Abstract
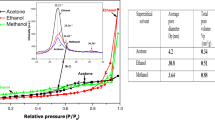
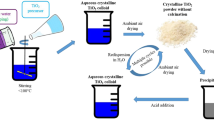
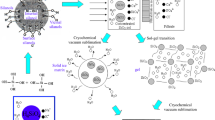
Stable highly concentrated TiO2 sol has been synthesized using binary titanyl ammonium sulfate monohydrate, (NH4)2TiO(SO4)2 · H2O. Treatment of the sol with an ammonia solution has yielded a stable hydrogel, which, after being dried, is transformed into a TiO2 xerogel. Study of the structure-related sorption and crystalline-chemical properties of the synthesized xerogel has shown that it represents a semicrystalline micro/mesoporous material with a rather developed specific surface area (S sp = 120 m2/g). According to potentiometric titration data, the point of zero charge (PZC) of this material is located at pH 3.9. Measurements of the electrophoretic mobility (by microelectrophoresis) of TiO2 xerogel particles in solutions of HCl, NaOH, and salts of mono-, bi-, and trivalent cations have shown that (1) the isoelectric point (IEP) of the particles lies in the vicinity of pH 6.2, i.e., at a much higher pH than that for PZC; (2) the presence of increasing amounts of 1: 1 and 2: 1 electrolytes causes a gradual and a dramatic reduction in the ζ potential of the particles, respectively; and (3), in the presence of an electrolyte with a trivalent counterion, the surface charge is reversed. The behavior of TiO2 xerogel in an electric field is similar to that of lyophobic particles, with the difference that there is no maximum in the ζ potential versus 1: 1 electrolyte concentration dependence and the measured IEP of the xerogel is much higher than its PZC. Possible reasons for this discrepancy have been discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goroshchenko, Ya.G., Khimiya titana (Chemistry of Titanium), Kiev Naukova Dumka, 1970.
Gerasimova, L.G. and Maslova, M.V., Gidroksidy titana i kompozitsii na ikh osnove (Titanium Hydroxides and Related Compositions), Moscow: OOO “Izd. LKM-press,” 2011.
Fujimoto, C., Electrophoresis, 2002, vol. 23, p. 2929.
Bandy, J., Zhang, Q., and Cao, G., Mater. Sci. Appl., 2011, vol. 2, p. 1427.
Yang, Y., Qu, L., Dai, L., Kang, T.-S., and Durstock, M., Adv. Mater. (Weinheim, Fed. Repub. Ger.), 2007, vol. 19, p. 1239.
Lee, P.F., Isran, M., and Wan Abdullah, W.A.T., Nano Sci. Nano Technol.: An Indian J., 2009, vol. 3, p. 1.
Shilov, V., Bárány, S., and Grosse, C., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2003, vol. 104, p. 159.
Visca, M. and Matijevic’, E., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1979, vol. 68, p. 308.
Bogdanova, N.F. Cand. Sci. (Chem.) Dissertation, St. Petersburg: St. Petersburg State Univ., 1999.
Yezek, L., Rowell, R.L., Holysz, L., and Chibowski, E., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2000, vol. 225, p. 227.
Shimanovskaya, V.V., Dvernyakova, A.A., and Strelko, V.V., Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Neorg. Mater., 1988, vol. 24, p. 1188.
Shimanovskaya, V.V., Puzii, A.P., Chashechnikova I.T., Strelko V.V, Ukr. Khim. Zh., 1990, vol. 56, p. 998.
Aivazov, B.V., Praktikum po khimii poverkhnostnykh yavlenii i adsorbtsii (Practical Manuel on Chemistry of Surface Phenomena and Adsorption), Moscow Vysshaya Shkola, 1973.
Adsorption from Solution on the Solid/Liquid Interface, Parfitt, G. and Rochester, C., Eds., London Academic, 1983.
Kuz’micheva, G.M., Rentgenografiya nanorazmernykh ob”ektov. Chast’ II (X-ray Analysis of Nano Objects), Moscow: MITKhT im. M.V. Lomonosova, 2010, Part 2.
Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science. vol. 2, Lyklema, J.J., De Keizer, A., Bijsterbosch, B.H., Fleer, G.J., and Cohen Stuart, M.A., Eds., London Academic, 1995.
Barany, S., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 1988, vol. 75, p. 45.
Dukhin, S.S. and Derjaguin, B.V., Elektroforez (Electrophoresis), Moscow Nauka, 1976.
Baran, A.A., Dudkina, L.M., and Soboleva, N.M., Kolloidn. Zh., 1981, vol. 43, p. 211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.P. Kobulei, V.V. Strelko, T.S. Psareva, S. Barany, 2016, published in Kolloidnyi Zhurnal, 2016, Vol. 78, No. 2, pp. 146–151.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobulei, O.P., Strelko, V.V., Psareva, T.S. et al. Structural and electrosurface characteristics of titanium dioxide xerogel prepared by the sol–gel method. Colloid J 78, 164–169 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061933X16020058
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061933X16020058