturbations, Neurochem. Int., 2020, vol. 137, p. 104747.
Arenas, E., Trupp, M., Åkerud, P., et al., GDNF prevents degeneration and promotes the phenotype of brain noradrenergic neurons in vivo, Neuron, 1995, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 1465–1473.
Asmus, S.E., Anderson, E.K., Ball, M.W., et al., Neurochemical characterization of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive interneurons in the developing rat cerebral cortex, Brain Res., 2008, vol. 1222, pp. 95–105.
Asmus, S.E., Cocanougher, B.T., Allen, D.L., et al., Increasing proportions of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive interneurons colocalize with choline acetyltransferase or vasoactive intestinal peptide in the developing rat cerebral cortex, Brain Res., 2011, vol. 1383, pp. 108–119.
Asmus, S.E., Raghanti, M.A., Beyerle, E.R., et al., Tyrosine hydroxylase-producing neurons in the human cerebral cortex do not colocalize with calcium-binding proteins or the serotonin 3A receptor, J. Chem. Neuroanat., 2016, vol. 78, pp. 1–9.
Barishpolets, V.V., Fedotova, Yu.O., and Sapronov, N.S., Structural and functional organization of the dopaminergic system of the brain, Eksp. Klin. Farmakol., 2009, vol. 72, no. 3, pp. 44–49.
Bell, K.F.S., Bennett, D.A., and Cuello, A.C., Paradoxical upregulation of glutamatergic presynaptic boutons during mild cognitive impairment, J. Neurosci., 2007, vol. 27, no. 40, pp. 10810–10817.
Benavides-Piccione, R. and DeFelipe, J., Distribution of neurons expressing tyrosine hydroxylase in the human cerebral cortex, J. Anat., 2007, vol. 211, no. 2, pp. 212–222.
Berger, B., Verney, C., Febvret, A., et al., Postnatal ontogenesis of the dopaminergic innervation in the rat anterior cingulate cortex (area 24). Immunocytochemical and catecholamine fluorescence histochemical analysis, Brain Res., 1985, vol. 353, no. 1, pp. 31–47.
Berger, B., Verney, C., Gaspar, P., et al., Transient expression of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity in some neurons of the rat neocortex during postnatal development, Brain Res., 1985, vol. 355, no. 1, pp. 141–144.
Bissonette, G.B. and Roesch, M.R., Development and function of the midbrain dopamine system: what we know and what we need to, Genes Brain Behav., 2016, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 62–73.
Björklund, A., Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy, vol. 21: Dopamine, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1992.
Bonnin, A., Miguel, R., Castro, J.G., et al., Effects of perinatal exposure to delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol on the fetal and early postnatal development of tyrosine hydroxylase-containing neurons in rat brain, J. Mol. Neurosci., 1996, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 291–308.
Brownstein, M., Saavedra, J.M., and Palkovits, M., Norepinephrine and dopamine in the limbic system of the rat, Brain Res., 1974, vol. 79, no. 3, pp. 431–436.
Cardozo-Pelaez, F., Song, S., Parthasarathy, A., et al., Oxidative DNA damage in the aging mouse brain, Mov. Disord., 1999, vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 972–980.
Cools, R., Role of dopamine in the motivational and cognitive control of behavior, Neuroscientist, 2008, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 381–395.
Fallon, J., Collateralization of monoamine neurons: mesotelencephalic dopamine projections to caudate, septum, and frontal cortex, J. Neurosci., 1981, vol. 1, no. 12, pp. 1361–1368.
Finkel, T. and Holbrook, N.J., Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing, Nature, 2000, vol. 408, no. 6809, pp. 239–247.
Gates, M.A., Torres, E.M., White, A., et al., Re-examining the ontogeny of substantia nigra dopamine neurons, Eur. J. Neurosci., 2006, vol. 23, no. 5, pp. 1384–1390.
Gogolla, N., The insular cortex, Curr. Biol., 2017, vol. 27, no. 12, pp. R580–R586.
Grigor’ev, I.P., Alekseeva, O.S., Kirik, O.V., et al., Distribution of low molecular weight proteins of neurofilaments in the cingulate cortex of the rat brain, Morfologiya, 2018, vol. 154, no. 5, pp. 7–12.
Grondin, R., Littrell, O.M., Zhang, Z., et al., GDNF revisited: a novel mammalian cell-derived variant form of GDNF increases dopamine turnover and improves brain biodistribution, Neuropharmacology, 2019, vol. 147, pp. 28–36.
Hamezah, H.S., Durani, L.W., Ibrahim, N.F., et al., Volumetric changes in the aging rat brain and its impact on cognitive and locomotor functions, Exp. Gerontol., 2017, vol. 99, pp. 69–79.
Kalinina, T.S. and Dygalo, N.N., Development of the noradrenergic system of the rat brain after prenatalexposure to corticosterone, Biol. Bull. (Moscow), 2013, vol. 40, no. 6, pp. 545–549.
Kalinina, T.S., Shishkina, G.T., and Dygalo, N.N., Induction of tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression by glucocorticoids in the perinatal rat brain is age-dependent, Neurochem. Res., 2012, vol. 37, no. 4, pp. 811–818.
Kortz, M.W. and Lillehei, K.O., Insular Cortex, FL: StatPearls Publishing, 2021.
Korzhevskii, D.E., Sukhorukova, E.G., Kirik, O.V., et al., Immunohistochemical demonstration of specific antigens in the human brain fixed in zinc–ethanol–formaldehyde, Eur. J. Histochem., 2015, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 5–9.
Latsari, M., Dori, I., Antonopoulos, J., et al., Noradrenergic innervation of the developing and mature visual and motor cortex of the rat brain: a light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical analysis, J. Comp. Neurol., 2002, vol. 445, no. 2, pp. 145–158.
Levitt, P. and Moore, R.Y., Development of the noradrenergic innervation of neocortex, Brain Res., 1979, vol. 162, no. 2, pp. 243–259.
Livneh, Y. and Andermann, M.L., Cellular activity in insular cortex across seconds to hours: sensations and predictions of bodily states, Neuron, 2021, vol. 109, pp. 1–18.
Luo, Y. and Roth, G.S., The roles of dopamine oxidative stress and dopamine receptor signaling in aging and age-related neurodegeneration, Antioxid. Redox Signal., 2004, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 449–460.
Matsunaga, W., Isobe, K., and Shirokawa, T., Involvement of neurotrophic factors in aging of noradrenergic innervations in hippocampus and frontal cortex, Neurosci. Res., 2006, vol. 54, no. 4, pp. 313–318.
Nomura, S., Bouhadana, M., Morel, C., et al., Noradrenalin and dopamine receptors both control cAMP-PKA signaling throughout the cerebral cortex, Front. Cell. Neurosci., 2014, vol. 8, article ID 247.
Norrara, B., Fiuza, F.P., Arrais, A.C., et al., Pattern of tyrosine hydroxylase expression during aging of mesolimbic pathway of the rat, J. Chem. Neuroanat., 2018, vol. 92, pp. 83–91.
Ohara, P.T., Granato, A., Moallem, T.M., et al., Dopaminergic input to GABAergic neurons in the rostral agranular insular cortex of the rat, J. Neurocytol., 2003, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 131–141.
Reynolds, L.M. and Flores, C., Mesocorticolimbic dopamine pathways across adolescence: diversity in development, Front. Neural Circuits, 2021, vol. 15, pp. 94–111.
Reynolds, L.M., Pokinko, M., Torres-Berrío, A., et al., Dcc receptors drive prefrontal cortex maturation by determining dopamine axon targeting in adolescence, Biol. Psychiatry, 2018, vol. 83, no. 2, pp. 181–192.
Rushworth, M.F.S., Noonan, M.A.P., Boorman, E.D., et al., Frontal cortex and reward-guided learning and decision-making, Neuron, 2011, vol. 70, no. 6, pp. 1054–1069.
Satoh, J. and Suzuki, K., Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons in the mouse cerebral cortex during the postnatal period, Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res, 1990, vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 1–5.
Sukhareva, E.V., Kalinina, T.S., Bulygina, V.V., et al., Brain tyrosine hydroxylase and its regulation by glucocorticoids, Vavilov. Zh. Genet. Sel., 2016, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 212–219.
Sukhorukova, E.G., Alekseeva, O.S., and Korzhevskii, D.E., Mammalian brain catecholaminergic neurons and neuromelanin, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2014, vol. 50, no. 5, pp. 336–342.
Tremblay, R., Lee, S., and Rudy, B., GABAergic interneurons in the neocortex: from cellular properties to circuits, Neuron, 2016, vol. 91, no. 2, pp. 260–292.
Ugrumov, M.V., Synthesis of monoamines by non-monoaminergic neurons: illusion or reality?, Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2009, vol. 95, no. 3, pp. 273–282.
Ugrumov, M.V., Taxi, J., Tixier-Vidal, A., et al., Ontogenesis of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunopositive structures in the rat hypothalamus. An atlas of neuronal cell bodies, Neuroscience, 1989, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 135–156.
Ugrumov, M.V., Melnikova, V., Ershov, P., et al., Tyrosine hydroxylase- and/or aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase-expressing neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus: ontogenesis and functional significance, Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2002, vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 533–548.
Vogt, B.A., Vogt, L., and Farber, N.B., Cingulate cortex and disease models, in The Rat Nervous System, New York: Elsevier, 2004, Chapter 22, pp. 705–727.
Voorn, P., Kalsbeek, A., Jorritsma-Byham, B., et al., The pre- and postnatal development of the dopaminergic cell groups in the ventral mesencephalon and the dopaminergic innervation of the striatum of the rat, Neuroscience, 1988, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 857–887.
Weihe, E., Depboylu, C., Schutz, B., et al., Three types of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive CNS neurons distinguished by DOPA decarboxylase and VMAT2 co-expression, Cell. Mol. Neurobiol., 2006, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 657–676.
Weiss, B., Greenberg, L., and Cantor, E., Age-related alterations in the development of adrenergic denervation supersensitivity, Fed. Proc., 1979, vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 1915–1921.
Zaman, V., Li, Z., Middaugh, L., et al., The noradrenergic system of aged GDNF heterozygous mice, Cell Transplant., 2003, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 291–303.
Funding
The work was carried out within the framework of the state task of the Federal State Budgetary Scientific Institution “Institute of Experimental Medicine.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
V.A. Razenkova: taking material, wiring and pouring into paraffin blocks, staining preparations, photographing and analyzing preparations, statistical analysis of the obtained preparations, working with drawings, writing the text of the article. D.E. Korzhevskii: design of the experiment, work with drawings and writing the text of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. During the study, all applicable international, national, and institutional (conclusion no. 1/20 dated February 27, 2020, of the local ethics committee of the IEM) principles of care and use of animals were observed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razenkova, V.A., Korzhevskii, D.E. Catecholaminergic Rat’s Forebrain Structures in Early Postnatal Development and Aging. Russ J Dev Biol 53, 208–216 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360422030067
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360422030067