Abstract
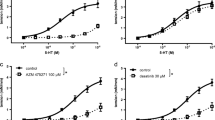
We found that the inhibitor of Rho-kinase fasudil selectively inhibited constriction of isolated rings of the aorta and mesenteric artery in rats in response to application of the agonists of 5HT2A-(DOI and TBC-2) and 5HT1A-receptors (8-OH-DPAT) and did not influence vasoconstriction induced by serotonin. We demonstrate for the first time that application of the agonists of 5HT2C-receptors (MK 212 and SCH 23390) did not influence the tone of “intact” vessels. The marked vasoconstrictory effect of the agonists of 5HT2C-receptors was observed in the vessels preconstricted due to angiotensin II or vasopressin. We found that the inhibitor of Rho-kinase did not influence negatively on MK 212 or SCH 23390-induced constriction of isolated rings of the aorta and mesenteric artery in rats. We suppose that, in the presence of fasudil, serotonin induces constriction of vessels through the interaction with 5HT2C-receptors and signal transduction from these receptors does not involve Rho-kinase activity. We found that fasudil attenuated vasoconstriction induced by norepinephrine and vasopressin by 40%. We demonstrated that tyrosine c-Src-kinase plays the most important role in signal transduction from 5HT-receptors because its effects are specific with relation to these receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alioua, A., Mahajan, A., Nishimaru, K., et al., Coupling of c-Src to large conductance voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channels as a new mechanism of agonist-induced vasoconstriction, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2002, vol. 99, pp. 14560–14565.
Armbruster, B.N. and Roth, B.L., Mining the receptorome, J. Biol. Chem., 2005, vol. 280, pp. 5129–5132.
Becamel, C., Gavarini, S., Chanrion, B., et al., The serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors interact with specific sets of PDZ proteins, J. Biol. Chem., 2004, vol. 279, no. 19, pp. 20257–20266.
Bockaert, J., Roussignol, G., Becamel, C., et al., GPCR-interacting proteins (GIPs): nature and functions, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 2004, vol. 32, pp. 851–855.
Calama, E., Moran, A., Ortiz de Urbina, A.V., et al., Vasoconstrictor responses to 5-hydroxytryptamine in the autoperfused hindquarters of spontaneously hypertensive rats, Pharmacology, 2004, vol. 71, pp. 66–72.
Dai, Y., Dudek, N.L., Li, Q., and Muma, N.A., Phospholipase C, Ca2+, and calmodulin signaling are required for 5-HT2A receptor-mediated transamidation of rac1 by transglutaminase, Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 2011, vol. 213, nos. 2–3, pp. 403–412.
Davis, R.P., Pattison, J., Thompson, J.M., et al., 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) reduces total peripheral resistance during chronic infusion: direct arterial mesenteric relaxation is not involved, BMC Pharmacol., 2012, vol. 12, p. 4.
Estévez, M.A., Henderson, J.A., Ahn, D., et al., The neuronal RhoA GEF, Tech, interacts with the synapticmulti-PDZ-domain-containing protein, MUPP1, J. Neurochem., 2008, vol. 106, no. 3, pp. 1287–1297.
Fernandez, M.M., Moran, A., Martin, M.L., and San Roman L., Mesenteric vasoconstrictor response to 5-hydroxytryptamine in the in situ blood autoperfused rat mesentery: involvement of 5-HT2B and/or 5-HT2C receptor activation, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2000, vol. 401, pp. 221–227.
Fukata, Y., Amano, M., and Kaibuchi, K., Rho-Rhokinase pathway in smooth muscle contraction and cytoskeletal reorganization of non-muscle cells, Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 2001, vol. 22, pp. 32–39.
Fuso, L., Baldi, F., and Di Perna, A., Therapeutic strategies in pulmonary hypertension, Front. Pharmacol., 2011, vol. 2, no. 21, pp. 1–15.
Gavarini, S., Becamel, C., Chanrion, B., et al., Molecular and functional characterization of proteins interacting with the C-terminal domains of 5-HT2 receptors: emergence of 5-HT2 “receptosomes,” Biol. Cell., 2004, vol. 96, pp. 373–381.
Ghisdal, P., Vandenberg, G., and Morel, N., Rho-dependent kinase is involved in agonist-activated calcium entry in rat arteries, J. Physiol., 2003, vol. 551, no. 3, pp. 855–867.
Hall, R.A. and Lefkowitz, R.J., Regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling by scaffold proteins, Circ. Res., 2002, vol. 91, pp. 672–680.
Hirano, K., Hirano, M., and Kanaide, H., Regulation of myosin phosphorylation and myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in vascular smooth muscle, J. Smooth Muscle Res., 2004, vol. 40, no. 6, pp. 219–236.
Hirano, K., Current topics in the regulatory mechanism underlying the Ca2+ sensitization of the contractile apparatus in vascular smooth muscle, J. Pharmacol. Sci., 2007, vol. 104, pp. 109–115.
Hoyer, D., Clarke, D.E., Fozard, J.R., et al., International union of pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), Pharmacol. Rev., 1994, vol. 46, pp. 157–203.
Kozhevnikova, L.M. and Avdonin, P.V., Disturbances in hormonal regulation of vascular tone during traumatic shock, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2006, vol. 141, no. 5, pp. 574–577.
Kozhevnikova, L.M. and Avdonin, P.V., Agonist of serotonin 5HT1A-receptors 8-OH-DPAT increases the force of contraction of rat aorta and mesenteric artery in the presence of endothelin-1 or vasopressin and causes relaxation of the vessels preconstricted with noradrenaline, Biol. Bull. (Moscow), 2010, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 35–43.
Kozhevnikova, L.M. and Avdonin, P.V., Involvement of calmodulin in realization of vasoconstrictive effects of serotonin and norepinephrine, Biol. Bull. (Moscow), 2012, vol. 39, no. 4, pp. 360–367.
Kozhevnikova, L.M., Avdonin, P.P., Sukhanova, I.F., and Avdonin, P.V., Role of desensitization of glucocorticoid receptors in the development of vascular resistance to endogenous vasoconstrictors in traumatic shock, Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk, 2007, no. 6, pp. 3–8.
Kozhevnikova, L.M., Avdonin, P.P., Sukhanova, I.F., and Avdonin, P.V., Inversion of the response to serotonin in rats with traumatic shock, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2008, vol. 145, no. 3, pp. 298–301.
Kozhevnikova, L.M., Davydova, A.G., and Avdonin, P.V., Plasma membrane depolarization and activation of receptors for endogenous vasoconstrictors as possible mechanisms of potentiation of vasoconstrictive response to serotonin in traumatic shock in rats, Biol. Bull. (Moscow), 2009, vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 285–297.
Labasque, M., Reiter, E., Becamel, C., et al., Physical interaction of calmodulin with the 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptor C-terminus is essential for G protein-independent, arrestin-dependent receptor signaling, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2008, vol. 19, no. 11, pp. 4640–4650.
Lin, L., Tran, T., Hu, S., et al., RHGF-2 is an essential Rho-1 specific RhoGEF that binds to the multi-PDZ domain scaffold protein MPZ-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 2, p. e31499.
Loirand, G. and Pacaud, P., The role of rho protein signaling in hypertension, Nat. Rev. Cardiol., 2010, vol. 7, pp. 637–647.
Lu, R., Alioua, A., Kumar, Y., et al., c-Src tyrosine kinase, a critical component for 5-HT2A receptor-mediated contraction in rat aorta, J. Physiol., 2008, vol. 586, no. 16, pp. 3855–3869.
MacLean M.R. Pulmonary hypertension and the serotonin hypothesis: where are we now?, Int. J. Clin. Pract. Suppl., 2007, vol. 156, pp. 27–31.
MacLean, M.R. and Dempsie, Y., The serotonin hypothesis of pulmonary hypertension revisited, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 2010, vol. 661, pp. 309–322.
Magalhaes, A., Dunn, H., and Ferguson, S.G., Regulation of GPCR activity, trafficking and localization by GPCR-interacting proteins, Br. J. Pharmacol., 2012, vol. 165, no. 6, pp. 1717–1736.
Nagaoka, T., Gebb, S.A., Karoor, V., et al., Involvement of RhoA/Rho kinase signaling in pulmonary hypertension of the fawn-hooded rat, J. Appl. Physiol., 2006, vol. 100, pp. 996–1002.
Noma, K., Oyama, N., and Liao, J.K., Physiological role of rocks in the cardiovascular system, Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol., 2006, vol. 290, no. 3, pp. C661–C668.
Nunes, K.P., Rigsby, C.S., and Webb, R.C., RhoA/Rhokinase and vascular diseases: what is the link?, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2010, vol. 67, no. 22, pp. 3823–3836.
Oda, Y., Renaux, B., Bjorge, J., et al., cSrc is a major cytosolic tyrosine kinase in vascular tissue, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 1999, vol. 77, pp. 606–617.
Ogden, K., Thomson, J.M., Hickner, Z., et al., A new signaling paradigm for serotonin: use of Crk-associated substrate in arterial contraction, Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol., 2006, vol. 291, no. 6, pp. H2857–H2863.
Raymond, J.R., Turner, J.H., Gelasco, A.K., et al., 5-HT Receptor signal transduction pathways, in The Receptors: The Serotonin Receptors: From Molecular Pharmacology to Human Therapeutics, Roth, B.L., Ed., Totowa; New Jersey: Humana Press Inc., 2006, pp. 143–207.
Satoh, K., Fukumoto, Y., and Shimokawa, H., Rho-kinase: important new therapeutic target in cardiovascular diseases, Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol., 2011, vol. 301, pp. H287–H296.
Smith, B.M., Thomsen, W.J., and Grottick, A.J., The potential use of selective 5-HT2C agonists in treating obesity, Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs, 2006, vol. 15, pp. 257–266.
Somlyo, A.P. and Somlyo, A.V., Ca2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: modulated by g proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase, Physiol. Rev., 2003, vol. 83, no. 4, pp. 1325–1358.
Surma, M., Wei, L., and Shi, J.K., Rho kinase as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease, Future Cardiol., 2011, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 657–671.
Tiniakov, R. and Scrogin, K.E., The spleen is required for 5-HT1A receptor agonist-mediated increases in mean circulatory filling pressure during hemorrhagic shock in the rat, Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol., 2009, vol. 296, no. 5, pp. R1392–R1401.
Tiniakov, R., Osei-Owusu, P., and Scrogin, K.E., The 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor agonist, (+)-8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)-tetralin, increases cardiac output and renal perfusion in rats subjected to hypovolemic shock, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 2007, vol. 320, no. 2, pp. 811–818.
Turner, J.H., Gelasco, A.K., and Raymond, J.R., Calmodulin interacts with the third intracellular loop of the serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor at two distinct sites: putative role in receptor phosphorylation by protein kinase C, J. Biol. Chem., 2004, vol. 279, pp. 17027–17037.
Turner, J.H. and Raymond, J.R., Interaction of calmodulin with the serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine2A receptor. A putative regulator of g protein coupling and receptor phosphorylation by protein kinase C, J. Biol. Chem., 2005, vol. 280, no. 35, pp. 30741–30750.
Wang, D., Post, M., and Cutz, E., Expression of serotonin receptor 2C in rat type II pneumocytes, Am. J. Resp. Cell. Mol., 1999, vol. 20, pp. 1175–1180.
Watts, S.W., 5-HT in systemic hypertension: foe, friend or fantasy?, Clin. Sci. (Lond.), 2005, vol. 108, no. 5, pp. 399–412.
Watts, S.W., Yang, P., Banes, A.K., and Baez, M., Activation of Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase proteins by vascular serotonin receptors, J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 2001, vol. 38, no. 4, pp. 539–551.
Watts, S.W., Priestley, J.R., and Thompson, J.M., Serotonylation of vascular proteins important to contraction, PLoS One, 2009, vol. 4, no. 5, p. e5682.
Watts, S., Morrison, S., Davis, R.P., and Barman, S.M., Serotonin and blood pressure regulation, Pharmacol. Rev., 2012, vol. 64, no. 2, pp. 359–388.
Wirth, A., Rho kinase and hypertension, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2010, vol. 1802, no. 12, pp. 1276–1284.
Wong, W.K., Knowles, J.A., and Morse, J.H., Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II C-terminus interacts with c-Src implication for a role in pulmonary arterial hypertension, Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol., 2005, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 438–446.
Zhang, B., Liu, Y., Luo, Y., et al., Alteration of serotonin 2C receptor expression in the aorta and the pulmonary artery in rats exposed to hypoxia, Chin. J. Physiol., 2008, vol. 51, no. 6, pp. 338–347.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.M. Kozhevnikova, A.A. Moskovtsev, M.V. Mesitov, 2014, published in Izvestiya Akademii Nauk, Seriya Biologicheskaya, 2014, No. 5, pp. 500–509.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozhevnikova, L.M., Moskovtsev, A.A. & Mesitov, M.V. The effects of inhibitors of Rho- and tyrosine c-Src-kinases on serotonin-induced constrictions of the aorta and mesenteric artery in rats. Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 41, 452–460 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359014050069
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359014050069