Abstract
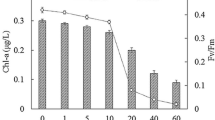
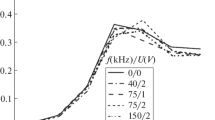
The effect of weak ultrasonic radiation with a frequency of 60 kHz on photosynthetic activity of living cells of cyanobacteria was studied using microspectrometric methods for the first time. An inhibitory effect on the physiological state of separate cells and the whole culture was demonstrated. A high efficiency of the method developed by the authors of this article for determination of the viability of cyanobacterial cultures in vivo for the purpose of operational environmental monitoring of the results of weak external influences was demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 November 2017
The surname of the second author should read Grigoryeva
References
V. A. Rumyantsev, in Promising Fields for Science Development in St. Petersburg (IP S. A. Permyakov, St. Petersburg, 2015), pp. 277–294 [in Russian].
Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time, Ed. by B. A. Whitton (Springer Science & Business Media, 2012), p. 741.
E. Granéle and J. T. Turner, Ecology of Harmful Algae (Springer, Berlin, 2006).
B. W. Ibelings, Harmful Algae 40, 63–74 (2014).
K. Sivonen and G. Jones, in Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management (Spon, London, 1999), pp. 41–111.
L. N. Voloshko and A. V. Pinevich, Astrakh. Vestn. Ekol. Obraz., No. 1 (27), 68–80 (2014).
G. A. Codd, in International Hydrologolical Programme. Initial Situation Assessment and Recommendations (UNESCO, Paris, 2006).
World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2011).
World Health Organization. Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments: Coastal and Fresh Waters (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2003), Vol. 1.
Methods for Physiological and Biochemical Researching Algae in Hydrobiological Practice (Naukova Dumka, Kiev, 1975) [in Russian].
P. Rajasekhar, Water Res. 46 (14), 4319–4329 (2012).
M. R. Doosti, R. Kargar, and M. H. Sayadi, Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2 (2), 96–110 (2012).
E. Yu. Kiselev, V. A. Rumyantsev, and V. N. Rybakin, Uch. Zap. Ross. Gos. Gidrometeorol. Univ., No. 37, 222–230 (2014).
H. Hao, et al., J. Environ. Sci. Health, Part A: Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 39 (6), 1435–1446 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.A. Rumyantsev, N.Yu. Grigor’eva, L.V. Chistyakova, 2017, published in Doklady Akademii Nauk, 2017, Vol. 475, No. 5, pp. 581–584.
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028334X17130025.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rumyantsev, V.A., Grigor’eva, N.Y. & Chistyakova, L.V. Study of changes in the physiological state of cyanobacteria caused by weak ultrasonic treatment. Dokl. Earth Sc. 475, 939–941 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028334X17080190
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028334X17080190