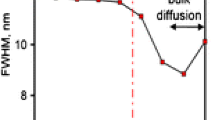
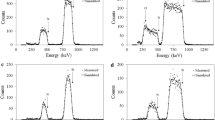
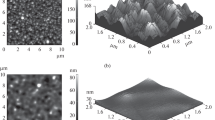
Knowing the distribution of the impurity concentration in the surface layers of solids is of great importance in technologies for modifying materials by methods of surface treatment. For these purposes, it is promising to use secondary-ion mass spectrometry. Due to the fact that the depths of the surface layers analyzed by this method do not exceed several microns, the task of reducing the influence of the microroughness of the analyzed surface on the results of measuring the distribution of the impurity concentration over depth becomes urgent. Using the example of the “zirconium ceramics–thin aluminum film” system, the methodological issues of minimizing the effect of the ceramic surface microrelief on measuring the distribution of aluminum impurity ions over the sample depth after thermal annealing are solved. It is shown that the measurement accuracy increases by an order of magnitude or more if, in addition to the main measurement of the sample after thermal annealing, the measurement of the base sample, which is identical to the control sample, is carried out before thermal annealing. The desired distribution of impurity ions over the depth of the sample is determined by subtracting the distribution obtained for the base sample from the distribution of the impurity in the control sample.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
C. Peng, X. Gao, L. Wu, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 114, 011905 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5054954
H. Zhong, J. Zhang, J. Shen, G. Liang, S. Zhang, M. Xu, X. Yu, S. Yan, G. E. Remnev, and X. Le, Vacuum 179, 109541 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109541
F. Konusov, S. Pavlov, A. Lauk, V. Tarbokov, S. Karpov, V. Karpov, R. Gadirov, E. Kashkarov, and G. Remnev, Surf. Coat. Technol. 389, 125564 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125564
V. E. Gromov, S. V. Gorbunov, Y. F. Ivanov, S. V. Vorobiev, and S. V. Konovalov, J. Surf. Invest.: X-ray, Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 5, 974 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451011100107
C. Zhang, P. Lv, H. Xia, Z. Yang, S. Konovalov, X. Chen, and Q. Guan, Vacuum 167, 263 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2019.06.022
S. Strazdaite, E. Navakauskas, J. Kirschner, T. Sneideris, and G. Niaura, Langmuir 36, 4766 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b03826
O. P. Choudhary and Priyanka, Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 6, 1877 (2017). https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.207
A. Grozdanov, P. Paunovic, V. V. Nikodinovska, and A. T. Dimitrov, Mater. Sci. Eng. Int. J. 3, 141 (2019). https://doi.org/10.15406/mseij.2019.03.00105
A. M. Palve and S. S. Garje, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 36, 025007 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6641/abcdfa
D. Kurouski, A. Dazzi, R. Zenobi, and A. Centrone, Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 3315 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cs00916c
R. P. Gunawardane and C. R. Arumainayagam, in Handbook of Applied Solid State Spectroscopy, Ed. by D. Vij (Springer, Boston, 2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-37590-2_10
H. Kambalathmana, A. M. Flatae, L. Hunold, F. Sledz, J. Müller, M. Hepp, P. Schmuki, M. S. Killian, S. Lagomarsino, N. Gelli, S. Sciortino, L. Giuntini, E. Wörner, C. Wild, B. Butz, and M. Agio, Carbon 174, 295 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.12.031
S. A. Gyngazov, A. P. Surzhikov, T. S. Frangul’yan, and A. V. Chernyavskii, Russ. Phys. J. 45, 753 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021956128414
S. A. Ghyngazov, A. V. Chernyavskii, and A. B. Petrova, Russ. Phys. J. 60, 812 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-017-1143-2
F. Benier, in Physics of Electrolytes, Vol. 1: Transport Processes in Solid Electrolytes and in Electrods, Ed. by J. Hladik (Academic, New York, 1972; Mir, Moscow, 1978).
Yu. A. Kudryavtsev, Poverkhn.: Rentgenovskie, Sinkhrotronnye Neitr. Issled., No. 1, 106 (2020). https://doi.org/10.31857/S1028096020010094
V. K. Larin, V. M. Kondakov, E. N. Malyi, V. A. Matyukha, N. V. Dedov, et al., Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Chern. Metall., No. 5, 59 (2003).
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation within the framework of the state assignment “Science” (project no. FSWW-2020-0008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghyngazov, A.S., Surzhikov, A.P. & Ghyngazov, S.A. Influence of the Substrate Roughness on the Accuracy of Measuring the Impurity Depth Distribution by Secondary-Ion Mass Spectrometry. J. Surf. Investig. 15, 1191–1194 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451021060094
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1027451021060094