Abstract
The effect of the degree of anisotropy (axial ratio) of gold nanoparticles on the structure and conductivity of ring deposits formed on a planar substrate upon evaporation of droplets of aqueous dispersions with different particle number concentrations has been studied. A nontrivial phenomenon of a decrease in the specific conductivity of the deposits with an increase in particle concentration in case of gold nanorods dispersions has been revealed.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Note that, in this case, the particles were redispersed in the same dispersion medium.
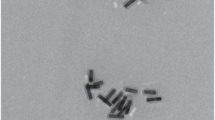
Note that GNR dispersions contain quasi-spherical Au nanoparticles. However, their fraction is no higher than 10–15% [13].
The relatively low contrast of the image is, in our opinion, due to the presence of some amount of residual CTAB on the particle surface.
REFERENCES
Deegan, R.G., Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Phys., Plasmas, Fluids, Relat. Interdiscip. Top., 2000, vol. 61, p. 475.
Deegan, R.D., Bakajin, O., Dupont, T.F., Huber, G., Nagel, S.R., and Witten, T.A., Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Phys., Plasmas, Fluids, Relat. Interdiscip. Top., 2000, vol. 62, p. 756.
Popov, Y.O., Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Phys., Plasmas, Fluids, Relat. Interdiscip. Top., 2005, vol. 71, p. 1.
Okubo, T., Yokota, N., and Tsuchida, A., Colloid Polym. Sci., 2007, vol. 285, p. 1257.
Dmitriev, A.S. and Makarov, P.G., Colloid J., 2015, vol. 77, p. 135.
Molchanov, S.P., Roldughin, V.I., and Chernova-Kharaeva, I.A., Colloid J., 2015, vol. 77, p. 761.
Molchanov, S.P., Roldughin, V.I., and Chernova-Kharaeva, I.A., Colloid J., 2015, vol. 77, p. 770.
Vysotskii, V.I., Roldughin, V.I., Uryupina, O.Ya., and Zaitseva, A.V., Colloid J., 2011, vol. 73, p. 176.
Vysotskii, V.V., Uryupina, O.Ya., Senchikhin, I.N., and Roldughin, V.I., Colloid J., 2013, vol. 75, p. 142.
Vysotskii, V.V., Uryupina, O.Ya., Senchikhin, I.N., and Roldughin, V.I., Colloid J., 2013, vol. 75, p. 634.
Vysotskii, V.V., Roldughin, V.I., Uryupina, O.Ya., Senchikhin, I.N., and Zaitseva, A.V., Colloid J., 2014, vol. 76, p. 531.
Lohse, S.E. and Murphy, C.J., Chem. Mater., 2013, vol. 25, p. 1250.
Salavatov, N.A., Dement’eva, O.V., Mikhailichenko, A.I., and Rudoy, V.M., Colloid J., 2018 (in press).
Li, P., Li, Y., Zhou, Z.-K., Tang, S., Yu, X.-F., Shu, X., Wu, Z., Xiao, Q., Zhao, Y., Wang, H., and Chu, P.K., Adv. Mater. (Weinheim, Fed. Repub. Ger.), 2016, vol. 28, p. 2511.
Dugyala, V.R. and Basavaraj, M.G., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2015, vol. 119, p. 3860.
Martin, A., Schopf, C., Pescaglini, A., Wang, J.J., and Iacopino, D., Langmuir, 2014, vol. 30, p. 10206.
Park, K., PhD Thesis (Georgia Inst. of Technology, Atlanta, 2006).
Sharma, V., Park, K., and Srinivasarao, M., Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 2009, vol. 65, p. 1.
Ramasamy, K. and Gupta, A., J. Mater. Res., 2013, vol. 28, p. 1761.
Reed, S.J.B., Electron Microprobe Analysis and Scanning Electron Microscopy in Geology, New York: Cambridge Univ. Press, 2005.
Kim, Y.-K., Na, H.-K., Ham, S., and Min, D.-H., RSC Adv., 2014, vol. 4, p. 50091.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Presidium of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Program of Fundamental Research no. 34).
The experiments were carried out using the equipment of the Center for Collective Use of the A.N. Frumkin Institute of Physical Chemistry and Electrochemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, and the Teaching and Methodical Center of Lithography and Microscopy of Moscow State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated by A. Kirilin
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vysotskii, V.V., Dement’eva, O.V., Salavatov, N.A. et al. Structure and Electrical Conductivity of Ring Deposits Resulting from Evaporation of Droplets of Dispersions Containing Gold Nanoparticles with Different Degrees of Anisotropy. Colloid J 80, 615–624 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061933X18060194
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061933X18060194