Abstract
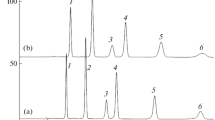
Specific features of chromatographic determination of xanthophyll esters are studied using an example of marigold flower lutein diesters under reversed-phase HPLC conditions. The developed two-column method made it possible to establish that, in samples with a low solubility of carotenoids in the used solvent and on a chromatography column in using a mobile phase with a low solubility of carotenoids, the precipitation of diesters is possible, which detrimentally affects the accuracy of the chromatographic determination. A critical factor in this case isì temperature: the storage of samples (solutions) in a refrigerator is not always advisable, because freezing of the main components is possible. It was shown that the use of a mobile phase containing from 0 to 10 vol % acetonitrile in acetone at a temperature not lower than 20°C is acceptable for the separation of all-trans-lutein diesters from cis-derivatives of lutein and zeaxanthin derivatives on “monomeric” C18-phases.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Mariutti, L.R.B. and Mercadante, A.Z., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 2018, vol. 648, p. 36.
Mercadante, A.Z., Rodrigues, D.B., Petry, F.C., and Mariutti, L.R.B., Food Res. Int., 2017, vol. 99, p. 830.
Sarkar, C.R., Bhagawati, B., Das, L., and Goswami, B.C., Ann. Biol. Res., 2012, vol. 3, p. 1461.
Abdala, A.F., Gallardo, A.P., Olvera, L.G., and Silva, E.M.E., Bioresour. Bioprocess., 2017, vol. 4, p. 5.
Raut, S. and Thaneshwari, T., Ecol. Environ. Conserv., 2022, vol. 28, special issue, p. S315.
Piccaglia, R., Marotti, M., and Grandi, S., Ind. Crops Prod., 1998, vol. 8, p. 45; Gregory, G.K., Chen, T.-S., and Philip, T., J. Food Sci., 1986, vol. 51, p. 1093; Rivas, J.D.L., J. Chromatogr. A, 1989, vol. 464, p. 442.
Tsao, R., Yang, R., Young, J.C., Zhu, H., and Manolis, T., J. Chromatogr. A, 2004, vol. 1045, p. 65.
Sowbhagya, H.B., Sampathu, S.R., and Krishnamurthy, N., Food Rev. Int., 2004, vol. 20, p. 33.
Jiang, X.-Y., Chen, L.-S., and Zhou, C.-S., J. Cent. South Univ. Technol., 2005, vol. 12, p. 306.
Hayashi, T., Oka, H., Ito, Y., Goto, T., Ozeki, N., Itakura, Y., Matsumoto, H., Ohno, H., Yoshida, K., Miyazawa, T., and Nagase, H., J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol., 2005, vol. 27, p. 335.
Vechpanich, J. and Shotipruk, A., Sep. Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 46, p. 265.
Lapshova, M.S., Deineka, V.I., Deineka, L.A., Blinova, I.P., and Tret’yakov, M.Yu., J. Anal. Chem., 2013, vol. 68, no. 11, p. 1014.
Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M., Rabalski, I., and Blackwell, B.A., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2007, vol. 55, p. 4965.
Deineka, V.I., Lapshova, M.S., Zakharenko, E.V., and Deineka, L.A., Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A, 2013, vol. 87, no. 11, p. 1912.
Epler, K.S., Sander, L.C., Ziegler, R.G., Wise, S.A., and Craft, N.E., J. Chromatogr. A, 1992, vol. 595, p. 89.
Craft, N.E. and Soares, J.H., Jr., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1992, vol. 40, p. 431.
Mrowicka, M., Mrowicki, J., Kucharska, E., and Majsterek, I., Nutrients, 2022, vol. 14, p. 827.
Turtygin, A.V., Deineka, V.I., and Deineka, L.A., J. Anal. Chem., 2013, vol. 68, no. 6, p. 558.
Deineka, V.I., Burzhinskaya, T.G., and Deineka, L.A., Anal. Kontrol’, 2019, no. 4, p. 501.
Deineka, V.I., Sidorov, A.N., Deineka, L.A., and Tynyanaya, I.I., Sorbtsionnye Khromatogr. Protsessy, 2016, vol. 16, no. 3, p. 384.
Deineka, V.I., Deineka, L.A., Sidorov, A.N., Kostenko, M.O., and Blinova, I.PRuss. J. Phys. Chem. A, 2016, vol. 90, p. 861.
Deineka, V.I., Deineka, L.A., Sidorov, A.N., Saenko, I.I., and Kostenko, O.M., Sorbtsionnye Khromatogr. Protsessy, 2016, vol. 16, no. 5, p. 624.
Weller, P. and Breithaupt, D.E., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2003, vol. 51, p. 7044.
Deineka, V.I. and Deineka, L.A., Sorbtsionnye Khromatogr. Protsessy, 2006, vol. 6, no. 3, p. 366.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by V. Kudrinskaya
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deineka, V.I., Burzhinskaya, T.G., Blinova, I.P. et al. Specific Features of the Determination of Xanthophyll Esters under Reversed-Phase HPLC Conditions. J Anal Chem 78, 759–765 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934823060023
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934823060023